Abstract
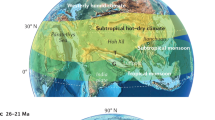
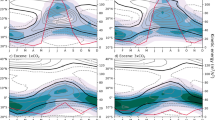
Climate in Eastern Asia is composed of monsoon climate in the east, arid and semi-arid climate in the north and west, and the cold and dry climate of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau in the southwest. The underlying causes for the evolution of East Asian climate during late Cenozoic have long been investigated and debated, particularly with regards to the role played by the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau uplift and the global cooling. In this paper, we reviewed major research developments in this area, and summarized the important results. Based on a synthesis of data, we propose that the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau uplift alone cannot fully explain the formation of monsoon and arid climates in Eastern Asia during the past 22–25 Ma. Other factors such as the global ice volume and high-latitude temperature changes have also played a vital role. Moreover, atmospheric CO2 changes may have modulated the monsoon and dry climate changes by affecting the location of the inter-tropical convergence zone (ITCZ), which controls the monsoon precipitation zone and the track of the East Asian winter monsoon during late Cenozoic. The integration of high-resolution geological record and numerical paleoclimate modeling could make new contributions to understanding the climate evolution and variation in eastern Asia in future studies. It could facilitate the investigation of the regional differences in East Asian environmental changes and the asynchronous nature between the uplift of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and their climatic effects. These would be the keys to understanding underlying driving forces for the evolution of the East Asian climate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
An Z S, Kutzbach J E, Prell W L, et al. 2001. Evolution of Asian monsoons and phased uplift of the Himalaya-Tibetan Plateau since late Miocene times. Nature, 411: 62–66
An Z S, Liu T S, Lu Y C, et al. 1990. The long-term paleomonsoon variation recorded by the loess-paleosol sequence in Central China. Quat Int, 7/8: 91–95
An Z S. 2000. The history and variability of East Asian monsoon climate. Quat Sci Rev, 19: 171–187
Biscaye P E, Grousset F E, Revel M, et al. 1997. Asian provenance of glacial dust (stage 2) in the Greenland Ice Sheet Project 2 Ice Core, Summit, Greenland. J Geophys Res, 102(C12): 26765–26782
Blisniuk P M, Hacker B R, Glodny J, et al. 2001. Normal faulting in central Tibet since at least 13.5 Myr ago. Nature, 412: 628–631
Boos W R, Kuang Z M. 2010. Dominant control of the South Asian monsoon by orographic insulation versus plateau heating. Nature, 463: 218–222
Cao J X, Cui H T. 1989. Research of Pliocene flora and palaeoenvironment of Yushe basin on Shanxi plateau, China (in Chinese). Sci Geol Sin, 47: 369–375
Chen J S, Huang B C, Sun L S. New constraints to the onset of the India-Asia collision: Paleomagnetic reconnaissance on the Linzizong Group in the Lhasa Block, China. Tectonophysics, 2010, 489: 189–209
Chen M Y. 1991. The evolution of Chinese aeolian deposits and global aridification (in Chinese). Quat Sci, (4): 361–371
Chung S, Lo C, Lee T, et al. 1998. Diachronous uplift of the Tibetan Plateau starting 40 Myr ago. Nature, 394: 769–773
Clark M K, Farley K A, Zheng D, et al. 2010. Early Cenozoic faulting of the northern Tibetan Plateau margin from apatite (U-Th)/He ages. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 296: 78–88
Clift P D, Blusztajn J, Nguyen D A. 2006. Large-scale drainage capture and surface uplift in Eastern Tibet before 24 Ma. Geophys Res Lett, 33: L19403, doi: 10.1029/2006GL027772
Clift P D, Hodges K V, Heslop D, et al. 2008. Correlation of Himalayan exhumation rates and Asian monsoon intensity. Nature Geosci, 1: 875–880
Coleman M, Hodges K. 1995. Evidence for Tibetan plateau uplift before 14 Myr ago from a new minimum age for east-west extension. Nature, 374: 49–52
Dai S, Fang X M, Song C H, et al. 2005. Early tectonic uplift of the northern Tibetan Plateau. Chin Sci Bull, 50: 1642–1652
Deng T, Wang S Q, Xie G P, et al. 2011. A mammalian fossil from the Dingqing Formation in the Lunpola Basin, northern Tibet, and its relevance to age and paleo-altimetry. Chin Sci Bull, 57: 261–269
Dettman D L, Fang X M, Garzione C N, et al. 2003. Uplift-driven climate change at 12 Ma: A long δ 18O record from the NE margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 214: 267–277
Ding Z L, Yu Z W, Rutter N W, et al. 1994. Towards an orbital time scale for Chinese loess deposit. Quat Sci Rev, 13: 39–70
Ding Z L, Liu T S, Rutter N W, et al. 1995. Ice-volume forcing of East Asian winter monsoon variations in the past 800, 000 years. Quat Res, 44: 149–159
Ding Z L, Sun J M, Liu T S, et al. 1998. Wind-blown origin of the Pliocene red clay formation in the central Loess Plateau, China. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 161: 135–143
Duce R A, Unni C K, Ray B J, et al. 1980. Long-range atmospheric transport of soil dust from Asia to the tropical North Pacific—Temporal variability. Science, 209: 1522–1524
Dupont-Nivet G, Dai S, Fang X, et al. 2008. Timing and distribution of tectonic rotations in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau. In: Burchfield B C, Wang E, eds. Investigations into the Tectonics of the Tibetan Plateau. Geol Soc Am Special Paper, 444: 73–87
Duvall A R, Clark M K, van der Pluijm B A, et al. 2011. Direct dating of Eocene reverse faulting in northeastern Tibet using Ar-dating of fault clays and low-temperature thermochronometry. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 304: 520–526
Fang X M, Zhao Z J, Li J J, et al. 2005. Magnetostratigraphy of the late Cenozoic Laojunmiao anticline in the northern Qilian Mountains and its implications for the northern Tibetan Plateau uplift. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 48: 1040–1051
Fortelius M, Jernvall J, Liu L P, et al. 2002. Fossil mammals resolve regional patterns of Eurasian climate change during 20 million years. Evo Eco Res, 4: 1005–1016
Fu K D, Gao J P, Fang X M, et al. 2001. Relationship model of sediment grain Size and Tibetan Plateau uplift in middle-west parts of Qilian Mountain. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 44: 210–217
Garzione C N, Quade J, Decelles P G, et al. 2000. Predicting paleoelevation of Tibet and the Himalaya from δ 18O vs. altitude gradients in meteoric water across the Nepal Himalaya. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 183: 215–229
Ge J, Guo Z, Zhan T, et al. 2012. Magnetostratigraphy of the Xihe loess-soil sequence and implication for late Neogene deformation of the West Qinling Mountains. Geophys J Int, 189: 1399–1408
Guo Z T, Liu T S, Fedoroff N, et al. 1998. Climate extremes in loess of China coupled with the strength of deep-water formation in the North Atlantic. Glob Planet Change, 18: 113–128
Guo Z T, Ruddiman W F, Hao Q Z, et al. 2002. Onset of Asian desertification by 22 Myr ago inferred from loess deposits in China. Nature, 416: 159–163
Guo Z T, Peng S Z, Hao Q Z, et al. 2004. Late Miocene-Pliocene development of Asian aridification as recorded in an eolian sequence in northern China. Glob Planet Change, 41: 135–145
Guo Z T, Sun B, Zhang Z S, et al. 2008. A major reorganization of Asian climate by the early Miocene. Clim Past, 4: 153–174
Guo Z T. 2010. The monsoon evolution history recorded by the eolian deposits during the interval of 22-8 Ma. In: Ding Z L, ed. Integrated Research on Environmental Evolution in West China (in Chinese). Beijing: China Meteorological Press. 1–19
Guo Z T, Zhou X, Wu H B. 2012. Glacial-interglacial water cycle, global monsoon and atmospheric methane changes. Clim Dyn, doi: 10.1007/ s00382-011-1147-5
Hao Q Z, Oldfield F, Bloemendal J, et al. 2008. Particle size separation and evidence for pedogenesis in samples from the Chinese Loess Plateau spanning the last 22 Ma. Geology, 36: 727–730
Jia G D, Peng P A, Zhao Q, et al. 2003. Changes in terrestrial ecosystem since 30 Ma in East Asia: Stable isotope evidence from black carbon in the South China Sea. Geology, 31: 1093–1096
Jiang H C, Ding Z L. 2008a. A 20 Ma pollen record of East-Asian summer monsoon evolution from Guyuan, Ningxia, China. Paleogeor Paleoclimatol Paleoecol, 265: 30–38
Jiang H C, Ji J L, Gao L, et al. 2008b. Cooling-driven climate change at 12-11 Ma: Multiproxy records from a long fluviolacustrine sequence at Guyuan, Ningxia, China. Paleogeogr Paleoclimatol Paleoecol, 265: 148–158
Jouzel J, Masson-Delmotte V, Olivier C, et al. 2007. Orbital and millennial Antarctic climate variability over the past 800, 000 years. Science, 317: 793–797
Kaakinen A, Sonninen E, Lunkka J P. 2006. Stable isotope record in paleosol carbonates from the Chinese Loess Plateau: Implications for late Neogene paleoclimate and paleovegetation. Paleogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol, 237: 359–369
Kutzbach J E, Guetter P J, Ruddiman W F, et al. 1989. Sensitivity of climate to Late Cenozoic uplift in Southern Asia and the American West: Numerical experiments. J Geophys Res, 94: 18393–18407
Li G J, Pettke T, Chen J. 2011. Increasing Nd isotopic ratio of Asian dust indicates progressive uplift of the north Tibetan Plateau since the middle Miocene. Geology, 39: 199–202
Li G J, Elderfield H. 2013. Evolution of carbon cycle over the past 100 million years. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2012.10.014
Li J J, Wen S X, Zhang Q S, et al. 1979. A discussion on the period, amplitude and type of the uplift of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Sci Sin, 22: 1314–1327
Li J J, Feng Z D, Tang L Y. 1988. Late Quaternary monsoon patterns on the Loess Plateau of China. Earth Sur Processes Landf, 13: 125–135
Li J J. 1999. Studies on the geomorphologic evolution of the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibetan Plateau) and Asian monsoon. Mar Geol Quat Geol, 19: 1–7
Li J J, Fang X M. 1999. Uplift of the Tibetan Plateau and environmental changes. Chin Sci Bull, 44: 2117–2124
Li X Z, Dong G R. 2006. Discussion on the formation age of arid environment in West China (in Chinese). Quat Sci, 26: 895–904
Liu J H, Zhang P Z, Zheng D W, et al. 2010. Pattern and timing of late Cenozoic rapid exhumation and uplift of the Helan Mountain, China. Sci China Earth Sci, 53: 345–355
Liu L, Eronen J T, Fortelius M. 2009. Significant mid-latitude aridity in the middle Miocene of East Asia. Paleogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol, 279: 201–206
Liu T S. 1985. Loess and Environment. Beijing: China Ocean Press. 31–67
Liu T S, Ding Z L. 1993. Stepwise coupling of monsoon circulations to global ice volume variations during the late Cenozoic. Glob Planet Change, 7: 119–130
Liu T S, Ding Z L. 1998. Chinese loess and the palaeomonsoon. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci, 26: 111–145
Liu T S, Zheng M P, Guo Z T. 1998. Initiation and evolution of the Asian monsoon system timely coupled with the ice-sheet growth and the tectonic movement in Asia (in Chinese). Quat Sci, (3): 194–204
Liu X D, Yin Z Y. 2002. Sensitivity of East Asian monsoon climate to the uplift of the Tibetan Plateau. Paleogeogr Paleoclimatol Palaeoecol, 183: 223–245
Liu X D, Dong B W. 2013. Influence of the Tibetan Plateau uplift on the Asian monsoon-arid environment evolution. Chin Sci Bull, 58, doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5987-8
Long L Q, Fang X M, Miao Y F, et al. 2011. Northern Tibetan Plateau cooling and aridification linked to Cenozoic global cooling: Evidence from n-alkane distributions of Paleogene sedimentary sequences in the Xining Basin. Chin Sci Bull, 56: 1569–1578
Lu H J, Xiong S F. 2009. Magnetostratigraphy of the Dahonggou section, northern Qaidam Basin and its bearing on Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Qilian Shan and Altyn Tagh Fault. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 288: 539–550
Lu H Y, Vandenberghe J F, An Z S. 2001. Aeolian origin and palaeoclimatic implications of the ‘Red Clay’ (North China) as evidenced by grain-size distribution. J Quat Sci, 16: 89–97
Lu H Y, Wang X Y, An Z S, et al. 2004a. Geomorphologic evidence of phased uplift of the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau since 14 million years ago. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 47: 822–833
Lu H Y, Zhang F Q, Liu X D, et al. 2004b. Periodicities of palaeoclimatic variations recorded by loess-palaeosol sequences in China. Quat Sci Rev, 23: 1891–1900
Lu H Y, Hu T, Wang X Y. 2009. Cycles and forcing mechanism of wet-dry variations in North China during the Past 11.0 million years revealed by wind-blown silt deposits, Geol J China Univ, 15: 149–158
Lu H Y, Wang X Y, Li L P. 2010. Aeolian sediment evidence that global cooling has driven late Cenozoic stepwise aridification in central Asia. In: Clift P D, Tada R, Zheng H, eds. Monsoon Evolution and Tectonics-climate Linkage in Asia. Geol Soc London Spec Publ, 342: 29–44
Lu H Y, Yi S W, Liu Z Y, et al. 2013. Variation of East Asian monsoon precipitation during the past 21 k.y. and potential CO2 forcing. Geology, 41: 1023–1026
Ma Y Z, Li J J, Fang X M. 1998. Pollen-spores in the red bed during 30.6–5.0 Ma in the Linxia Basin and climatic evolution. Chin Sci Bull, 43: 301–304
Manabe S, Terpstra T B. 1974. The effects of mountains on the general circulation of the atmosphere as identified by numerical experiments. J Atmos Sci, 31: 3–42
Métivier F, Gaudemer Y, Tapponnier P, et al. 1998. Northeastward growth of the Tibet Plateau deduced from balanced reconstruction of two depo-sitional areas: The Qaidam and Hexi Corridor basins, China. Tectonics, 17: 823–842
Miao Y F, Herrmann M, Wu F L, et al. 2012. What controlled Mid-Late Miocene long-term aridification in Central Asia? -Global cooling or Tibetan Plateau uplift: A review. Earth-Sci Rev, 112: 155–172
Miller K G, Fairbanks R G, Mountain G S. 1987. Tertiary oxygen isotope synthesis, sea-level history, and continental margin erosion. Paleoceanography, 2: 1–19
Molnar P, Boos W R, Battisti D S. 2010. Orographic controls on climate and paleoclimate of Asia: Thermal and mechanical roles for the Tibetan Plateau. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci, 38: 77–102
Molnar P. 2005. Mil-Pliocene growth of the Tibetan Plateau and evolution of East Asian climate. Palaeontol Electron, 8: 1–23
Molnar P, Stock J M. 2009. Slowing of India’s convergence with Eurasia since 20 Ma and its implications for Tibetan mantle dynamics. Tectonics, 28: TC3001, doi: 10.1029/2008TC002271
Parrenin F, Masson-Delmotte V, Köhler P, et al. 2013. Synchronous change of atmospheric CO2 and Antarctic temperature during the last deglacial warming. Science, 339: 1060–1063
Qiang X K, Li Z X, Powell C M, et al. 2001. Magnetostrratigraphic record of the late Miocene, onset of the East Asian monsoon, and Pliocene uplift of northern Tibet. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 187: 83–93
Qiang X K, An Z S, Song Y G, et al. 2011. New eolian red clay sequence on the western Chinese Loess Plateau linked to onset of Asian desertification about 25 Ma ago. Sci China Earth Sci, 54: 136–144
Qiao Y S, Guo Z T, Hao Q Z, et al. 2006. Grain-size features of a Miocene loess-soil sequence at Qinan: Implications on its origin. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 49: 731–738
Qiu J. 2013. Monsoon melee. Science, 340: 1400–1401
Ramstein G, Fluteau F, Besse J, et al. 1997. Effect of orogeny, plate motion and land-sea distribution on Eurasian climate change over the past 30 million years. Nature, 386: 788–795
Raymo M E, Ruddiman W F. 1992. Tectonic forcing of late Cenozoic climate. Nature, 359: 117–122
Rowley D B, Currie B S. 2006. Palaeo-altimetry of the late Eocene to Miocene Lunpola basin, central Tibet. Nature, 439: 677–681
Royden L H, Burchfiel B C, van der Hilst R D. 2008. The geological evolution of the Tibetan Plateau. Science, 321:1054–1058
Shackleton N J, Backman J, Zimmerman H, et al. 1984. Oxygen isotope calibration of the onset of ice-rafting and history of glaciation in the North Atlantic region. Nature, 307: 620–623
Shakun J D, Clark P U, He F. 2012. CO2 forcing of global climate during the last deglaciation. Nature, 484: 49–55
Shi Y F, Tang M C, Ma Y Z. 1999. Linkage between the second uplifting of the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibetan) Plateau and the initiation of the Asian monsoon system. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 42: 303–312
Sigman D M, Boyle E A. 2000. Glacial/interglacial variations in atmospheric carbon dioxide. Nature. 407: 859–869
Spicer R A, Harris N B W, Widdowson M, et al. 2003. Constant elevation of southern Tibet over the past 15 million years. Nature, 421: 622–624
Sun D H, Liu D S, Chen M Y, et al. 1997. Magnetostratigraphy and palaeoclimate of red clay sequences from Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 40: 337–343
Sun D H, Bloemendal J, Yi Z Y, et al. 2011. Palaeomagnetic and palaeoenvironmental study of two parallel sections of late Cenozoic strata in the central Taklimakan Desert: Implications for the desertification of the Tarim Basin. Paleogeogr Paleoclimatol Paleoecol, 300: 1–10
Sun J M, Ye J, Wu W. et al. 2010. Late Oligocece-Miocene mid-latitude aridification and wind patterns in the Asian interior. Geology, 38: 515–518
Sun J M, Jiang M S. 2013. Eocene seawater retreat from the southwest Tarim Basin and implications for early Cenozoic tectonic evolution in the Pamir Plateau. Tectonophysics, 588: 27–38
Sun X J, Wang P X. 2005. How old is the Asian monsoon system?—Palaeobotanical records from China. Paleogeogr Paleoclimatol Paleoecol, 222: 181–222
Tang Z H, Ding Z L, White P D, et al. 2011. Late Cenozoic central Asian drying inferred from a palynological record from the northern Tian Shan. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 302: 439–447
Tapponnier P, Xu Z, Roger F, et al. 2001. Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibet Plateau. Science, 294: 1671–1677
Tripati A, Roberts C, Eagle R. 2009. Coupling of CO2 and ice sheet stability over major climate transitions of the last 20 million years. Science, 326: 1394–1397
Vincent E, Berger W H. 1985. Carbon dioxide and polar cooling in the Miocene—The Monterey hypothesis. In: Sundquist E T, Broecker W S, eds. The Carbon Cycle and Atmospheric CO2: Natural Variations Archean to Present. Washington DC: American Geophysical Union. 455–468
Wan S M, Li A, Clift P D, et al. 2007. Development of the East Asian monsoon: Mineralogical and sedimentologic records in the northern South China Sea since 20 Ma. Paleogeogr Paleoclimatol Paleoecol, 254: 561–582
Wang C S, Zhao X X, Liu Z F, et al. 2008. Constraints on the early uplift history of the Tibetan Plateau. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 105: 4987–4992
Wang G C, Cao K, Zhang K X, et al. 2011. Spatio-temporal framework of tectonic uplift stages of the Tibetan Plateau in Cenozoic. Sci China Earth Sci, 54: 29–44
Wang J L, Fang X M, Li J J. 1999. Eolian sand deposition and its environmental significance in the northeastern margin of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Chin Sci Bull, 44: 2250–2255
Wang P X, Clemens S, Beaufort L, et al. 2005. Evolution and variability of the Asian monsoon system: state of the art and outstanding issues. Quat Sci Rev, 24: 595–629
Wang P X, Zhao Q, Jian Z, et al. 2003. Thirty million year deep-sea records in the South China Sea. Chin Sci Bull, 48: 2524–2535
Wang P X. 2009. Global monsoon in a geological perspective. Chin Sci Bull, 54: 1113–1136
Wang X Y, Lu H Y, Vandenberghe J, et al. 2012. Late Miocene uplift of the NE Tibetan Plateau inferred from basin filling, planation and fluvial terraces in the Huang Shui catchment. Glob Planet Change, 88/89: 10–19
Wang Y, Deng T. 2005. A 25 m.y. isotopic record of palaeodiet and environmental change from fossil mammals and palaeosols from the NE margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 236: 322–338
Wen L J, Lu H Y, Qiang X K. 2005. Changes in grain-size and sedimentation rate of the Neogene Red Clay deposits along the Chinese Loess Plateau and implications for the palaeowind system. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 48: 1452–1462
Willenbring J K, von Blanckenburg F. 2010. Long-term stability of global erosion rates and weathering during late-Cenozoic cooling. Nature, 465: 211–214
Wu G, Liu Y M, He B, et al. 2012. Thermal controls on the Asian Summer monsoon. Scient Report, 2: 404, doi: 10.1038/srep00404
Xiao G Q, Abels H A, Yao Z, et al. 2010. Asian aridification linked to the first step of the Eocene-Oligocene climate Transition (EOT) in obliquity-dominated terrestrial records (Xining Basin, China). Clim Past, 6: 627–657
Xu Z Q, Wang Q, Arnaud P, et al. 2013. Orogen-parallel ductile extension and extrusion of the Greater Himalaya in the late Oligocene and Miocene. Tectonics, 32: 191–215
Xue X X, Zhang Y X, Yue L P. 2006. Paleoenvironments indicated by the fossil mammalian assemblages from red clay-loess sequence in the Chinese Loess Plateau since 8.0 Ma B.P. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 49: 518–530
Yang H R. 1987. Quaternary Geology (in Chinese). Beijing: Higher Education Press. 125–136
Yin A, Harrison T M. 2000. Geological evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan Orogen: Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci, 28: 211–280
Yin A. 2006. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Himalayan orogen as constrained by along-strike variation of structural geometry, exhumation history, and foreland sedimentation. Earth-Sci Rev, 76: 1–131
Yu H B, Remer L A, Chin M, et al. 2012. Aerosols from overseas rival domestic emissions over North America. Science, 337: 566–569
Yu K F, Lu H Y, Frank L, et al. 2013. A preliminary quantitative paleoclimate reconstruction of the dune fields if northern China during the last glacial maximum and Holocene Optimum. Quat Sci, 33: 293–302
Zachos J C, Pagani M, Sloan L, et al. 2001. Trends, rhythms, and aberrations in global climate 65 Ma to present. Science, 292: 686–693
Zeng L, Lu H Y, Yi S W, et al. 2011. Magnetostratigraphy of loess in northeastern China and paleoclimatic changes (in Chinese). Chin Sci Bull, 56: 2267–2275
Zhan T, Guo Z T, Wu H B, et al. 2011. Thick Miocene eolian deposits on the Huajialing Mountains: The geomorphic evolution of the western Loess Plateau. Sci China Earth Sci, 54: 241–248
Zhang K X, Wang G C, Cao K, et al. 2008. Cenozoic sedimentary records and geochronological constraints of differential uplift of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 51: 1658–1672
Zhang K X, Wang G C, Ji J L, et al. 2010. Paleogene-Neogene stratigraphic realm and sedimentary sequence of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and their response to uplift of the plateau. Sci China Earth Sci, 53: 1271–1294
Zhang L Y, Ding L, Yang D, et al. 2012. Origin of middle Miocene leucogranites and rhyolites on the Tibetan Plateau: Constraints on the timing of crustal thickening and uplift of its northern boundary. Chin Sci Bull, 57: 511–524
Zhang L Y. 1981. The influence of the uplift of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau on the Quaternary environmental evolution in China (in Chinese). J Lanzhou Univ (Natural Sci), (3): 142–155
Zhang R, Jiang D B, Liu X D, et al. 2012. Modeling the climate effects of different subregional uplifts within the Himalaya-Tibetan Plateau on Asian summer monsoon evolution. Chin Sci Bull, 57: 4617–4626
Zhang Z S, Wang H J, Guo Z T, et al. 2007a. What triggers the transition of palaeoenvironmental patterns in China, the Tibetan Plateau uplift or the Paratetbys Sea retreat? Paleogeogr Paleoclimatol Paleoecol, 245: 317–331
Zhang Z S, Wang H J, Guo Z T, et al. 2007b. Impacts of tectonic changes on the reorganization of the Cenozoic paleoclimatic patterns in China. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 257: 622–634
Zhao J B. 1989. The study on the red soil of Neogene in Xi’an and Baode of Shanxi (in Chinese). Acta Sedimentol Sin, 7: 113–120
Zheng H B, Powell C M, An Z S, et al. 2000. Pliocene uplift of the northern Tibetan Plateau. Geology, 28: 715–718
Zhong D L, Ding L. 1996. Rising process of the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau and its mechanism. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 39: 369–379
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, H., Guo, Z. Evolution of the monsoon and dry climate in East Asia during late Cenozoic: A review. Sci. China Earth Sci. 57, 70–79 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-013-4790-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-013-4790-3