Abstract
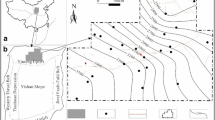
Based on an analysis of the present geo-temperature field and the thermal conductivity (K) of 62 samples from the central-south area of the Huaibei coalfield in eastern China, we calculated the heat flow and plotted its distribution map. The results show that the average heat flow in the research area is about 60 mW/m2. It is different from other major energy basins in the North China Plate, but has close relationship with the regional geology and the deep geological setting. The heat flow is comparatively higher in the southeastern, central, and northwestern areas than in the northeastern and southwestern areas. The geo-temperature distribution map of the bottom interface of the Permian coal measure was drawn by calculating its embedding depth and geo-temperature gradients. Finally, the present gas generation condition of the Permian coal measure is discussed by associating with the temperature condition, the vitrinite reflectance (R o), the metamorphism of coal and tectonic-burial evolution. The study indicates all present characters of the Permian coal measure, such as lower present temperature, higher R o value, middle-high rank coals, and uplift and extension events after the coal measure sediment, are favorable for the generation of secondary biogenic gas, but not thermogenic gas or primary biogenic gas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang L S, Li C, Liu S W, et al. Geo-temperature gradient distribution of Kuqa foreland basin, North Tarim, China (in Chinese). Chin J Geophys, 2003, 46: 403–407
Sun Z X, Zhang W, Hu B Q, et al. Geothermal field and its relation with coalbed methane distribution of the Qinshui Basin. Chin Sci Bull, 2005, 50(Suppl I): 111–117
Cui J P, Ren Z L, Su Y, et al. Relationship between present geo-temperature and hydrocarbon generation in Haila’er Basin (in Chinese). Petrol Expl Dev, 2007, 34: 445–450
Zhou Q H, Feng Z H, Men G T. Present geotemperature and its suggestion to natural gas generation in Xujiaweizi fault-depression of the northern Songliao Basin. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 2008, 51(Suppl I): 207–220
Gong Y L, Wang L S, Liu S W, et al. Distribution of temperature at the bottoms of Cenozoic source rocks in the Bohai Bay Basin (in Chinese). Chin J Geol, 2008, 43: 1–11
Wang L S, Li C, Liu S W, et al. Terrestrial heat flow distribution in Kuqa foreland basin, Tarim, NW China (in Chinese). Petrol Expl Dev, 2005, 32: 79–83
Gong Y L, Wang L S, Liu S W, et al. Mantle heat flow and deep temperature of Jiyang depression, Shandong, North China (in Chinese). Earth Sci-J China Univ Geosci, 2005, 30: 121–128
Sun Z X, Zhang W, Hu B Q, et al. Features of heat flow and the geothermal field of the Qinshui Basin (in Chinese). Chin J Geophys, 2006, 49: 130–134
Tan S Y, Yi D L, Fu X Z. Analysis on Qidong ground temperature characters and geology factors (in Chinese). Coal Tech, 2001, 20: 39–40
Yuan W H, Gui H R, The characteristics of geothermal temperature and its application in distinguishing the source of water in Renlou mine (in Chinese). J Anhui Univer Sci Tech (Nat Sci), 2005, 25: 9–11
Tao M X, Wang W C, Xie G X, et al. Secondary biogenic coalbed gas in some coalfields of China. Chin Sci Bull, 2005, 50(Suppl I): 24–29
Pashin J C. Stratigraphy and structure of coalbed methane reservoirs in the United States: A review. Int J Coal Geol, 1998, 35: 209–240
Scott A R. Hydrogeologic factors affecting gas content distribution in coal beds. Int J Coal Geol, 2002, 50: 363–387
Henry M E, Finn T M. Evaluation of undiscovered natural gas in the Upper Cretaceous Ferron Coal/Wasatch Plateau total petroleum system, Wasatch Plateau and Castle Vally Utah. Int J Coal Geol, 2003, 56: 3–37
Ju Y W, Jiang B, Hou Q L, et al. 13C NMR spectra of tectonic coals and the effects of stress on structural components. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 2005, 48: 1418–1437
Ju Y W, Wang G L. Tectonic characteristics and evolution of the Sulin mine area in the Huaibei coalfield (in Chinese). J Liaoning Tech Univ (Nat Sci), 2002, 21: 286–289
Ju Y W, Jiang B, Hou Q L, et al. Structural evolution of nano-scale pores of tectonic coals in southern North China and its mechanism (in Chinese). Acta Geol Sin, 2005, 79: 269–285
Han S F. Coalfield Geology and Prediction of Huainan-Huaibei Region (in Chinese). Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1990. 6–8
Tan J Q, Ju Y W, Hou Q L, et al. Distribution characteristics and influence factors of present geo-temperature field in Su-Lin mine area (in Chinese), Huaibei coalfield. Chin J Geophys, 2009, 52: 732–739
Tan J Q, Ju Y W, Zhang W Y, et al. Structure controls on present geo-temperature field in Su-Lin mine area of Huaibei coalfield (in Chinese). J China Coal Geol, 2009, 34: 449–454
Yang S C, Hu S B, Cai D S, et al. Geothermal field and thermotectonic evolution in southern South Yellow Sea Basin. Chin Sci Bull, 2003, 48: 1564–1569
Qiu N S, Hu S B, He L J. Theory and Application of Thermal System Research in Sedimentary Basin (in Chinese). Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2004. 10–24
Hu S B, He L J, Wang J Y. Heat flow in the continental area of China: A new data set. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 2000, 179: 407–419
Wang L S, Li C, Shi Y S, et al. Distribution of geo-temperature terrestrial heat flow density in low Yangtze area (in Chinese). Chin J Geophys, 1995, 38: 469–476
Wang Y. Heat flow pattern and lateral variations of lithosphere strength in China mainland: Constraints on active deformation. Phys Earth Planet Inter, 2001, 126: 121–146
Zhang P, Wang L S, Liu S W, et al. Geothermal field in the south Huabei basins (in Chinese). Prog Geophys, 2007, 22: 604–608
Wang G L, Cao D Y, Jiang B, et al. Thrust Nappe, Extensional Gliding Nappe and Gravity Gliding Structures in the Southern Part of North China, in Addition on the Research Methods of Decollement (in Chinese). Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology Press, 1992. 5–14
Wang J, Huang S Y, Huang G S, et al. Basic Characteristics of Geo-temperature Distribution in China (in Chinese). Beijing: Seismological Press, 1990. 48–50
Wang G L, Ju Y W, Zheng M L, et al. Tectonics of Energy Resource Basins in the North China (in Chinese). Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology Press, 2007. 1–2
Zhou X H, Sun M, Zhang G H, et al. continental crust and lithospheric mantle interaction beneath North China: Isotopic evidence from granulite xenoliths in Hannuoba, Sino-Korean craton. Lithos, 2002, 62: 111–124
Flower M F J. Mantle Plane and Plate Interaction in East Asia, Geodynamics Series 27. Washington: American Geophysical Union, 1998. 67–68
Ma Z J, Chen X L, Ye S H, et al. Contemporary crustal movement of continental China obtained by global positioning system (GPS) measurements. Chin Sci Bull, 2001, 46: 1552–1554
Qiu R Z, Deng J F, Zhou S, et al. Lithosphere types in North China: Evidence from geology and geophysics. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 2005, 48: 1809–1827
Yan J, Chen J F. Model of the lithospheric non-uniform thinning and alteration from late Mesozoic to Cenozoic in the North China Block (in Chinese). Geol Rev, 2005, 51: 16–26
Xing Z Y, Xing J S, Zhao B. Stratigraphic record in a whole episode of foreland basin tectonic evolution: The lower Cretaceous in Kuqa depression (in Chinese). Geol Sci Tech Inf, 2006, 25: 17–24
Deng J F, Wei W B, Qiu R Z, et al. The Three-dimensional Structure of Lithosphere and Its Evolution in North China (in Chinese). Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2007. 37
Zhang P, Wang L S, Liu S W, et al. Thermo-rheological structure of the lithosphere in the south Huabei Basin (in Chinese). Geol J China Univ, 2006, 12: 530–536
Scott A R, Kaiser W R, Ayers W B, et al. Thermogenic and secondary biogenic gases, San Juan Basin, Colorado and New Mexico— Implication for coalbed gas producibility. AAPG Bull, 1994, 78: 1186–1209
Li J Y, Tao M X. International study on the origin and composition of coalbed gas (in Chinese). Adv Earth Sci, 1998, 13: 467–473
Rice D D. Composition and origins of coalbed gas. In: Law B E, Rice D D, eds. Hydrocarbons from Coal. Tulsa: American Association of Petroleum Geologists, 1993. 159–184
Ayers W B, Jr Kaiser W R. Coalbed Methane in the Upper Cretaceous Fruitland Formation, San Juan Basin. New Mexico and Colorado. Socorro: New Mexico Bureau of Mines and Mineral Resources, 1994. 165–186
Ju Y W, Jiang B, Wang G L, et al. Tectonic Coals: Structures and Physical Properties of Reservoirs (in Chinese). Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology Press, 2005. 38–39
Yao Y B, Liu D M, Huang W H, et al. Research on the pore-fractures system properties of coalbed methane reservoirs and recovery in Huainan and Huaibei coal-fields (in Chinese). J China Coal Soc, 2006, 31: 163–168
Zhang H, Cui Y J, Tao M X, et al. Evolution of the CBM reservoir-forming dynamic system with mixed secondary biogenic and thermogenic gases in the Huainan Coalfield, China. Chin Sci Bull, 2005, 50(Suppl I): 30
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, J., Ju, Y., Zhang, W. et al. Heat flow and its coalbed gas effects in the central-south area of the Huaibei coalfield, eastern China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 53, 672–682 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-010-0050-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-010-0050-y