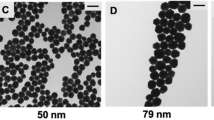
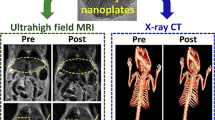
Abstract
X-ray computed tomography (CT) has been widely used as a powerful diagnostic tool in clinics because it can provide high-resolution 3D tomography of the anatomic structure based on the distinctive X-ray absorptions between different tissues. Currently, CT contrast agents are mainly small iodinated molecules, which suffer from drawbacks such as short bloodretention time, nonspecific in vivo biodistribution, and renal toxicity. Utilization of nanoparticles as potential CT contrast agents to overcome the aforementioned issues has advanced rapidly. In this mini review, we introduce current research efforts in the development of nanoparticulate CT contrast agents and discuss the challenges for additional breakthroughs in this field.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kalender WA. X-ray computed tomography. Phys Med Biol, 2006, 51: R29–R43
Ahn S, Jung SY, Lee JP, Lee SJ. Properties of iopamidol-incorporated poly(vinyl alcohol) microparticle as an X-ray imaging flow tracer. J Phy Chem B, 2011, 115: 889–901
Aillon KL, El-Gendy N, Dennis C, Norenberg JP, McDonald J, Berkland C. Iodinated nano clusters as an inhaled computed tomography contrast agent for lung visualization. Mol Pharmaceut, 2010, 7: 1274–1282
Alric C, Taleb J, Le DG, Mandon C, Billotey C, Le Meur-Herland A, Brochard T, Vocanson F, Janier M, Perriat P, Roux S, Tillement O. Gadolinium chelate coated gold nanoparticles as contrast agents for both X-ray computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Chem Soc, 2008, 130: 5908–5915
Yu SB, Watson AD. Metal-based X-ray contrast media. Chem Rev, 1999, 99: 2353–2377
Lee N, Choi SH, Hyeon T. Nano-sized CT contrast agents. Adv Mater, 2013, 25: 2641–2660
Liu YL, Ai KL, Lu LH. Nanoparticulate X-ray computed tomography contrast agents: from design validation to in vivo applications. Acc Chem Res, 2012, 45: 1817–1827
Lusic H, Grinstaff MW. X-ray-computed tomography contrast agents. Chem Rev, 2013, 113: 1641–1666
Osborne ED, Sutherland CG, Scholl AJJr, Rowntree LG. Roentgenography of urinary tract during excretion of sodium iodide. J Am Med Assoc, 1923, 80: 368–373
Shilo M, Reuveni T, Motiei M, Popovtzer R. Nanoparticles as computed tomography contrast agents: current status and future perspectives. Nanomedicine, 2012, 7: 257–269
Hallouard F, Anton N, Choquet P, Constantinesco A, Vandamme T. Iodinated blood pool contrast media for preclinical X-ray imaging applications: a review. Biomaterials, 2010, 31: 6249–6268
Chung YE, Hyung WJ, Kweon S, Lim SJ, Choi J, Lee MH, Kim H, Myoung S, Lim JS. Feasibility of interstitial CT lymphography using optimized iodized oil emulsion in rats. Invest Radiol, 2010, 45: 142–148
Ashokan A, Menon D, Nair S, Koyakutty M. A molecular receptor targeted, hydroxyapatite nanocrystal based multi-modal contrast agent. Biomaterials, 2010, 31: 2606–2616
Montet X, Pastor CM, Vallee JP, Becker CD, Geissbuhler A, Morel DR, Meda P. Improved visualization of vessels and hepatic tumors by micro-computed tomography (CT) using iodinated liposomes. Invest Radiol, 2007, 42: 652–658
Li X, Anton N, Zuber G, Zhao MJ, Messaddeq N, Hallouard F, Fessi H, Vandamme TF. Iodinated α-tocopherol nano-emulsions as nontoxic contrast agents for preclinical X-ray imaging. Biomaterials, 2013, 34: 481–491
Desser TS, Rubin DL, Muller H, Mclntire GL, Bacon ER, Toner JL. Blood pool and liver enhancement in CT with liposomal iodixanol. Acad Radiol, 1999, 6: 176–183
Kao CY, Hoffman EA, Beck KC, Bellamkonda RV, Annapragada AV. Long-residence-time nano-scale liposomal lohexol for X-ray-based blood pool imaging. Acad Radiol, 2003, 10: 475–483
Burke SJ, Annapragada A, Hoffman EA, Chen E, Ghaghada KB, Sieren J, van Beek EJR. Imaging of pulmonary embolism and t-PA therapy effects using MDCT and liposomal lohexol blood pool agent: preliminary results in a rabbit model. Acad Radiol, 2007, 14: 355–362
Zingel C, Sachse A, Rössling GL, Müller RH. Lyophilization and rehydration of iopromide-carrying liposomes. Int J Pharm, 1996, 140: 13–24
Schneider T, Sachse A, Rossling G, Brandl M. Generation of contrast-carrying liposomes of defined size with a new continuous high pressure extrusion method. Int J Pharm, 1995, 117: 1–12
Elrod DB, Partha R, Danila D, Casscells SW, Conyers JL. An iodinated liposomal computed tomographic contrast agent prepared from a diiodophosphatidylcholine lipid. Nanomedicine: NBM, 2009, 5: 42–45
Ho KW, Jae LW, Yun CZ, Hyun BK, Gwan PT, Hoon KJ. Nanoparticulate carrier containing water-insoluble iodinated oil as a multifunctional contrast agent for computed tomography imaging. Biomaterials, 2007, 28: 5555–5561
Rogers WJ, Basu P. Factors regulating macrophage endocytosis of nanoparticles: implications for targeted magnetic resonance plaque imaging. Atherosclerosis, 2005, 178: 67–73
Galperin A, Margel D, Baniel J, Dank G, Biton H, Margel S. Radiopaque iodinated polymeric nanoparticles for X-ray imaging applications. Biomaterials, 2007, 28: 4461–4468
Aviv H, Bartling S, Kieslling F, Margel S. Radiopaque iodinated copolymeric nanoparticles for X-ray imaging applications. Biomaterials, 2009, 30: 5610–5616
Yin Q, Yap FY, Yin LC, Ma L, Zhou Q, Dobrucki LW, Fan TM, Gaba RC, Cheng JJ. Poly(iohexol) nanoparticles as contrast agents for in vivo X-ray computed tomography imaging. J Am Chem Soc, 2013, 135: 13620–13623
Liu YL, Liu JH, Ai KL, Yuan QH, Lu LH. Recent advances in ytterbium- based contrast agents for in vivo X-ray computed tomography imaging: promises and prospects. Contrast Media Mol Imaging, 2014, 9: 26–36
Hainfeld JF, Slatkin DN, Focella TM, Smilowitz HM. Gold nanoparticles: a new X-ray contrast agent. Br J Radiol, 2006, 79: 248–253
Rogers WJ, Basu P. Factors regulating macrophage endocytosis of nanoparticles: implications for targeted magnetic resonance plaque imaging. Atherosclerosis, 2005, 178: 67–73
Raynal I, Prigent P, Peyramaure S, Najid A, Rebuzzi C, Corot C. Macrophage endocytosis of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles- mechanisms and comparison of ferumoxides and ferumoxtran-10. Invest Radiol, 2004, 39: 56–63
Kim D, Park S, Lee JH, Jeong YY, Jon S. Antibiofouling polymercoated gold nanoparticles as a contrast agent for in vivo X-ray computed tomography imaging. J Am Chem Soc, 2007, 129: 7661–7665
Gulsun M, Demirkazik FB, Ariyürek M. Evaluation of breast microcalcifications according to breast imaging reporting and data system criteria and Le Gal’s classification. Eur J Radiol, 2003, 47: 227–231
Cole LE, Vargo-Gogola T, Roeder RK. Bisphosphonate-functionalized gold nanoparticles for contrast-enhanced X-ray detection of breast microcalcifications. Biomaterials, 2014, 35: 2312–2321
Ai KL, Liu YL, Liu JH, Yuan QH, He YY, Lu LH. Large-scale synthesis of Bi2S3 nanodots as a contrast agent for in vivo X-ray computed tomography imaging. Adv Mater, 2011, 23: 4886–4891
Rabin O, Perez JM, Grimm J, Wojtkiewicz G, Weissleder R. An X-ray computed tomography imaging agent based on long-circulating bismuth sulphide nanoparticles. Nat Mater, 2006, 5: 118–122
Pan D, Roessl E, Schlomka JP, Caruthers SD, Senpan A, Scott MJ, Allen JS, Zhang H, Hu G, Gaffney PJ, Choi ET, Rasche V, Wickline SA, Proksa R, Lanza GM. Computed tomography in color: nanoKenhanced spectral CT molecular imaging. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2010, 49: 9635–9639
Kinsella JM, Jimenez RE, Karmali PP, Rush AM, Kotamraju VR, Gianneschi NC, Ruoslahti E, Stupack D, Sailor MJ. X-ray computed tomography imaging of breast cancer by using targeted peptidelabeled bismuth sulfide nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2011, 50: 12308–12311
Xiao Q, Bu W, Ren Q, Zhang S, Xing H, Chen F, Li M, Zheng X, Huab Y, Zhou L, Peng W, Qu H, Wang Z, Zhao K, Shi J. Radiopaque fluorescence-transparent TaOx decorated upconversion nanophosphors for in vivo CT/MR/UCL trimodal imaging. Biomaterials, 2012, 33: 7530–7539
Bonitatibus PJ Jr, Torres AS, Goddard GD, FitzGerald PF, Kulkarni AM. Synthesis, characterization, and computed tomography imaging of a tantalum oxide nanoparticle imaging agent. Chem Commun, 2010, 46: 8956–8958
Oh MH, Lee N, Kim H, Park SP, Piao Y, Lee J, Jun SW, Moon WK, Choi SH, Hyeon T. Large-scale synthesis of bioinert tantalum oxide nanoparticles for X-ray computed tomography imaging and bimodal image-guided sentinel lymph node mapping. J Am Chem Soc, 2011, 133: 5508–5515
Freedman JD, Lusic H, Snyder BD, Grinstaff MW. Tantalum oxide nanoparticles for the imaging of articular cartilage using X-ray computed tomography: visualization of ex vivo/in vivo murine tibia and ex vivo human index finger cartilage. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2014, 53: 8406–8410
Liu YL, Ai KL, Liu JH, Yuan QH, He YY, Lu LH. A high-performance ytterbium-based nanoparticulate contrast agent for in vivo X-ray computed tomography imaging. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2012, 51: 1437–1442
Liu YL, Ai KL, Liu JH, Yuan QH, He YY, Lu LH. Hybrid BaYbF5 nanoparticles: novel binary contrast agent for high-resolution in vivo X-ray computed tomography angiography. Adv Healthcare Mater, 2012, 1: 461–466
Dong K, Liu Z, Liu JH, Huang S, Li ZH, Yuan QH, Ren JS, Qu XG. Biocompatible and high-performance amino acids-capped MnWO4 nanocasting as a novel non-lanthanide contrast agent for X-ray computed tomography and T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Nanoscale, 2014, 6: 2211–2217
Jakhmola A, Anton N, Anton H, Messaddeq N, Hallouard F, Klymchenko A, Mely Y, Vandamme TF. Poly-epsilon-caprolactone tungsten oxide nanoparticles as a contrast agent for X-ray computed tomography. Biomaterials, 2014, 35: 2981–2986
Chou SW, Shau YH, Wu PC, Yang YS, Shieh DB, Chen CC. In vitro and in vivo studies of FePt nanoparticles for dual modal CT/MRI molecular imaging. J Am Chem Soc, 2010, 132: 13270–13278
Zeng SJ, Wang HB, Lu W, Yi ZG, Rao L, Liu HR, Hao JH. Dualmodal upconversion fluorescent/X-ray imaging using ligand-free hexagonal phase NaLuF4:Gd/Yb/Er nanorods for blood vessel visualization. Biomaterials, 2014, 35: 2934–2941
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, W., Ai, K. & Lu, L. Nanoparticulate X-ray CT contrast agents. Sci. China Chem. 58, 753–760 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-015-5351-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-015-5351-8