Abstract
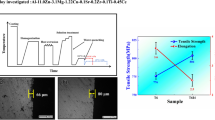
The effect of one-step aging temper on the mechanical properties, electrical conductivity and the microstructure of a novel Al-7.5Zn-1.6Mg-1.4Cu-0.12Zr alloy has been investigated. The results indicated that with elevating the aging temperature from 100°C to 160°C, the aging response rate was greatly accelerated, and the UTS at peak aging condition decreased, while the corresponding TYS increased. However, the electrical conductivity of the alloy became higher. After aging for 24 h at 120°C, the peak UTS and TYS values were achieved as 591 MPa and 541 MPa, respectively; but the alloy achieved a lower conductivity, 20.4 MS/m. When T6 temper was performed at 140°C for 14 h, the UTS decreased only by 1% of the former, whereas the TYS and the electrical conductivity increased obviously, which were up to 559 MPa and 22.6 MS/m, respectively. The major strengthening precipitates of the peak-aged alloy were GP zones and η′ phase. The precipitates in both the matrix and the grain boundary became coarser with rising aging temperature. There were obvious PFZs along the grain boundary both in T6 conditions aged at 140°C and 160°C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heinz A, Haszler A, Keidel C, et al. Recent development in aluminium alloys for aerospace applications. Mater Sci Eng A, 2000, 280(3): 102–107
John L. Advanced aluminum and hybrid aerostructures for future aircraft. Mater Sci Forum, 2006, 519–521: 1233–1238
Warner T. Rencently-developed aluminum solutions for aerospace applications. Mater Sci Forum, 2006, 519–521:1271–1278
Chakrabarti D J, Liu J, Sawtell R R, et al. New generation high strength high damage tolerance 7085 thick alloy product with low quench sensitivity. In: Proceedings of ICAA9, Melbourne: Institute of Materials Engineering Australasia Ltd, 2004. 969–974
Ilyushenko R, Nesterenkov V. Novel technique for joining of thick section difficult -to-weld aluminium alloys. Mater Sci Forum, 2006, 519–521: 1125–1130
Karabin M E, Barlat F, Schultz R W. Numerical and experimental study of the cold expansion process in 7085 plate using a modified split sleeve. J Mater Proc Tech, 2007, 189(1): 45–57
Jabra J, Romios M, Lai J, et al. The effect of thermal exposure on the mechanical properties of 2099-T6 die forgings, 2099-T83 extrusions, 7075-T7651 plate, 7085 -T7452 die forgings, 7085-T7651 plate, and 2397-T87 plate aluminum alloys. J Mater Eng Perform, 2006, 15(5): 601–607
Li X Z, Hansen V, Gjϕnnes J, et al. HREM study and structure modeling of the η′ phase, the hardening precipitates in commercial Al-Zn-Mg alloys. Acta Mater, 1999, 47(9): 2651–2659
Berg L K, Gjϕnnes J, Hansen V, et al. GP-zones in Al-Zn-Mg alloys and their role in artificial aging. Acta Mater, 2001, 49(12): 3443–3451
Jiang X J, Noble B, Holme B, et al. Differential scanning calorimetry and electron diffraction investigation on low-temperature aging in Al-Zn-Mg alloys. Metall Mater Trans A, 2000, 31(2): 339–348
Gjϕnnes J, Simensen Chr J. An electron microscope investigation of the microstructure in an aluminium-zinc-magnesium alloy. Acta Metall, 1970, 18: 881–890
Gang S, Alfred C. Early-stage precipitation in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy (7050). Acta Mater, 2004, 52(15): 4503–4516
Fan X G, Jiang D M, Meng Q C, et al. Characterization of precipitation microstructure and properties of 7150 aluminium alloy. Mater Sci Eng A, 2006, 427(1): 130–135
Starink M J, Li X M. A model for the electrical conductivity of peak-aged and overaged Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys. Metall Mater Trans A, 2003, 34A(4): 899–911
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Hi-Tech Research and Development Program of China (“863” Project) (Grant No. 2008AA03Z506)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Xiong, B., Zhang, Y. et al. Effect of one-step aging on microstructure and properties of a novel Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr alloy. Sci. China Ser. E-Technol. Sci. 52, 67–71 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-008-0277-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-008-0277-4