Abstract
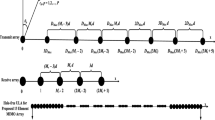
A new direction synthetic method for monostatic multiple input multiple output (MIMO) radar is presented based on synthetic impulse and aperture radar (SIAR) system. Concerned with the monostatic MIMO radar which simultaneously emits orthogonal signals with multi-carrier-frequency and possesses sparsely distributed transmitting and receiving arrays with respective location, as well as the situation for the presence of multipath propagation in the low flying target’s echo, the method integrates the aperture of the transmitting arrays with the receiving arrays to form the digital beam-forming (DBF) in azimuth and elevation dimensions. And a study has been made of planar general MUSIC algorithm based on decorrelating the multipath signals of multi-carrier-frequency MIMO radar. Through compensating the phase delay of both the transmitting and the receiving arrays and synthesizing the transmitting beam in two dimensions at the receiver, the angular resolution and measurement accuracy are improved and the computational complexity is reduced after transforming the three-dimensional (3D) parameter estimation problem into a two-dimensional (2D) one. Finally, the Cramer-Rao Bounds (CRBs) of DOA estimation for azimuth and elevation is put forward with the exsiting multipath propagation. Results of computer simulation demonstrate the validity of the new method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fishler E, Haimovich A, Blum R, et al. MIMO radar: An idea whose time has come. Proc IEEE Radar Conference, 2004, 71–78.
Khan H A, Malik W Q, Edwards D J, et al. Ultra wideband multiple-input multi-output radar. IEEE International Radar Conference, 2005, 900–904
Forsythe K W, Bliss D W, Fawcett G S. Multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) radar: Performance issues. Proc 38th Asilomar Conf Signals, Syst, Comput, vol.1, 2004, 310–314
Fuhrmann D R, Antonio G S. Transmit beamforming for MIMO radar systems using partial signal correlation. Proc 38th Asilomar Conf Signals, Syst, Comput, vol.1, 2004. 295–299
Robey F C, Coutts S, Weikle D D, et al. MIMO radar theory and exprimental results. Proc 38th Asilomar Conf Signals, Syst, Comput, vol.1, 2004, 300–304
Bliss D W, Forsythe K W. Multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) radar and imaging: degrees of freedom and resolution. Proc 37th Asilomar Conf Signals, Syst, Comput, vol.1, 2003. 54–59
Dorey J, Garnier G, Auvray G. RIAS, synthetic impulse and antenna radar. Proceedings of International Conference on Radar, Paris, 1989, AES-3: 556–562
Bao Z, Zhang Q W. A new kind of VHF radar: synthetic impulse and aperture radar. Modern Radar, 1995, 17(1): 1–13
Chen B X. Researches on 4-dimensional tracking and long-time coherent integation for synthetic impulse and aperture radar. Doctoral Dissertation (in Chinese), Xi’an: Xidian University, 1997
Schmidt R O. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation. IEEE, 1986, AP-34: 276–280
Kumaresan R, Tufts D W. Estimating the angles of arrival of multiple plane waves. IEEE, 1983, AES-19: 134–139
Rao B D, Hari K V S. On spatial smoothing and weighted subspace methods. Proc 24th Asilomar Conf Signals, Syst, Comput, 1990, 936–940
Ziskind I, Wax M. Maximum likelihood localization of multiple sources by alternating projection. IEEE Trans, ASSP, 1988, 36:1553–1560
Zhao G H, Chen B X. Pattern synthesis of antenna array in MIMO radar by using two-layer coding. Systems Engineering and Electronics. Accepted.
Chen B X, Xu H, Zhang S H. Ship-based passive synthetic impulse and aperture radar and some key questions. Acta Electronica Sin, 2003, 13(12): 1776–1779
Su H T. Study of target detection and interference mitigation for over-the-horizon radar. Doctoral Dissertation (in Chinese), Xi’an: Xidian University, 2004
Zoltowski M. A vector space approach to direction finding in a coherent multipath environment. IEEE Trans on Antennas and Propagation, 1986, AP-34(9): 1069–1079
Chen B X, Zhang S H. 4-Dimensional ambiguity function and the resolution for synthetic impulse and aperture radar. Signal Processing China, 1998, 14: 33–37
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (Grant No. NCET-06-0856) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 60772068)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, G., Chen, B. & Zhu, S. Direction synthesis in DOA estimation for monostatic multiple input multiple output (MIMO) radar based on synthetic impulse and aperture radar (SIAR) and its performance analysis. Sci. China Ser. E-Technol. Sci. 51, 656–673 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-008-0048-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-008-0048-2