Abstract
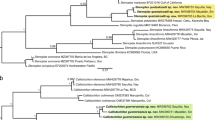
The phylogenetic relationships of 13 snapper species from the South China Sea have been established using the combined DNA sequences of three full-length mitochondrial genes (COI, COII and CYTB) and two partial nuclear genes (RAG1, RAG2). The 13 species (genus Lutjanus) were selected after DNA barcoding 72 individuals, representing 20 species. Our study suggests that although DNA barcoding aims to develop species identification systems, it may also be useful in the construction of phylogenies by aiding the selection of taxa. Combined mitochondrial and nuclear gene data has an advantage over an individual dataset because of its higher resolving power.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Russ G R, Alcala A C. Effects of intense fishing pressure on an assemblage of coral reef fishes. Mar Ecol Prog Ser, 1989, 56:13–27, 10.3354/meps056013
Marko P B, Lee S C, Rice A M, et al. Fisheries: Mislabelling of a depleted reef fish. Nature, 2004, 430:309–310, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXls1eqsro%3D, 10.1038/430309b, 15254528
Zhang J, Huang L, Huo H. Larval identification of Lutjanus Bloch in Nansha coral reefs by AFLP molecular method. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol, 2004, 298:3–20, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXpvF2rt7Y%3D, 10.1016/S0022-0981(03)00341-1
Chen G H, Yin S, Lei C, et al. Artificial reproduction and rearing of snapper hybrids (Lutjanus erythropterus×L. sebae). Fisheries Sci, 2006, 25, 1–4
Domeier M L, Clarke M E. A laboratory produced hybrid between Lutjanus synagris and Ocyurus chrysurus and a probable hybrid between L. Griseus and O. Chrysurus (Perciformes: Lutjanidae). B Mar Sci, 1992, 50:501–507
Loftus W F. Lutjanus ambiguus (Poey), a natural intergeneric hybrid of Ocyurus chrysurus (Bloch) and Lutjanus synagris (Linnaeus). B Mar Sci, 1992, 50:489–499
Camper J D, Barber R C, Richardson L R, et al. Mitochondrial DNA variation among red snapper (Lutjanus campechanus) from the Gulf of Mexico. Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol, 1993, 2:154–161, 1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXisVSltbY%3D, 8103412
Gold J R, Richardson L R. Genetic homogeneity among geographic samples of snappers and groupers: Evidence of continuous gene flow. Proc Gulf Carib Fish Inst, 1998, 50:709–726
Gold J R, Sun F, Richardson L R. Population structure of red snapper from the Gulf of Mexico as inferred from analysis of mitochondrial DNA. T Am Fish Soc, 1997, 126:386–396, 1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXlt1Ckuro%3D, 10.1577/1548-8659(1997)126<0386:PSORSF>2.3.CO;2
Gold J R, Richardson L R, Furman C, et al. Mitochondrial DNA diversity and population structure in marine fish species from the Gulf of Mexico. Can J Fish Aquat Sci, 1994, 51(Supplement 1):205–214, 1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXls1ersrw%3D, 10.1139/f94-306
Sarver S K, Freshwater D W, Walsh P J. Phylogenetic relationships of Western Atlantic Snappers (Family Lutjanidae) based on mitochondrial DNA sequences. Copeia, 1996, 1996:715–721, 10.2307/1447537
Kristmundsdo A, Barber R C, Gold J R. Restriction enzyme maps of mitochondrial DNA from red snapper, Lutjanus campechanus, and king mackerel, Scomberomorus cavalla. Gulf Mex Sci, 1996, 14:31–35
Guo Y S, Wang Z D, Liu C W, et al. Phylogenetic relationships of South China Sea Snappers (Genus Lutjanus; Family Lutjanidae) based on mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mar Biotechnol, 2007, 9:682–688, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2sXhtlyitLjE, 10.1007/s10126-007-9012-6, 17909901
Yaakub S M, Bellwood D R, Herwerden L, et al. Hybridization in coral reef fishes: Introgression and bi-directional gene exchange in Thalassoma (family Labridae). Mol Phylogenet Evol, 2006, 40:84–100, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD28XlvF2msLk%3D, 10.1016/j.ympev.2006.02.012, 16581267
Iwatsuki Y, Akazaki M, Yoshino T. Validiity of a Lutjanid Fish, Lutjanus ophuysenii (Bleeker) with a related species, L.vitta (Quoy et Gaimard). Japan J Ichthyol, 1993, 40:47–59
Sambrook J, Fritsch E F, Maniatis T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual: Cold Spring Harbor. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, 1989. 40
Ward R D, Zemlak T S, Innes B H, et al. DNA barcoding Australia’s fish species. Phil Trans Biol Sci, 2005, 360:1847–1857, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXhtlSjsrjK, 10.1098/rstb.2005.1716
Quenouille B, Bermingham E, Planes S. Molecular systematics of the damselfishes (Teleostei: Pomacentridae): Bayesian phylogenetic analyses of mitochondrial and nuclear DNA sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol, 2004, 31:66–88, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXhvFSks74%3D, 10.1016/S1055-7903(03)00278-1, 15019609
Westneat M W, Alfaro M E. Phylogenetic relationships and evolutionary history of the reef fish family Labridae. Mol Phylogenet Evol, 2005, 36:370–390, 10.1016/j.ympev.2005.02.001, 15955516
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, et al. MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) Software Version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol, 2007, 24:1596–1599, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2sXpsVGrsL8%3D, 10.1093/molbev/msm092, 17488738
Xia X, Xie Z. DAMBE: Data analysis in molecular biology and evolution. Heredity, 2001, 92:371–373, 1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MvptlagtA%3D%3D, 10.1093/jhered/92.4.371
Russell D J. Biology, management and genetic stock structure of Mangrove Jack (Lutjanus argentimaculatus) in Australia. Department of Primary Industries, Fisheries Research and Development Corporation, 2003. 87
Ward R D, Holmes B H, Yearsley G K. DNA barcoding reveals a likely second species of Asian sea bass (barramundi) (Lates calcarifer). J Fish Biol, 2008, 72:458–463, 10.1111/j.1095-8649.2007.01703.x
Hajibabaei M, Singer G A, Hebert P D, et al. DNA barcoding: how it complements taxonomy, molecular phylogenetics and population genetics. Trends Genet, 2007, 23:167–172, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2sXjslShur8%3D, 10.1016/j.tig.2007.02.001, 17316886
Felsenstein J. Inferring Phylogenies. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates, 2004. 664
Hajibabaei M, Singer G A, Hickey D A. Benchmarking DNA barcodes: an assessment using available primate sequences. Genome, 2006, 49:851, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD28XhtFCht7%2FF, 10.1139/G06-025, 16936793
Min X I, Hickey D O. Assessing the effect of varying sequence length on DNA barcoding of fungi. Mol Ecol Notes, 2007, 7:365–373, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2sXntVyktr4%3D, 10.1111/j.1471-8286.2007.01698.x, 18784789
Hackett S J, Kimball R T, Reddy S, et al. A Phylogenomic study of birds reveals their evolutionary history. Science, 2008, 320: 1763–1768, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD1cXnsF2qsr4%3D, 10.1126/science.1157704, 18583609
Keck B P, Near T J. Assessing phylogenetic resolution among mitochondrial, nuclear, and morphological datasets in Nothonotus darters (Teleostei: Percidae). Mol Phylogenet Evol, 2008, 46:708–720, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD1cXhvF2gtL8%3D, 10.1016/j.ympev.2007.08.015, 17920301
Wang X Z, Li J B, He S P. Molecular evidence for the monophyly of East Asian groups of Cyprinidae (Teleostei: Cypriniformes) derived from the nuclear recombination activating gene 2 sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol, 2007, 42:157–170, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD28Xht1CgsbrP, 10.1016/j.ympev.2006.06.014, 16919973
Mccormack J E, Peterson A T, Bonaccorso E, et al. Speciation in the highlands of Mexico: genetic and phenotypic divergence in the Mexican jay (Aphelocoma ultramarina). Mol Ecol, 2008, 17: 2505–2521, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD1cXotVOksL4%3D, 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2008.03776.x, 18430143
Rocha L A, Lindeman K C, Rocha C R, et al. Historical biogeography and speciation in the reef fish genus Haemulon (Teleostei: Haemulidae). Mol Phylogenet Evol, 2008, 48:918–928, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD1cXhtVyntL3L, 10.1016/j.ympev.2008.05.024, 18599320
Barreto F S, Mccartney M A. Extraordinary aflp fingerprint similarity despite strong assortative mating between reef fish color morphospecies. Evolution, 2008, 62:226–233, 10.1111/j.1558-5646.2007.00285.x, 18053072
Gray S M, Mckinnon J S. Linking color polymorphism maintenance and speciation. Trends Ecol Evol, 2007, 22:71–79, 10.1016/j.tree.2006.10.005, 17055107
Seehausen O, Terai Y, Magalhaes I S, et al. Speciation through sensory drive in cichlid fish. Nature, 2008, 455:620–626, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD1cXhtF2hsbrL, 10.1038/nature07285, 18833272
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Guo, Y., Tan, W. et al. DNA barcoding, phylogenetic relationships and speciation of snappers (genus Lutjanus). Sci. China Life Sci. 53, 1025–1030 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-010-4034-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-010-4034-0