Abstract
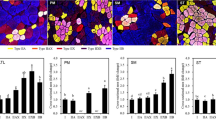
In order to explain the mechanism of high meat quality in Laiwu pigs and investigate the relation between myosin heavy chains (MyHC) composition and meat quality, meat quality analysis was conducted and mRNA expression of MyHC I, IIa, IIx, IIb was quantified by real-time fluorescence PCR in longissimus muscle (LM) and semimembranous muscle of Laiwu pigs and Duroc. The result indicated that, compared with Duroc, mRNA expression of MyHC IIa, IIx in LM and semimembranous muscle of Laiwu pigs was significantly increased, mRNA expression of MyHC IIb was dramatically decreased. However, the expression of MyHC I was not significantly affected by breeds. The correlation between mRNA expression of MyHC I, IIa, IIx in LM and meat color, pH value, marbling, intramuscular fat content was positive, but shear value of LM was negative. The relation between MyHC IIb mRNA expression and marbling, intramuscular fat content was dramatically negative, whereas shear value was strikingly positive, as well as fiber diameter, but without reaching statistical significance. Therefore, the composition of MyHC I, IIa, IIx, IIb affected meat quality, furthermore, expression of MyHC I, IIa, IIx, IIb mRNA prominently influenced meat characteristics, especially edible quality of muscle, suggesting that mRNA expression level of MyHC I, IIa, IIx, IIb can exactly and impersonally estimate meat quality.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weiss A D, Mcdonough B, Wertman L, et al. Organization of human and mouse skeletal myosin heavy chain gene clusters is highly conserved. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1999, 96: 2958–2963
Shrager J B, Desjardins P R, Burkman J M, et al. Human skeletalmyosinheavychaingenes aretightly linked in the order embryonic-IIa-IId/x-IIb-perinatal-extraocular. J Muscle Res Cell Motil, 2000, 21: 345–355
Davoli R, Fontanesi L, ambonelli P Z, et al. Isolation of porcine expressed sequence tags for the construction of a first genomic transcript map of the skeletal muscle in pig. Anim Genet, 2002, 33: 3–18
Lefaucheur L, Ecolan P, Plantard L, et al. New insights into muscle fiber types in the pig. J Histochem Cytochem, 2002, 50(5): 719–730
Chang K C, Costaa N D, Black leya R, et al. Relationship of myosin heavy chain fibers types to meat quality traits in traditional and modern pigs. Meat Sci, 2003, 64: 93–103
Eggert J M, Depreux F F S, Schinckel A P. Myosin heavy chain isoforms account for variation in pork quality. Meat Sci, 2002, 61: 117–126
Chikuni K, Tanabe R, Muroya S, et al. Difference in molecular structure among the porcine myosin in heavy chain −2a,2x and −2b isoforms. Meat Sci, 2001, 57: 311–317
Schiaffino S, Reggiani C. Molecular diversity of myofibril-lar proteins: Gene regulation and functional significance. Physiol Rev, 1996, 76: 371–423
Tanabe R, Nakajima I, Muroya S, et al. Differences in myosin heavy chain isoform expressions among porcin breeds. Meat Sci Technol, 1999, 45: 254–255
Yang X J, Zhao R Q, Chen J, et al. The developmental changes of myofibre types in LD muscle of Erhualian and Large White pigs. Chin J Vet Sci (in Chinese), 2005, 25(2): 89–94
Lefaucheur L, Milan D, Ecolan P, et al. Myosin heavy chain composition of different skeletal muscles in Large White and Meishan pigs. J Anim Sci, 2004, 82: 1931–1941
Li C S, Chen Y S, Wang C, et al. Cloning and analysis of differentially expressed ESTs in swine muscle tissue. Sci China Ser C-Life Sci, 2006, 49(4): 342–348
Zhang W L. Improvemt and assee of meat quality. Swine Production (in Chinese), 2001, 3: 31–33
Wang H Y, Yan D W, Lu S X, et al. Study of meat quality in Saba pigs and its crossbreed. Swine Production (in Chinese), 1997, 3: 29–31
Pellegrino M A, Canepari M, Rossi R, et al. Orthologous myosin isoforms and scaling of shortening velocity with body size in mouse, rat, rabbit and human muscles. J Physiol, 2003, 546: 677–689
Immonen K, Ruusunen M, Hissa K, et al. Bovine muscle glycogen concentration in relation to finishing diet, slaughter and ultimate pH. Meat Sci, 2000, 55: 25–31
Maltin C A, Warkup C C, Mattewa K R, et al. Pig muscle fibre characteristics as source of variation in eating quality. Meat Sci, 1997, 47: 237–248
Maltin C A, Sinclair K D, Warriss P D, et al. The effects of age at slaughter,genotype and finishing system on the biochemical properties, muscle fibre type characteristics and eating quality of bull beef from suckled calves. Anim Sci, 1998, 66: 341–348
Larzul C, Lefaucheur L, Ecolan P, et al. Phenotypic and genetic parameters for longissimus muscle fiber characteristics in relation to growth, carcass, and meat quality traits in Large White pigs. J Anim Sci, 1997, 75: 3126–3137
Wei S D, Cao H F, Xu Y H, et al. Breeding of Laiwu pigs. China J Anim Sci (in Chinese), 2001, 37(6): 30–31
Rahelic S, Puac S. Fiber types in longissimus dorsi from wild and highly selected pig breeds. Meat Sci, 1981, 5: 439–450
Weiler U, Appell H J, remser M K, et al. Consequences of selection on muscle composition: A comparative study on gracilis muscle in wild and domestic pigs. Anat Histol Embryol, 1995, 24: 77–80
Nostvold O, Schie K A, Froystein T. Muscle fiber characteristics in lines of pigs selected for rate of gain and backfat thickness. Acta Agric Scand, 1979, 21: 136–142
Henckel P, Oksbjerg N, Erlandsen E, et al. Histo-and biochemical characteristics of the longissimus dorsi muscle in pigs and their relationships to performance and meat quality. Meat Sci, 1997, 47: 311–321
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by Shandong agricultural breeding project(Grant No. 2006LZ08) and Shandong Academy Agricultural Sciences fund for young scholars (Grant No. 2005YQ041)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, H., Wang, J., Zhu, R. et al. Effect of myosin heavy chain composition of muscles on meat quality in Laiwu pigs and Duroc. Sci. China Ser. C-Life Sci. 51, 127–132 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-008-0016-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-008-0016-x