Abstract
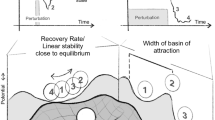
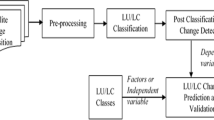
We propose a fundamental theorem for eco-environmental surface modelling (FTEEM) in order to apply it into the fields of ecology and environmental science more easily after the fundamental theorem for Earth’s surface system modeling (FTESM). The Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei (BTH) region is taken as a case area to conduct empirical studies of algorithms for spatial upscaling, spatial downscaling, spatial interpolation, data fusion and model-data assimilation, which are based on high accuracy surface modelling (HASM), corresponding with corollaries of FTEEM. The case studies demonstrate how eco-environmental surface modelling is substantially improved when both extrinsic and intrinsic information are used along with an appropriate method of HASM. Compared with classic algorithms, the HASM-based algorithm for spatial upscaling reduced the root-mean-square error of the BTH elevation surface by 9 m. The HASM-based algorithm for spatial downscaling reduced the relative error of future scenarios of annual mean temperature by 16%. The HASM-based algorithm for spatial interpolation reduced the relative error of change trend of annual mean precipitation by 0.2%. The HASM-based algorithm for data fusion reduced the relative error of change trend of annual mean temperature by 70%. The HASM-based algorithm for model-data assimilation reduced the relative error of carbon stocks by 40%. We propose five theoretical challenges and three application problems of HASM that need to be addressed to improve FTEEM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akima H. 1978a. A method of bivariate interpolation and smooth surface fitting for irregularly distributed data points. ACM Trans Math Softw, 4: 148–159.
Akima H. 1978b. Algorithm 526: Bivariate interpolation and smooth surface fitting for irregularly distributed data points. ACM Trans Math Softw, 4: 160–164.
Bagnara M, Silveyra Gonzalez R, Reifenberg S, Steinkamp J, Hickler T, Werner C, Dormann C F, Hartig F. 2019. An R package facilitating sensitivity analysis, calibration and forward simulations with the LPJ-GUESS dynamic vegetation model. Environ Model Softw, 111: 55–60.
Bengtsson B E, Nordbeck S. 1964. Construction of isarithms and isarithmic maps by computers. BIT, 4: 87–105.
Birkhoff G, Garabedian H L. 1960. Smooth surface interpolation. J Math Phys, 39: 258–268.
Brill K F, Uccellini L W, Manobianco J, Kocin P J, Homan J H. 1991. The use of successive dynamic initialization by nudging to simulate cyclogenesis during GALE IOP 1. Meteorol Atmos Phys, 45: 15–40.
Chen C F, Yue T X. 2010. A method of DEM construction and related error analysis. Comput Geosci, 36: 717–725.
Chen C F, Yue T X, Dai H L, Tian M Y. 2013a. The smoothness of HASM. Int J Geogr Inf Sci, 27: 1651–1667.
Chen C F, Li Y Y, Yue T X. 2013b. Surface modeling of DEMs based on a sequential adjustment method. Int J Geogr Inf Sci, 27: 1272–1291.
Cheng W M, Zhou C H, Chai H X, Zhao S M, Liu H J, Zhou Z P. 2011. Research and compilation of the geomorphologic atlas of the People’s Republic of China (1:1000000). J Geogr Sci, 21: 89–100.
Crow W T, Berg A A, Cosh M H, Loew A, Mohanty B P, Panciera R, de Rosnay P, Ryu D, Walker J P. 2012. Upscaling sparse ground-based soil moisture observations for the validation of coarse-resolution satellite soil moisture products. Rev Geophys, 50: RG2002
De Boor C. 1962. Bicubic spline interpolation. J Math Phys, 41: 212–218.
Djaferis T E, Schick I C. 2000. System theory: Modeling, analysis, and control. Boston: Kluwer
Editorial Committee of Vegetation Map of China. 2007. Vegetation map of the People’s Republic of China. Beijing: Geological Publishing House
Evans I S. 1980. An integrated system of terrain analysis and slope mapping. Z Geomorphol Suppl Bd, 36: 274–295.
Foley T A, Nielson G M. 1980. Multivariate interpolation to scattered data using delta iteration. In: Cheney E W, ed. Approximation Theory III. New York: Academic Press
Franke R. 1982. Scattered data interpolation: Tests of some methods. Math Comput, 38: 181
Fry J, Guber A K, Ladoni M, Munoz J D, Kravchenko A N. 2017. The effect of up-scaling soil properties and model parameters on predictive accuracy of DSSAT crop simulation model under variable weather conditions. Geoderma, 287: 105–115.
Hamed K H. 2009. Exact distribution of the Mann-Kendall trend test statistic for persistent data. J Hydrol, 365: 86–94.
Harder R L, Desmarais R N. 1972. Interpolation using surface Splines. J Aircraft, 9: 189–191.
Hirsch A L, Pitman A J, Seneviratne S I, Evans J P, Haverd V. 2014. Summertime maximum and minimum temperature coupling asymmetry over Australia determined using WRF. Geophys Res Lett, 41: 1546–1552.
Hull D J. 2003. Optimal Control Theory for Applications. New York: Springer
IPBES (The Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services). 2016. The Methodological Assessment Report on Scenarios and Models of Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. Secretariat of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity Ecosystem Services, Bonn, Germany
IPBES (The Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services). 2019. Global Assessment on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. Secretariat of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity Ecosystem Services, Bonn, Germany
Isaaks E H, Srivastava R M. 1989. Applied Geostatistics. New York: Oxford University Press
Kendall M G. 1948. Rank Correlation Methods. London: Griffin
Kerimov I A. 2009. F-approximation of the Earth’s surface topography. Izv Phys Solid Earth, 45: 719–729.
Krige D G. 1951. A statistical approach to some basic mine valuation problems on the Witwatersrand. J Chem Metall Min Soc South Africa, 52: 119–139.
Laflamme E M, Linder E, Pan Y B. 2016. Statistical downscaling of regional climate model output to achieve projections of precipitation extremes. Weather Clim Extremes, 12: 15–23.
Le Roux R, Katurji M, Zawar-Reza P, Quénol H, Sturman A. 2018. Comparison of statistical and dynamical downscaling results from the WRF model. Environ Model Softw, 100: 67–73.
Li H K, Lei Y C. 2010. Evaluation of Forest Biomass and Carbon Storage in China (in Chinese). Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House
Li J, Heap A D. 2014. Spatial interpolation methods applied in the environmental sciences: A review. Environ Model Softw, 53: 173–189.
Li K, Jackson A, Livermore P W. 2014. Variational data assimilation for a forced, inertia-free magnetohydrodynamic dynamo model. Geophys J Int, 199: 1662–1676.
Li Z L. 2007. Algorithmic Foundation of Multi-Scale Spatial Representation. London: CRC Press
Magnussen S, Næsset E, Wulder M A. 2007. Efficient multiresolution spatial predictions for large data arrays. Remote Sens Environ, 109: 451–463.
Mann H B. 1945. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica, 13: 245–259.
Maude A D. 1973. Interpolation—Mainly for graph plotters. Comput J, 16: 64–65.
Misaghian N, Assareh M, Sadeghi M T. 2018. An upscaling approach using adaptive multi-resolution upgridding and automated relative permeability adjustment. Comput Geosci, 22: 261–282.
Mitchell M N B. 2012. Data fusion: Concepts and Ideas. Berlin: Springer-Verlag
National Bureau of Statistics of China. 2018. China Statistical Yearbook. Beijing: China Statistics Press
Nichols N K. 2010. Mathematical concepts of data assimilation. In: Lahoz W, Khattatov B, Menard R, eds. Data Assimilation: Making Sense of Observations. Berlin: Springer. 13–39
Peng C H, Guiot J, Wu H B, Jiang H, Luo Y Q. 2011. Integrating models with data in ecology and palaeoecology: Advances towards a model-data fusion approach. Ecol Lett, 14: 522–536.
Phillips J D. 2002. Global and local factors in earth surface systems. Ecol Model, 149: 257–272.
Ponsar S, Luyten P, Dulière V. 2016. Data assimilation with the ensemble Kalman filter in a numerical model of the North Sea. Ocean Dyn, 66: 955–971.
Schneider B. 2001. Phenomenon-based specification of the digital representation of terrain surfaces. Trans GIS, 5: 39–52.
Schoenberg I J. 1946. Contributions to the problem of approximation of equidistant data by analytic functions. Quar Appl Math, 4: 45–99., 112–141
Seppelt R, Lautenbach S, Volk M. 2013. Identifying trade-offs between ecosystem services, land use, and biodiversity: A plea for combining scenario analysis and optimization on different spatial scales. Curr Opin Env Sust, 5: 458–463.
Shepard D. 1968. A two-dimensional interpolation function for irregularly-spaced data. In: Proceedings of the 1968 23rd ACM National Conference. New York: Association for Computing Machinery
Shi W J, Yue T X, Fan Z M. 2011. An overview of high accuracy surface modeling of soil properties. Procedia Environ Sci, 13: 2304–2309.
Shi W, Liu J, Du Z, Song Y, Chen C, Yue T. 2009. Surface modelling of soil pH. Geoderma, 150: 113–119.
Smith B, Prentice I C, Sykes M T. 2001. Representation of vegetation dynamics in the modelling of terrestrial ecosystems: Comparing two contrasting approaches within European climate space. Glob Ecol Biogeogr, 10: 621–637.
Smith B, Wårlind D, Arneth A, Hickler T, Leadley P, Siltberg J, Zaehle S. 2014. Implications of incorporating N cycling and N limitations on primary production in an individual-based dynamic vegetation model. Biogeosciences, 11: 2027–2054.
Somasundaram D. 2005. Differential Geometry. Harrow: Alpha Science International
Spivak M. 1979. A Comprehensive Introduction to Differential Geometry (Vol. 3). Boston: Publish or Peril
Talmi A, Gilat G. 1977. Method for smooth approximation of data. J Comput Phys, 23: 93–123.
Tse R O C, Gold C. 2004. TIN meets CAD—Extending the TIN concept in GIS. Future Generation Comput Syst, 20: 1171–1184.
Usery E L, McMaster R B. 2005. Introduction to the UCGIS research agenda. In: Usery E L, McMaster R B, eds. A Research Agenda for Geographic Information Science. London: CRC Press. 1–16
Wang H W, Wang Y H. 2012. Analysis of spatial interpolation methods. In: Qian Z H, Cao L, Su W L, Wang T K, Yang H M, eds. Recent Advances in Computer Science and Information Engineering (Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering Vol. 129). Berlin: Springer. 507–512
Yue T X, Ai N S. 1990. The mathematic model of cirque morphology. J Glaciol Geocryol, 12: 227–34.
Yue T X, Chen S P, Xu B, Liu Q S, Li H G, Liu G H, Ye Q H. 2002. A curve-theorem based approach for change detection and its application to Yellow River Delta. Int J Remote Sens, 23: 2283–2292.
Yue T X, Du Z P, Liu J Y. 2004. High accuracy surface modelling and its error analysis (in Chinese). Prog Nat Sci, 14: 300–306.
Yue T X, Du Z P, Song D J, Gong Y. 2007. A new method of surface modeling and its application to DEM construction. Geomorphology, 91: 161–172.
Yue T X, Song Y J. 2008. The YUE-HASM method. In: Li D, Ge Y, Foody G M, eds. Accuracy in Geomatics. Edgbaston: World Academic Union. 148–153
Yue T X, Wang S H. 2010. Adjustment computation of HASM: A high-accuracy and high-speed method. Int J Geogr Inf Sci, 24: 1725–1743.
Yue T X, Chen C F, Li B L. 2010a. An adaptive method of high accuracy surface modeling and its application to simulating elevation surfaces. Trans GIS, 14: 615–630.
Yue T X, Song D J, Du Z P, Wang W. 2010b. High-accuracy surface modelling and its application to DEM generation. Int J Remote Sens, 31: 2205–2226.
Yue T X. 2011. Surface Modelling: High Accuracy and High Speed Methods. Boca Raton: CRC Press
Yue T X, Chen C F, Li B L. 2012. A high-accuracy method for filling voids and its verification. Int J Remote Sens, 33: 2815–2830.
Yue T X, Zhao N, Yang H, Song Y J, Du Z P, Fan Z M, Song D J. 2013a. A multi-grid method of high accuracy surface modeling and its validation. Trans GIS, 17: 943–952.
Yue T X, Zhao N, Ramsey R D, Wang C L, Fan Z M, Chen C F, Lu Y M, Li B L. 2013b. Climate change trend in China, with improved accuracy. Clim Change, 120: 137–151.
Yue T X, Zhang L L, Zhao N, Zhao M W, Chen C F, Du Z P, Song D J, Fan Z M, Shi W J, Wang S H, Yan C Q, Li Q Q, Sun X F, Yang H, Wilson J, Xu B. 2015a. A review of recent developments in HASM. Environ Earth Sci, 74: 6541–6549.
Yue T X, Zhao M W, Zhang X Y. 2015b. A high-accuracy method for filling voids on remotely sensed XCO2 surfaces and its verification. J Cleaner Product, 103: 819–827.
Yue T X, Du Z P, Lu M, Fan Z M, Wang C L, Tian Y Z, Xu B. 2015c. Surface modeling of ecosystem responses to climatic change in Poyang Lake Basin of China. Ecol Model, 306: 16–23.
Yue T X, Liu Y, Zhao M W, Du Z P, Zhao N. 2016a. A fundamental theorem of Earth’s surface modelling. Environ Earth Sci, 75: 751
Yue T X, Zhao N, Fan Z M, Li J, Chen C F, Lu Y M, Wang C L, Xu B, Wilson J. 2016b. CMIP5 Downscaling and its uncertainty in China. Glob Planet Change, 146: 30–37.
Yue T X, Wang Y F, Du Z P, Zhao M W, Li Zhang L, Zhao N, Lu M, Larocque G R, Wilson J P. 2016c. Analysing the uncertainty of estimating forest carbon stocks in China. Biogeosciences, 13: 3991–4004.
Zhang L L, Yue T X, Wilson J P, Zhao N, Zhao Y P, Du Z P, Liu Y. 2017a. A comparison of satellite observations with the XCO2 surface obtained by fusing TCCON measurements and GEOS-Chem model outputs. Sci Total Env, 601–602: 1575–1590
Zhao C Y, Nan Z G, Cheng G D. 2005. Methods for modelling of temporal and spatial distribution of air temperature at landscape scale in the southern Qilian mountains, China. Ecol Model, 189: 209–220.
Zhao M W, Zhang X Y, Yue T X, Wang C, Jiang L, Sun J L. 2017. A high-accuracy method for simulating the XCO2 global distribution using GOSAT retrieval data. Sci China Earth Sci, 60: 143–155.
Zhao N, Yue T. 2014a. A modification of HASM for interpolating precipitation in China. Theor Appl Climatol, 116: 273–285.
Zhao N, Yue T X. 2014b. Sensitivity studies of a high accuracy surface modelling method. Sci China Earth Sci, 57: 1–11.
Zhao N, Yue T, Chen C, Zhao M, Du Z. 2018. An improved HASM method for dealing with large spatial data sets. Sci China Earth Sci, 61: 1078–1087.
Zhu A X. 2005. Research issues on uncertainty in geographic data and GIS-based analysis. In: Usery E L, McMaster R B, eds. A Research Agenda for Geographic Information Science. London: CRC Press. 197–223
Zienkiewlcz O C. 1967. The Finite Element Method in Structural and Continuum Mechanics. London: McGraw Hill
Acknowledgements
All data, corresponding to Figures 3–17, can be found from appended datasets at https://link.springer.com/journal/11430. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41930647, 41590844, 41421001 & 41971358), the Strategic Priority Research Program (A) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. XDA20030203), the Innovation Project of LREIS (Grant No. O88RA600YA) and the Biodiversity Investigation, Observation and Assessment Program (2019–2023) of the Ministry of Ecology and Environment of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, T., Zhao, N., Liu, Y. et al. A fundamental theorem for eco-environmental surface modelling and its applications. Sci. China Earth Sci. 63, 1092–1112 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-019-9594-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-019-9594-3