Abstract
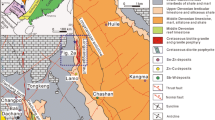
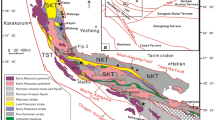
The large-scale Huangshaping Pb-Zn-W-Mo polymetallic deposit is located in the central Nanling mineralization zone, South China. Six molybdenite samples from the Huangshaping deposit were selected for Re-Os isotope measurement in order to define the mineralization age of the deposit. It yields a Re-Os isochron age of 154.8±1.9 Ma (2σ), which is in accordance with the Re-Os model ages of 150.9–156.9 Ma. This age is about 7 Ma younger than their host granite porphyry, which was dated as 161.6±1.1 Ma by zircon U-Pb method using LA-ICPMS. All these ages demonstrate that the Huangshaping granite and related Pb-Zn-W-Mo deposit occurred in the middle Yanshanian period, when many other granitoid and related ore deposits emplaced and formed, e.g. the Qitianling granite and Furong tin deposit, the Qianlishan granite and giant Shizhuyuan W-Sn-Mo-Bi deposit and Jinchuantang Sn-Bi deposit in the nearby area. They constitute the main part of the magmatic-metallogenic belt of southern Hunan, and represent the large-scale metallogeny in middle Yanshanian in the area. The lower rhenium content in molybdenite of Huangshaping deposit suggests that the ore-forming material was mainly of crust origin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tong Q M, Li R Q, Zhang J X. Deposit metallogenetic series across the Chenzhou-Linwu deep-seated fault. Geol Miner Resour South China (in Chinese), 2000, (3): 34–41
Hua R M, Chen P R, Zhang W L, et al. Metallogenic systems related to Mesozoic and Cenozoic granitoids in south China. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 2003, 46(8): 816–829
Yang S Y, Liu H Q, Zhang X L, et al. A study of two typies of porphyry in Baoping district, south Hunan and their mineralization. In: Institute of Mineral Deposits, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, eds. Nanling Geology and Deposit Thesis (in Chinese). Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1986. 157–167
Zhong Z C. Magma rocks and their ore-controlling characteristics in the Huangshaping mining area. Miner Resour Geol (in Chinese), 1996, 10(6): 400–405
Mao J W, Li H Y, Pei R F. Sr and Nd isotope and its origin of Qianlishan rock body in Hunan province. Miner Depos (in Chinese), 1995, 14(3): 235–242
Shen W Z, Wang D Z, Xie Y L, et al. Geochemical characteristics and material sources of the Qianlishan composite granite body, Hunan Province. Acta Petrol Mineral (in Chinese), 1995, 14(3): 193–202
Liu Y M, Dai T M, Lu H Z, et al. 40Ar–39Ar and Sm-Nd isotopic ages of the lithogenesis and mineralization of the Qianlishan granite. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci (in Chinese), 1997, 27(5): 425–430
Li H Y, Mao J W, Sun Y L, et al. Re-Os isotopic chronology of molybdenites in the Shizhuyuan polymetallic tungsten deposit, southern Hunan. Geol Rev (in Chinese), 1996, 12(3): 261–267
Huang G F. Discussion on emplacement time of Qitianling composite rock masses. Geol Prospect (in Chinese), 1992, 28(11): 7–11
Liu Y M, Xu J F, Dai T M, et al. 40Ar/39Ar isotopic age of Qitianling granite and its geological significance. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci (in Chinese), 2002, 32(suppl.): 41–48
Huang G F, Zeng Q W, Wei S L, et al. Geological characteristics and ore-controlling factors of the Furong orefield, Qitianling, Hunan. Geol China (in Chinese), 2001, 28(10): 30–34
Wei S L, Zeng Q W, Xu Y M, et al. Characteristics and ore prospects of tin deposits in the Qitianling area, Hunan. Geol China (in Chinese), 2002, 29(1): 67–75
Wang X W, Wang X D, Liu J Q, et al. Relationship of Qitianling granite to Sn mineralization in Hunan province. Geol Sci Technol Inf (in Chinese), 2004, 23(2): 1–12
Deng X G, Li X H, Liu Y M, et al. Geochemical characteristics of Qitianling granites and their implications for mineralization. Acta Petrol Mineral (in Chinese), 2005, 24(2): 93–102
Zheng J J, Jia B H. Geological characteristics and related tin-polymetallic mineralization of the Qitianling granite complex in southern Hunan Province. Geol Miner Resour South China (in Chinese), 2001, (4): 50–57
Yao J M, Hua R M, Lin J F. Zircon LA-ICPMS U-Pb dating and geochemical characteristics of Huangshaping granite in southeast Hunan Province, China. Acta Petrol Sin (in Chinese), 2005, 21(3): 688–696
Li X H, Liu D Y, Sun M, et al. Precise Sm-Nd and U-Pb isotopic dating of the supergiant Shizhuyuan polymetallic deposit and its host granite, SE China. Geol Mag, 2004, 141(2): 225–231
Zhu J C, Huang G F, Zhang P H, et al. On the emplacement age and material sources for the granites of Cailing superunit, Qitianling pluton, south Hunan Province. Geol Rev (in Chinese), 2003, 49(3): 245–252
Fu J M, Ma C Q, Xie C F, et al. Zircon SHRIMP dating of the Cailing granite on the eastern margin of the Qitianling granite, Hunan, south China, and its significance. Geol China (in Chinese), 2004, 31(1): 96–100
Zhu J C, Zhang H, Xie C F, et al. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb geochronology, petrology and geochemistry of the Zhujianshui granite, Qitianling pluton, southern Hunan Province. Geol J China Univ (in Chinese), 2005, 11(3): 335–342
Li J D, Bai D Y, Wu G Y, et al. Zircon SHRIMP dating of the Qitianling granite, Chenzhou, southern Hunan, and its geological significance. Geol Bull China (in Chinese), 2005, 24(5): 411–414
Mao J W, Li X F, Lehmann B, et al. Ar-Ar dating of tin ores and related granite in Furong tin orefield, Hunan province, and its geodynamic significance. Miner Depos (in Chinese), 2004, 22(2): 164–175
Tong Q M, Wu R H, Pen Q L, et al. Metallogeny of W, Sn, Pb-Zn, Au and Ag Deposits in the Chenxian-Guiyang Region, South Hunan, China (in Chinese). Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1995. 1–98
Tong Q M, Jiang S Z, Li R Q, et al. A study of geological characteristics and ore forming process of the Huangshaping lead-zinc ore deposit, Hunan. Hunan Geol (in Chinese), 1986, (suppl): 1–42
Wang J C, Yao Y, Wang K Y, et al. The mineralization characteristics study of the associated silver in the Huangshaping Pb-Zn ore field. Geol Prospect (in Chinese), 1993, 29(1): 20–27
Zhu E J, Wang J G, Qiu Y M. The distribution regularity and occurrence of the associated silver in the Huangshaping Pb-Zn ore field, Hunan Province. Geol Explor Non-ferrous Metals (in Chinese), 1995, 4(2): 89–95
Zhong Z C, Deng S F, Wang L H. Association of silver mineralization in the Huangshaping lead zinc deposit. Miner Resour Geol (in Chinese), 1997, 11(1): 46–52
Deng S F. Zoning regularity of mineral assemblages in the Huangshaping lead-zinc deposit. Miner Resour Geol (in Chinese), 1997, 11(5): 314–318
Song X Y, Zhang J H, Lin J H, et al. Mechanism of Fe2+ occupancy of the marmatite in the inner zone of the Huangshaping Pb-Zn deposit, Hunan. Geol Prospect (in Chinese), 1999, 35(2): 21–24
Li S J. A simple explanation to ore-controlling structure characteristics and ore-forming process analysis of Huangshaping Pb-Zn deposit in Hunan Province. Geotecton Metall (in Chinese), 1997, 21(2): 339–346
Shen S. Ore mineral composition and deposit factors-controlled of copper deposit in Huangshaping ore area. Hunan Geol (in Chinese), 1999, 18(2/3): 75–78
Gu L. On the Genesis of the lead-zinc polymetallic deposit in Huangshaping. Hunan Geol (in Chinese), 1997, 16(4): 232–235, 238
Zeng Z X. Geological characteristics and genesis of the copper deposit of the Huangshaping ore field. Huan Nonferrous Metals (in Chinese), 2001, 17(3): 8–9
Mao J W, Zhang Z C, Zhang Z H, et al. Re-Os isotopic dating of molybdenites in the Xiaoliugou W (Mo) deposit in the northern Qilian mountains and its geological significance. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 1999, 63(11/12): 1815–1818
Raith J, Stein H. Re-Os dating and sulfur isotope composition of molybdenite from tungsten deposits in western Namaqualand, South Africa: implications for ore genesis and the timing of metamorphism. Miner Deposita, 2000, 35: 741–753
Zhang L C, Xiao W J, Qin K Z, et al. Re-Os isotopic dating of molybdenite and pyrite in the Baishan Mo-Re deposit, eastern Tianshan, NW China, and its geological significance. Miner Deposita, 2005, 39: 960–969
Du A D, He H L, Yin N W, et al. A study on the rhenium-osmium geochronometry of molybdenites. Acta Geol Sin (in Chinese), 1994, 68(4): 339–347
Shirey S, Walker R. Carius tube digestion for low-blank rhenium-osmium analysis. Anal Chem, 1995, 67: 2136–2141
Du A D, Wu S Q, Sun D Z, et al. Preparation and Certification of Re-Os Dating Reference Materials: Molybdenite HLP and JDC. Geostandard Newslett, 2004, 28(04/05): 41–52
Qu W J, Du A D. Highly precise Re-Os dating of molybdenite by ICP-MS with carius tube sample digestion. Rock Miner Anal (in Chinese), 2003, 22(4): 254–257
Stein H, Markey R, Morgan J, et al. The remarkable Re-Os chronometer in molybdenite: how and why it works. Terra Nova, 2001, 13(6): 479–486
Ludwig K. Isoplot/Ex 3.0. A geochronogical toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley Geochronology Center, Berkeley, CA, USA, Special Publication No. 4, 2003
Hua R M, Chen P R, Zhang W L, et al. Three major metallogenic events in Mesozoic in south China. Miner Deposita (in Chinese), 2005, 24(2): 99–107
Hua R M, Chen P R, Zhang W L, et al. Metallogeneses related to Mesozoic granitoids in the Nanling Range, and their geodynamic settings. Acta Geol Sin Engl Ed, 2005b, 79(6): 801–811
Mao J W, Xie G Q, Li X F, et al. Mesozoic large scale mineralization and multiple lithospheric extension in south china. Earth Sci Front (in Chinese), 2004, 11(1): 45–55
Xiao H Q, Zhao K D, Jiang S Y, et al. Lead isotope geochemistry and ore-forming age of Jinchuantang Sn-Bi deposit in Dongpo ore field, Hunan Province. Miner Deposita (in Chinese), 2003, 22(3): 264–270
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the State Key Fundamental Research Project (Grant No. G1999CB403209) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 40572057)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, J., Hua, R., Qu, W. et al. Re-Os isotope dating of molybdenites in the Huangshaping Pb-Zn-W-Mo polymetallic deposit, Hunan Province, South China and its geological significance. SCI CHINA SER D 50, 519–526 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-007-2052-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-007-2052-y