Abstract
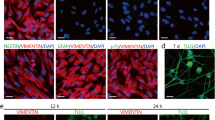
Transplantation of motor neurons can provide long-term functional benefits in animal models of neurodegenerative motor neuron diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and traumatic spinal cord injury. Although embryonic stem cells can differentiate into motor neurons, alternative sources of motor neurons may be controllable for disease modeling and transplantation. Here, we show that human and mouse fibroblasts can be efficiently and directly converted into motor neurons by a cocktail of five small molecules, without the involvement of the neural progenitor stage. The chemically-induced motor neurons display the distinct neuronal morphology and express motor neuron markers. Interestingly, when the same chemical compounds were soaked in beads and implanted in the hypodermis of the back skins of mice, surrounding cells begin to express motor neuron markers, indicating in vivo motor neuron reprogramming. Taken together, we provide an efficient approach for chemically converting human and mouse fibroblasts into motor neurons suitable for cell replacement therapy and neurodegenerative disease modeling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, K.L., Rousso, D.L., Umbach, J.A., and Novitch, B.G. (2015). Foxp1-mediated programming of limb-innervating motor neurons from mouse and human embryonic stem cells. Nat Commun 6, 6778.
Amoroso, M.W., Croft, G.F., Williams, D.J., O’Keeffe, S., Carrasco, M.A., Davis, A.R., Roybon, L., Oakley, D.H., Maniatis, T., Henderson, C.E., et al. (2013). Accelerated high-yield generation of limb-innervating motor neurons from human stem cells. J Neurosci 33, 574–586.
Ben-Shushan, E., Feldman, E., and Reubinoff, B.E. (2015). Notch signaling regulates motor neuron differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 33, 403–415.
Chambers, S.M., Fasano, C.A., Papapetrou, E.P., Tomishima, M., Sadelain, M., and Studer, L. (2009). Highly efficient neural conversion of human ES and iPS cells by dual inhibition of SMAD signaling. Nat Biotechnol 27, 275–280.
Chambers, S.M., Qi, Y., Mica, Y., Lee, G., Zhang, X.J., Niu, L., Bilsland, J., Cao, L., Stevens, E., Whiting, P., et al. (2012). Combined small-molecule inhibition accelerates developmental timing and converts human pluripotent stem cells into nociceptors. Nat Biotechnol 30, 715–720.
Cheng, L., Gao, L., Guan, W., Mao, J., Hu, W., Qiu, B., Zhao, J., Yu, Y., and Pei, G. (2015). Direct conversion of astrocytes into neuronal cells by drug cocktail. Cell Res 25, 1269–1272.
Cheng, L., Hu, W., Qiu, B., Zhao, J., Yu, Y., Guan, W., Wang, M., Yang, W., and Pei, G. (2014). Generation of neural progenitor cells by chemical cocktails and hypoxia. Cell Res 24, 665–679.
Dai, P., Harada, Y., and Takamatsu, T. (2015). Highly efficient direct conversion of human fibroblasts to neuronal cells by chemical compounds. J Clin Biochem Nutr 56, 166–170.
Gao, L., Guan, W., Wang, M., Wang, H., Yu, J., Liu, Q., Qiu, B., Yu, Y., Ping, Y., Bian, X., et al. (2017). Direct generation of human neuronal cells from adult astrocytes by small molecules. Stem Cell Rep 8, 538–547.
Hester, M.E., Murtha, M.J., Song, S.W., Rao, M., Miranda, C.J., Meyer, K., Tian, J., Boulting, G., Schaffer, D.V., Zhu, M.X., et al. (2011). Rapid and efficient generation of functional motor neurons from human pluripotent stem cells using gene delivered transcription factor codes. Mol Ther 19, 1905–1912.
Hu, B.Y., and Zhang, S.C. (2009). Differentiation of spinal motor neurons from pluripotent human stem cells. Nat Protoc 4, 1295–1304.
Hu, W., Qiu, B., Guan, W., Wang, Q., Wang, M., Li, W., Gao, L., Shen, L., Huang, Y., Xie, G., et al. (2015). Direct conversion of normal and Alzheimer’s disease human fibroblasts into neuronal cells by small molecules. Cell Stem Cell 17, 204–212.
Kim, W.Y., Wang, X., Wu, Y., Doble, B.W., Patel, S., Woodgett, J.R., and Snider, W.D. (2009). GSK-3 is a master regulator of neural progenitor homeostasis. Nat Neurosci 12, 1390–1397.
Ladewig, J., Mertens, J., Kesavan, J., Doerr, J., Poppe, D., Glaue, F., Herms, S., Wernet, P., Kögler, G., Müller, F.J., et al. (2012). Small molecules enable highly efficient neuronal conversion of human fibroblasts. Nat Methods 9, 575–578.
Lee, S.K., Lee, B., Ruiz, E.C., and Pfaff, S.L. (2005). Olig2 and Ngn2 function in opposition to modulate gene expression in motor neuron progenitor cells. Genes Dev 19, 282–294.
Li, W., Sun, W., Zhang, Y., Wei, W., Ambasudhan, R., Xia, P., Talantova, M., Lin, T., Kim, J., Wang, X., et al. (2011). Rapid induction and longterm self-renewal of primitive neural precursors from human embryonic stem cells by small molecule inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, 8299–8304.
Li, X., Zuo, X., Jing, J., Ma, Y., Wang, J., Liu, D., Zhu, J., Du, X., Xiong, L., Du, Y., et al. (2015). Small-molecule-driven direct reprogramming of mouse fibroblasts into functional neurons. Cell Stem Cell 17, 195–203.
Li, X.J., Du, Z.W., Zarnowska, E.D., Pankratz, M., Hansen, L.O., Pearce, R.A., and Zhang, S.C. (2005). Specification of motoneurons from human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol 23, 215–221.
Li, X.J., Hu, B.Y., Jones, S.A., Zhang, Y.S., Lavaute, T., Du, Z.W., and Zhang, S.C. (2008). Directed differentiation of ventral spinal progenitors and motor neurons from human embryonic stem cells by small molecules. Stem Cells 26, 886–893.
Liu, M.L., Zang, T., and Zhang, C.L. (2016). Direct lineage reprogramming reveals disease-specific phenotypes of motor neurons from human ALS patients. Cell Rep 14, 115–128.
Liu, M.L., Zang, T., Zou, Y., Chang, J.C., Gibson, J.R., Huber, K.M., and Zhang, C.L. (2013). Small molecules enable neurogenin 2 to efficiently convert human fibroblasts into cholinergic neurons. Nat Commun 4, 2183.
Lu, P., Chen, X., Feng, Y., Zeng, Q., Jiang, C., Zhu, X., Fan, G., and Xue, Z. (2016). Integrated transcriptome analysis of human iPS cells derived from a fragile X syndrome patient during neuronal differentiation. Sci China Life Sci 59, 1093–1105.
Lunn, M.R., and Wang, C.H. (2008). Spinal muscular atrophy. Lancet 371, 2120–2133.
Mizuguchi, R., Sugimori, M., Takebayashi, H., Kosako, H., Nagao, M., Yoshida, S., Nabeshima, Y., Shimamura, K., and Nakafuku, M. (2001). Combinatorial roles of olig2 and neurogenin2 in the coordinated induction of pan-neuronal and subtype-specific properties of motoneurons. Neuron 31, 757–771.
Pfisterer, U., Ek, F., Lang, S., Soneji, S., Olsson, R., and Parmar, M. (2016). Small molecules increase direct neural conversion of human fibroblasts. Sci Rep 6, 38290.
Qin, H., Zhao, A., and Fu, X. (2017). Small molecules for reprogramming and transdifferentiation. Cell Mol Life Sci 74, 3553–3575.
Qin, H., Zhao, A., Zhang, C., and Fu, X. (2016). Epigenetic control of reprogramming and transdifferentiation by histone modifications. Stem Cell Rev Rep 12, 708–720.
Qu, Q., Li, D., Louis, K.R., Li, X., Yang, H., Sun, Q., Crandall, S.R., Tsang, S., Zhou, J., Cox, C.L., et al. (2014). High-efficiency motor neuron differentiation from human pluripotent stem cells and the function of Islet-1. Nat Commun 5, 3449.
Rowland, L.P., and Shneider, N.A. (2001). Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. N Engl J Med 344, 1688–1700.
Sahni, V., and Kessler, J.A. (2010). Stem cell therapies for spinal cord injury. Nat Rev Neurol 6, 363–372.
Son, E.Y., Ichida, J.K., Wainger, B.J., Toma, J.S., Rafuse, V.F., Woolf, C.J., and Eggan, K. (2011). Conversion of mouse and human fibroblasts into functional spinal motor neurons. Cell Stem Cell 9, 205–218.
Takahashi, K., and Yamanaka, S. (2006). Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 126, 663–676.
Wang, Y., Yang, H., Yang, Q., Yang, J., Wang, H., Xu, H., and Gao, W.Q. (2016). Chemical conversion of mouse fibroblasts into functional dopaminergic neurons. Exp Cell Res 347, 283–292.
Wichterle, H., Lieberam, I., Porter, J.A., and Jessell, T.M. (2002). Directed differentiation of embryonic stem cells into motor neurons. Cell 110, 385–397.
Xu, H., Wang, Y., He, Z., Yang, H., and Gao, W.Q. (2015a). Direct conversion of mouse fibroblasts to GABAergic neurons with combined medium without the introduction of transcription factors or miRNAs. Cell Cycle 14, 2451–2460.
Xu, J., Du, Y., and Deng, H. (2015b). Direct lineage reprogramming: strategies, mechanisms, and applications. Cell Stem Cell 16, 119–134.
Yang, Y.M., Gupta, S.K., Kim, K.J., Powers, B.E., Cerqueira, A., Wainger, B.J., Ngo, H.D., Rosowski, K.A., Schein, P.A., Ackeifi, C.A., et al. (2013). A small molecule screen in stem-cell-derived motor neurons identifies a kinase inhibitor as a candidate therapeutic for ALS. Cell Stem Cell 12, 713–726.
Zhang, C., Cao, J., Li, X., Xu, H., Wang, W., Wang, L., Zhao, X., Li, W., Jiao, J., Hu, B., et al. (2016). Treatment of multiple sclerosis by transplantation of neural stem cells derived from induced pluripotent stem cells. Sci China Life Sci 59, 950–957.
Zhang, L., Yin, J.C., Yeh, H., Ma, N.X., Lee, G., Chen, X.A., Wang, Y., Lin, L., Chen, L., Jin, P., et al. (2015). Small molecules efficiently reprogram human astroglial cells into functional neurons. Cell Stem Cell 17, 735–747.
Zhang, Q.J., Li, J.J., Lin, X., Lu, Y.Q., Guo, X.X., Dong, E.L., Zhao, M., He, J., Wang, N., and Chen, W.J. (2017). Modeling the phenotype of spinal muscular atrophy by the direct conversion of human fibroblasts to motor neurons. Oncotarget 8, 10945–10953.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81721092) and the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFC1103304).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, H., Zhao, A., Ma, K. et al. Chemical conversion of human and mouse fibroblasts into motor neurons. Sci. China Life Sci. 61, 1151–1167 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-018-9359-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-018-9359-8