Abstract
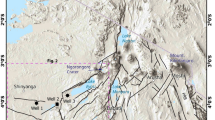
Significant uncertainties remain regarding the temporal evolution of natural vegetation during the Quaternary, and drivers of past vegetation change, on the Chinese Loess Plateau (CLP). This study presents analyses of total organic carbon isotopic composition (TOC) and n-alkane ratios (C31/C27) from the Lingtai loess-palaeosol sequence on the central CLP over the last 450 kyr. The results demonstrate that the vegetation in this region comprised a mix of C3 and C4 plants of herb and woody growth-form. C3 plants dominated for most of the last 450 kyr, but this did not lead to extensive forest. C3 woody plants were more abundant in MIS9 (S3 period) and MIS5 (S1 period) during warm and humid climate conditions. Herbs increased in the region since 130 kyr, possibly as a result of increased aridity. On the orbital timescales, there was a reduction of C3 herbal plants in MIS11 (S4) than in MIS12 (L5), and in Holocene than in the last glacial period. Our isotope and n-alkane proxy records are in agreement with Artemisia pollen changes in the region, which is/was the dominant species in this area and varying due to different heat and water conditions between glacial and interglacial periods. Though the climate in MIS1 (S0) was similar to that in MIS11 (S4), a significant increase in woody plants during the Holocene suggests the impact of human activities and ecological effects of changes in fire activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
An Z S, Huang Y S, Liu W G, Guo Z T, Clemens S, Li L, Preww W, Ning Y F, Cai Y F, Zhou W J, Lin B H, Zhang Q L, Cao Y N, Qiang X K, Chang H, Wu Z K. 2005. Multiple expansions of C4 plant biomass in East Asia since 7 Ma coupled with strengthened monsoon circulation. Geology, 33: 705–708
Bai Y, Fang X, Nie J, Wang Y, Wu F L. 2009. A preliminary reconstruction of the paleoecological and paleoclimatic history of the Chinese Loess Plateau from the application of biomarkers. Paleogeogr Paleoclimatol Paleoecol, 271: 161–169
Bi X H, Sheng G Y, Liu X H, Fu J M. 2005. Molecular and carbon and hydrogen isotopic composition of n-alkanes in plant leaf waxes. Org Geochem, 36: 1405–1417
Bird M I, Grocke D. 1997. Determination of the abundane and carbon- isotope composition of elemental carbon in sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 61: 3413–3423
Bond W J, Keeley J E. 2005. Fire as a lobal ‘herbivore’: The ecology and evolution of flammable ecosystems. Trends Ecol Evol, 20: 387–394
Chen F H, Rao Z G, Zhang J W, Jin M, Ma J Y. 2006. Variations of organic carbon isotopic composition and its environmental significance during the last glacial on western Chinese Loess Plateau. Chin Sci Bull, 51: 1593–1602
Chen J, Dong X F. 1990. Agriculture, forestry and animal husbandry study of Longdong area under natural background. J Gansu Sci, 4: 69–73
Chen P N, Wang G A, Han J M, Liu X J, Liu M. 2010. d13C difference between plants and soil organic matter along the eastern slope of Mount Gongga. Chin Sci Bull, 55: 55–62
Cheng J, Hu T M, Cheng J M. 2011. Responses of distribution of Artemisia sacrorum community to climate in semi-arid and semi-humid areas of Loess Plateau. Sci Soil Water Conserv, 9: 51–56
Cranwell P A, Eglinton G, Robinson N. 1987. Lipids of aquatic organisms as potential contributors to lacustrine sediments-II. Org Geochem, 11: 513–527
Deines P. 1980. The isotopic composition of reduced organic carbon. In: Fritz P, Fontes J C, eds. Handbook of Environmental Isotope Geochemistry I, the Terrestrial Environment. Amsterdam: Elsevier. 329–406
Ding Z, Yang S. 2000. C3/C4 vegetation evolution over the last 7.0 Myr in the Chinese Loess Plateau: Evidence from pedogenic carbonate d13C. Paleogeogr Paleoclimatol Paleoecol, 160: 291–299
Eglinton G, Hamilton R J. 1967. Leaf epicuticular waxes. Science, 56: 1322–1335
Gu Z Y, Liu Q, Xu B, Han J M, Yang S L, Ding Z L. 2003. Climate change as the dominant control on glacial-interglacial variation in C3 and C4 plant abundance in the Loess Plateau. Chin Sci Bull, 48: 1271–1276
Guo Z T, Hou Y J. 2010). The general situation of natural environment changes in the Loess Plateau since the Holocene. In: Tian J L, ed. Study on the Environmental Effects of Ecological Construction in the Loess Plateau (in Chinese). Beijing: Meteorology Press. 1–47
Guo Z T, Liu T S, Fedoroff N, An Z S. 1993. Shift of the monsoon intensity on the Loess Plateau at ca. 0.85 Ma BP. Chin Sci Bull, 38: 586–591
Hao Q Z, Wang L, Oldfield F, Peng S Z, Qin L, Song Y, Xu B, Qian Y S, Bloemendal J, Guo Z T. 2012. Delayed build-up of Arctic ice sheets during 400 kyr minima in insolation variability. Nature, 490: 393–396
Imbrie J, Hays J D, Martinson D G, McIntyre A, Mix A C, Morley J J, Pisias N G, Prell W L. 1984). The orbital theory of Pleistocene climate: Support from a revised chronology of the marine 18O record. In: Berger A, Imbrie J, Hays J, eds. Milankovitch and Climate. Dordrecht: Reidel. 269–306
Keeley J E, Rundel P W. 2005. Fire and the Miocene expansion of C4 grasslands. Ecol Lett, 8: 683–690
Lin B H, Liu R M. 1992. The stable isotopic evidence of the monsoon variation on Chinese Loess Plateau since the last 800 ka years. Chin Sci Bull, 37: 178–182
Liu J F, Su Y. 1994. The changes of vegetation and climate in Pingliang region, Gansu Province since about 800000 yr B.P. (in Chinese). Geograph Res, 13: 90–97
Liu L, Yang S, Cui L L, Hao Z G. 2013. Stable carbon isotopic composition of black carbon in surface soil as a proxy for reconstructing vegetation on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Paleogeogr Paleoclimatol Paleoecol, 388: 109–114
Liu W G, HuangY S, An Z S, Wu Z H, Lu H Y, Cao Y N. 2005. Summer monsoon intensity controls C4/C3 plant abundance during the last 35 ka in the Chinese Loess Plateau: Carbon isotope evidence from bulk organic matter and individual leaf waxes. Paleogeogr Paleoclimatol Paleoecol, 220: 243–254
Liu W G, Ning Y F, An Z S, Wu Z H, Lu H Y, Cao Y N. 2002. Carbon isotopic composition of modern soil and paleosol as a response to vegetation change on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 48: 93–99
Liu W G, Zhang P, Sun Y B, Huang Y S, Guo Z T, An Z S. 2008. Molecule fossil evidence for paleovegetation changes in the central of Chinese Loess Plateau during 7–2 Ma: Zhangjiachuang profile as an example. Quat Sci, 2008, 28: 806–811
Liu W, Yang H, Ning Y, An Z S. 2007. Contribution of inherent organic carbon to the bulk d13C signal in loess deposits from the arid western Chinese Loess Plateau. Org Geochem, 38: 1571–1579
Long L Q, Fang X M, Miao Y F, Bai Y, Wang Y L. 2011. Northern Tibetan Plateau cooling and aridification linked to Cenozoic global cooling: Evidence from n-alkane distributions of Paleogene sedimentary sequences in the Xining Basin. Chin Sci Bull, 56: 1569–1578
Lv H Y, Liu T S. 1999. Phytolith record of vegetation succession in the Southern Loess Plateau since late Pleistocene. Quat Sci, 4: 336–349
Marino B D, McElroy M B, Salawitch R J, Spaulding W G. 1992. Glacial- to-interglacial variations in the carbon isotopic composition of atmospheric CO2. Nature, 357: 461–462
Peterse F, Martinez-Garcia A, Zhou B, Beets C J, Prins M A, Zheng H B, Eglinton T I. 2014. Molecular records of continental air temperature and monsoon precipitation variability in East Asia spanning the past 130000 years. Quat Sci Rev, 83: 1–7
Peterse F, Zhou B, Magill C, Eglinton T I. 2015. Combined records of monsoon precipitation, temperature, and vegetation changes in East Asia over the past 200000 years. IMOG Meeting. 846
Rao Z G, Zhu Z Y, Chen F F, Zhang J W. 2006. Reviews on the stable carbon isotopic researches of organic matter of Chinese Loess (in Chinese). Adv Earth Sci, 21: 62–69
Rao Z G, Wu Y, Zhu Z Y, Jia G D, Henderson A. 2011. Is the maximum carbon number of long-chain n-alkanes an indicator of grassland or forest? Evidence from surface soils and modern plants. Chin Sci Bull, 56: 1714–1720
Shen J, Chu H. 1997. Preparation of organic carbon isotopic sample for Mass Spectrometric analysis by Static Combustion. Anal Test Tech Instrum, 3: 113–116
Shi H Z, Li F C, Sun X H, Wu F, Luo X P, Li X L, Jin Z D. 2011. Distribution of organic carbon in the Luochuan Loess/paleosol and its relationship with clay minerals. Geol China, 2011, 38: 1355–1362
Sun J, Lu T, Zhang Z, Wang X, Liu W G. 2012. Stepwise expansions of C4 biomass and enhanced seasonal precipitation and regional aridity during the Quaternary on the southern Chinese Loess Plateau. Quat Sci Rev, 34: 57–65
Sun X J, Song C Q, Wang F Y, Sun M R. 1997. Vegetation history of the Loess Plateau of China during the last 100000 years based on pollen data. Quat Int, 37: 25–36
Sun Y B, An Z S, Clemens S C, Jan Bloemendal J, Vandenberghe J. 2010. Seven million years of wind and precipitation variability on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 297: 525–535
Vidic N J, Montanez I P. 2004. Climatically driven glacial-interglacial variations in C3 and C4 plant proportions on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Geology, 32: 337–340
Volkman J K, Gillan F T, Johns R B, Eglinton G. 1981. Sources of neutral lipids in a temperate intertidal sediment. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 45: 1817–1828
Wang G A, Feng X B, Han J M, Zhou L H, Tan W B, Su F. 2008. Paleovegetation reconstruction using d13C of soil organic matter. Biogeo Sciences, 5: 1325–1337
Wang G A, Jia Y, Li W. 2015. Effects of environmental and biotic factors on carbon isotopic fractionation during decomposition of soil organic matter. Sci Rep, 5: 11043, doi: 10.1038/srep11043
Wang H B, Feng Z D. 2014. Geographic Differentiation of the Last Interglacial Paleosol S1 in the Chinese Loess Plateau-Significance of Soil Genesis and Soil Morphology (in Chinese). Lanzhou: Lanzhou University Press. 37
Wang Y L, Fang X M, Bai Y, Xi X X, Yang S L, Wang Y X. 2007. Distribution of lipids in modern soils from various regions with continuous climate (moisture-heat) change in China and their climate significance. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 50: 600–612
Wu F L, Fang X M, Ma Y Z, An Z S, Li J J. 2004. A 1.5 Ma sporopollen record of paleoecologic environment evolution in the central Chinese Loess. Chin Sci Bull, 49: 295–302
Xie S C, Wang Z Y, Wang H M, Chen F H, An C B. 2002. The occurrence of grassy vegetation over the loess plateau since the last interglacier: the molecular fossil record. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 45: 53–62
Xie S, Guo J, Huang J, Chen F H, Wang H B, Farrimond P. 2004. Restricted utility of d13C of bulk organic matter as a record of paleovegetation in some loess-paleosol sequences in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Quat Res, 62: 86–93
Yang S L, Ding Z L, Wang X, Tang Z H, Gu Z Y. 2012. Negative d18O–d13C relationship of pedogenic carbonate from northern China indicates a strong response of C3/C4 biomass to the seasonality of Asian monsoon precipitation. Paleogeogr Paleoclimatol Paleoecol, 317-318: 32–40
Zhang H C, Yang M S, Zhang W X, Lei G L, Chang F Q, Pu Y, Fan H F. 2004. Molecular fossil and paleovegetation records of paleosol S4 and adjacent loess layers in the Luochuan loess section, NW China. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 51: 321–330
Zhang P, Liu W G, Qiang X K. 2013. Vegetation coverage and monsoon variation recorded by stable carbon isotope of Loess since 2.5 Ma. Mar Geol Quat Geol, 2013, 33: 137–143
Zhang Z H, Zhao M X, Eglinton G, Lu H Y, Huang C Y. 2006. Leaf wax lipids as paleovegetational and paleoenvironmental proxies for the Chinese Loess Plateau over the last 170 kyr. Quat Sci Rev, 25: 575–594
Zhang Z H, Zhao M X, Lu H Y, Faiia A M. 2003. Lower temperature as the main cause of C4 plant declines during the glacial periods on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 214: 467–481
Zheng S X, Shangguan Z P. 2007. Foliar d13C values of nine dominant species in the Loess Plateau of China. Photosynthetica, 45: 110–119
Zhong Y X, Xue Q, Chen F H. 2009. Alkane distributions in Modern vegetation and surface soil from western Loess Plateau. Quat Sci, 29: 767–773
Zhou B, Shen C D, Sun W D, Zheng H B, Yang Y, Sun Y B, An Z S. 2007. The history of wildfire in the Chinese Loess Plateau during the last 420 ka and its implications to environmental and climate changes. Paleogeogr Paleoclimatol Paleoecol, 252: 617–625
Zhou B, Shen C D, Sun W D, Bird M I, Ma W T, Taylor D, Liu W G, Peterse F, Yi W X, Zheng H B. 2014. Late Pliocene–Pleistocene expansion of C4 vegetation in semiarid East Asia linked to increased burning. Geology, 42: 1067–1070
Zhou B, Shen C D, Zheng H B, Sun Y M. 2009. Vegetation evolution on the central Chinese Loess Plateau since late Quaternary evidenced by elemental carbon isotopic composition. Chin Sci Bull, 2009, 54: 2082–2089
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, B., Wali, G., Peterse, F. et al. Organic carbon isotope and molecular fossil records of vegetation evolution in central Loess Plateau since 450 kyr. Sci. China Earth Sci. 59, 1206–1215 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-016-5276-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-016-5276-x