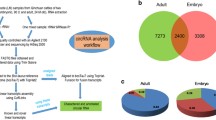
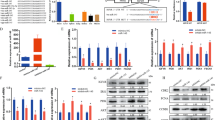
Abstract
Circular RNAs (circRNAs), a novel class of non-coding RNAs with a loop structure, have recently been shown to participate in various pathophysiological processes. However, the precise role of circRNAs in myoblasts remains unclear. In this report, circSVIL was screened and identified from our previous sequencing analysis; we then performed gain- and loss-of-function experiments on bovine myoblasts by CCK8, EdU, flow cytometry, qRT-PCR, and Western blotting. The results indicate that circSVIL facilitates bovine myoblast proliferation and inhibits cell apoptosis. Using mechanism assays such as bioinformatics prediction, RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP), and cytoplasmic separation, we demonstrate that circSVIL could interact with STAT1 and inhibit STAT1 phosphorylation, thereby restraining STAT1’s nuclear translocation and affecting its downstream signal cascade. Our results may elucidate a new regulatory pathway for bovine skeletal muscle development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barik, A., C, N., Pilla, S.P., and Bahadur, R.P. (2015). Molecular architecture of protein-RNA recognition sites. J Biomol Structure Dyn 33, 2738–2751.
Bhattacharyya, S.N., Habermacher, R., Martine, U., Closs, E.I., and Filipowicz, W. (2006). Relief of microRNA-mediated translational repression in human cells subjected to stress. Cell 125, 1111–1124.
Black, B.L., and Olson, E.N. (1998). Transcriptional control of muscle development by myocyte enhancer factor-2 (MEF2) proteins. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 14, 167–196.
Calò, V., Migliavacca, M., Bazan, V., Macaluso, M., Buscemi, M., Gebbia, N., and Russo, A. (2003). STAT proteins: from normal control of cellular events to tumorigenesis. J Cell Physiol 197, 157–168.
Cesana, M., Cacchiarelli, D., Legnini, I., Santini, T., Sthandier, O., Chinappi, M., Tramontano, A., and Bozzoni, I. (2011). A long noncoding RNA controls muscle differentiation by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Cell 147, 358–369.
Chargé, S.B.P., and Rudnicki, M.A. (2004). Cellular and molecular regulation of muscle regeneration. Physiol Rev 84, 209–238.
Chen, L.L., and Yang, L. (2015). Regulation of circRNA biogenesis. RNA Biol 12, 381–388.
Chen, Y., Yang, F., Fang, E., Xiao, W., Mei, H., Li, H., Li, D., Song, H., Wang, J., Hong, M., et al. (2019). Circular RNA circAGO2 drives cancer progression through facilitating HuR-repressed functions of AGO2-miRNA complexes. Cell Death Differ 26, 1346–1364.
Chin, Y.E., Kitagawa, M., Su, W.C.S., You, Z.H., Iwamoto, Y., and Fu, X.Y. (1996). Cell growth arrest and induction of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21WAF1/CIP1 mediated by STAT1. Science 272, 719–722.
Conlon, E.G., and Manley, J.L. (2017). RNA-binding proteins in neurodegeneration: mechanisms in aggregate. Genes Dev 31, 1509–1528.
Corley, M., Burns, M.C., and Yeo, G.W. (2020). How RNA-binding proteins interact with RNA: molecules and mechanisms. Mol Cell 78, 9–29.
Dahmane Gošnak, R., Eržen, I., Holcman, A., and Škorjanc, D. (2010). Effects of divergent selection for 8-week body weight on postnatal enzyme activity pattern of 3 fiber types in fast muscles of male broilers (Gallus gallus domesticus). Poult Sci 89, 2651–2659.
Dimberg, A., Karlberg, I., Nilsson, K., and Oberg, F. (2003). Ser727/Tyr701-phosphorylated Stat1 is required for the regulation of c-Myc, cyclins, and p27Kip1 associated with ATRA-induced G0/G1 arrest of U-937 cells. Blood 102, 254–261.
Dimco, G., Knight, R.A., Latchman, D.S., and Stephanou, A. (2010). STAT1 interacts directly with cyclin D1/Cdk4 and mediates cell cycle arrest. Cell Cycle 9, 4638–4649.
Du, W.W., Zhang, C., Yang, W., Yong, T., Awan, F.M., and Yang, B.B. (2017a). Identifying and characterizing circRNA-protein interaction. Theranostics 7, 4183–4191.
Du, W.W., Fang, L., Yang, W., Wu, N., Awan, F.M., Yang, Z., and Yang, B. B. (2017b). Induction of tumor apoptosis through a circular RNA enhancing Foxo3 activity. Cell Death Differ 24, 357–370.
Egan, B., and Zierath, J.R. (2013). Exercise metabolism and the molecular regulation of skeletal muscle adaptation. Cell Metab 17, 162–184.
Flores, J.K., and Ataide, S.F. (2018). Structural changes of RNA in complex with proteins in the SRP. Front Mol Biosci 5, 7–10.
Greggio, C., Jha, P., Kulkarni, S.S., Lagarrigue, S., Broskey, N.T., Boutant, M., Wang, X., Conde Alonso, S., Ofori, E., Auwerx, J., et al. (2017). Enhanced respiratory chain supercomplex formation in response to exercise in human skeletal muscle. Cell Metab 25, 301–311.
Gupta, A., and Gribskov, M. (2011). The role of RNA sequence and structure in RNA-protein interactions. J Mol Biol 409, 574–587.
Hu, W., Qin, L., Li, M., Pu, X., and Guo, Y. (2018). A structural dissection of protein-RNA interactions based on different RNA base areas of interfaces. RSC Adv 8, 10582–10592.
Huang, G.W., Li, C.Q., Liao, L.D., Jiao, J.W., Long, L., Ding, J.Y., Guo, J. C., Li, E.M., and Xu, L.Y. (2019). LncRNA625 inhibits STAT1-mediated transactivation potential in esophageal cancer cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 117, 105626.
Huang, A., Zheng, H., Wu, Z., Chen, M., and Huang, Y. (2020). Circular RNA-protein interactions: functions, mechanisms, and identification. Theranostics 10, 3503–3517.
Kristensen, L.S., Andersen, M.S., Stagsted, L.V.W., Ebbesen, K.K., Hansen, T.B., and Kjems, J. (2019). The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet 20, 675–691.
Leulliot, N., and Varani, G. (2001). Current topics in RNA-protein recognition: control of specificity and biological function through induced fit and conformational capture. Biochemistry 40, 7947–7956.
Li, H., Yang, J., Wei, X., Song, C., Dong, D., Huang, Y., Lan, X., Plath, M., Lei, C., Ma, Y., et al. (2018). CircFUT10 reduces proliferation and facilitates differentiation of myoblasts by sponging miR-133a. J Cell Physiol 233, 4643–4651.
Miyake, M., Takahashi, H., Kitagawa, E., Watanabe, H., Sakurada, T., Aso, H., and Yamaguchi, T. (2012). AMPK activation by AICAR inhibits myogenic differentiation and myostatin expression in cattle. Cell Tissue Res 349, 615–623.
Moresi, V., Adamo, S., and Berghella, L. (2019). The JAK/STAT pathway in skeletal muscle pathophysiology. Front Physiol 10.
Murphy, D., Detjen, K.M., Welzel, M., Wiedenmann, B., and Rosewicz, S. (2001). Interferon-α delays S-phase progression in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells via inhibition of specific cyclin-dependent kinases. Hepatology 33, 346–356.
Pandey, P.R., Yang, J.H., Tsitsipatis, D., Panda, A.C., Noh, J.H., Kim, K. M., Munk, R., Nicholson, T., Hanniford, D., Argibay, D., et al. (2020). circSamd4 represses myogenic transcriptional activity of PUR proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 48, 3789–3805.
Pownall, M.E., Gustafsson, M.K., and Emerson Jr, C.P. (2002). Myogenic regulatory factors and the specification of muscle progenitors in vertebrate embryos. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 18, 747–783.
Salvatore, D., Simonides, W.S., Dentice, M., Zavacki, A.M., and Larsen, P. R. (2014). Thyroid hormones and skeletal muscle—new insights and potential implications. Nat Rev Endocrinol 10, 206–214.
Salmena, L., Poliseno, L., Tay, Y., Kats, L., and Pandolfi, P.P. (2011). A ceRNA hypothesis: the rosetta stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 146, 353–358.
Shen, X., Zhang, X., Ru, W., Huang, Y., Lan, X., Lei, C., and Chen, H. (2020). circINSR promotes proliferation and reduces apoptosis of embryonic myoblasts by sponging miR-34a. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 19, 986–999.
Stephanou, A., Brar, B.K., Knight, R.A., and Latchman, D.S. (2000). Opposing actions of STAT-1 and STAT-3 on the Bcl-2 and Bcl-x promoters. Cell Death Differ 7, 329–330.
Su, H., Tao, T., Yang, Z., Kang, X., Zhang, X., Kang, D., Wu, S., and Li, C. (2019). Circular RNA cTFRC acts as the sponge of MicroRNA-107 to promote bladder carcinoma progression. Mol Cancer 18, 27.
Tay, Y., Rinn, J., and Pandolfi, P.P. (2014). The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature 505, 344–352.
Thomson, D.W., and Dinger, M.E. (2016). Endogenous microRNA sponges: evidence and controversy. Nat Rev Genet 17, 272–283.
Townsend, P.A., Scarabelli, T.M., Davidson, S.M., Knight, R.A., Latchman, D.S., and Stephanou, A. (2004). STAT-1 interacts with p53 to enhance DNA damage-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 279, 5811–5820.
Wilson, K.A., Holland, D.J., and Wetmore, S.D. (2016). Topology of RNA-protein nucleobase-amino acid π-π interactions and comparison to analogous DNA-protein π-π contacts. RNA 22, 696–708.
Wüst, S., Dröse, S., Heidler, J., Wittig, I., Klockner, I., Franko, A., Bonke, E., Günther, S., Gärtner, U., Boettger, T., et al. (2018). Metabolic maturation during muscle stem cell differentiation is achieved by miR-1/133a-mediated inhibition of the Dlk1-Dio3 Mega gene cluster. Cell Metab 27, 1026–1039.e6.
Yang, Z.G., Awan, F.M., Du, W.W., Zeng, Y., Lyu, J., Wu, D., Gupta, S., Yang, W., and Yang, B.B. (2017). The circular RNA interacts with STAT3, increasing its nuclear translocation and wound repair by modulating Dnmt3a and miR-17 function. Mol Ther 25, 2062–2074.
Yue, B., Wang, J., Ru, W., Wu, J., Cao, X., Yang, H., Huang, Y., Lan, X., Lei, C., Huang, B., et al. (2020). The circular RNA circHUWE1 sponges the miR-29b-AKT3 axis to regulate myoblast development. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 19, 1086–1097.
Zhang, Y., and Liu, Z. (2017). STAT1 in cancer: friend or foe? Discov Med 24, 19–29.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31772574).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Compliance and ethics The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest. All animal experiments were maintained according to the Regulation for the Administration of Affairs Concerning Experimental Animals (State Council of China, 2017 Revision), and our study was approved by Northwest A&F University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, B., Yang, H., Wu, J. et al. circSVIL regulates bovine myoblast development by inhibiting STAT1 phosphorylation. Sci. China Life Sci. 65, 376–386 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1908-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1908-2