Abstract
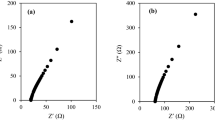
The sunlight is the largest single available source of clean and renewable energy to ensure human society’s sustainable development. Owing to their low production cost and high energy conversion efficiency, dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) have been regarded as good alternatives to conventional photovoltaic devices. Herein, a series of composite electrolytes based on poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) and the binary ionic liquids 1-propyl-3-methy-imidazolium iodide ([PMIm]I) and 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium thiocyanate ([EMIm][SCN]) were prepared and then applied to fabricate six DSSCs. The composite electrolytes were characterized by fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and electrochemical impedance spectra (EIS). It was shown that the addition of binary ionic liquids would reduce the degree of crystallinity of PEO, thus improving the ionic conductivities of the electrolytes by about 2 orders of magnitude. Investigation on the photovoltaic performances of these DSSCs showed that the fill factor (FF) could reach up to 0.67 and energy conversion efficiency (η) could reach up to 4.04% under AM 1.5 full sunlight (100 mW/cm2).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
International Energy Outlook 2011, Energy Information Administration, U.S. Department of Energy, Washington, DC, 2011; http://www.eia.gov/oiaf/ieo/index.html (updated on 19th Sep. 2011)
Sambandam A. Recent improvements and arising challenges in dye-sensitized solar cells. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells, 2007, 91(9): 843–846
Ramírez RE, Sánchez EM. Molten phosphonium iodides as electrolytes in dye-sensitized nanocrystalline solar cells. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells, 2006, 90(15): 2384–2390
Balzani V, Credi A, Venturi M. Photochemical conversion of solar energy. ChemSusChem, 2008, 1(1–2): 26–58
Hu YH, Wang H, Hu B. Thinnest two-dimensional nanomaterial—graphene for solar energy. ChemSusChem, 2010, 3(7): 782–796
O’Regan B, Grätzel M. A low-cost, high-efficiency solar cell based on dye-sensitized colloidal TiO2 films. Nature, 1991, 353(6346): 737–740
Fabregat SF, Bisquert J, Palomares E, Otero L, Kuang DB, Zakeeruddin SM, Grätzel M. Correlation between photovoltaic performance and impedance spectroscopy of dye-sensitized solar cells based on ionic liquids. J Phys Chem C, 2007, 111(17): 6550–6560
Gorlov M, Pettersson H, Hagfeldt A, Kloo L. Electrolytes for dye-sensitized solar cells based on interhalogen ionic salts and liquids. Inorg Chem, 2007, 46(9): 3566–3575
Bai Y, Cao YM, Zhang J, Wang M, Li RZ, Wang P, Zakeeruddin SM, Grätzel M. High-performance dye-sensitized solar cells based on solvent-free electrolytes produced from eutectic melts. Nat Mater, 2008, 7(8): 626–630
Nazeeruddin MK, De Angelis F, Fantacci S, Selloni A, Viscardi G, Liska P, Ito S, Bessho T, Grätzel M. Combined experimental and DFT-TDDFT computational study of photoelectrochemical cell ruthenium sensitizers. J Am Chem Soc, 2005, 127(48): 16835–16847
Ren Y, Zhang Z, Fang S, Yang M, Cai S. Application of PEO based gel network polymer electrolytes in dye-sensitized photoelectrochemical cells. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells, 2002, 71(2): 253–259
Zafer C, Ocakoglu K, Ozsoy C, Icli S. Dicationic bis-imidazolium molten salts for efficient dye sensitized solar cells: Synthesis and photovoltaic properties. Electrochim Acta, 2009, 54(24): 5709–5714
Ileperuma OA, Dissanayake MAKL, Somasunderam S, Bandara LRAK. Photoelectrochemical solar cells with polyacrylonitrile-based and polyethylene oxide-based polymer electrolytes. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells, 2004, 84(1–4): 117–124
de Freitas JN, Nogueira AF, De Paoli MA. New insights into dye-sensitized solar cells with polymer electrolytes. J Mater Chem, 2009, 19(30): 5279–5294
Parvez MK, In I, Park JM, Lee SH, Kim SR. Long-term stable dye-sensitized solar cells based on UV photo-crosslinkable poly(ethylene glycol) and poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate based electrolytes. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells, 2011, 95(1): 318–322
Singh PK, Kim KI, Lee JW, Rhee HW. Polymer electrolyte with ionic liquid for DSSC application. Phys Status Solidi A: Appl Mat, 2006, 203(11): R88–R90
Chen D, Zhang Q, Wang G, Zhang H, Li JH. A novel composite polymer electrolyte containing room-temperature ionic liquids and heteropolyacids for dye-sensitized solar cells. Electrochem Commun, 2007, 9(12): 2755–2759
Singh PK, Kim KW, Rhee HW. Electrical, optical and photoelectrochemical studies on a solid PEO-polymer electrolyte doped with low viscosity ionic liquid. Electrochem Commun, 2008, 10(11): 1769–1772
Singh PK, Kang WK, Nagarale RK, Hee WR. Preparation, characterization and application of ionic liquid doped solid polymer electrolyte membranes. J Phys D: Appl Phys, 2009, 42(12): 125101–125104
Mohmeyer N, Kuang DB, Wang P, Schmidt HW, Zakeeruddin SM, Grätzel M. An efficient organogelator for ionic liquids to prepare stable quasi-solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells. J Mater Chem, 2006, 16(29): 2978–2983
Huang M, Yang H, Wu J, Lin J, Lan Z, Li P, Hao S, Han P, Jiang Q. Preparation of a novel polymer gel electrolyte based on N-methylquinoline iodide and its application in quasi-solid-state dye-sensitized solar cell. J Sol-Gel Sci Techn, 2007, 42: 65–70
Huo ZP, Zhang CN, Fang XQ, Cai ML, Dai SY, Wang KJ. Low molecular mass organogelator based gel electrolyte gelated by a quaternary ammonium halide salt for quasi-solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells. J Power Sources, 2010, 195(13): 4384–4390
Kuang DB, Ito S, Wenger B, Klein C, Moser JE, Humphry-Baker R, Zakeeruddin SM, Grätzel M. High molar extinction coefficient heteroleptic ruthenium complexes for thin film dye-sensitized solar cells. J Am Chem Soc, 2006, 128(12): 4146–4154
Zistler M, Wachter P, Wasserscheid P, Gerhard D, Hinsch A, Sastrawan R, Gores HJ. Comparison of electrochemical methods for triiodide diffusion coefficient measurements and observation of non-Stokesian diffusion behaviour in binary mixtures of two ionic liquids. Electrochim Acta, 2006, 52(1): 161–169
Berginc M, Opara Krašovec U, Jankovec M, Topič M. The effect of temperature on the performance of dye-sensitized solar cells based on a propyl-methyl-imidazolium iodide electrolyte. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells, 2007, 91(9): 821–828
Wang YQ, Sun YM, Song B, Xi JT. Ionic liquid electrolytes based on 1-vinyl-3-alkylimidazolium iodides for dye-sensitized solar cells. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells, 2008, 92(6): 660–666
Kato N, Higuchi K, Tanaka H, Nakajima J, Sano T, Toyoda T. Improvement in long-term stability of dye-sensitized solar cell for outdoor use. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells, 2011, 95(1): 301–305
Bonhôte P, Dias A-P, Papageorgiou N, Kalyanasundaram K, Grätzel M. Hydrophobic, highly conductive ambient-temperature molten salts. Inorg Chem, 1996, 35(5): 1168–1178
Sun GH, Li KX, Sun CG. Application of 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium thiocyanate to the electrolyte of electrochemical double layer capacitors. J Power Sources, 2006, 162(2): 1444–1450
Lu HL, Shen TFR, Huang ST, Tung YL, Yang TCK. The degradation of dye sensitized solar cell in the presence of water isotopes. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells, 2011, 95(7): 1624–1629
Jerman I, Jovanovski V, Šurca Vuk A, Hočevar SB, Gaberšček M, Jesih A, Orel B. Ionic conductivity, infrared and Raman spectroscopic studies of 1-methyl-3-propylimidazolium iodide ionic liquid with added iodine. Electrochim Acta, 2008, 53(5): 2281–2288
Fei ZF, Zhao DB, Geldbach TJ, Scopelliti R, Dyson PJ. Brønsted acidic ionic liquids and their zwitterions: Synthesis, characterization and pKa determination. Chem Eur J, 2004, 10(19): 4886–4893
Singh PK, Bhattacharya B, Nagarale RK, Kim KW, Rhee HW. Synthesis, characterization and application of biopolymer-ionic liquid composite membranes. Synth Met, 2010, 160(1–2): 139–142
Singh PK, Bhattacharya B, Nagarale RK, Pandey SP, Kim KW, Rhee HW. Ionic liquid doped poly(N-methyl 4-vinylpyridine iodide) solid polymer electrolyte for dye-sensitized solar cell. Synth Met, 2010, 160(9–10): 950–954
Ramesh S, Yuen TF, Shen CJ. Conductivity and FTIR studies on PEO-LiX [\(X: CF_3 SO_{3^ - } ,SO_4^{2 - } \)] polymer electrolytes. Spectrochim Acta A, 2008, 69(2): 670–675
Zivanovic S, Li J, Davidson PM, Kit K. Physical, mechanical, and antibacterial properties of Chitosan/PEO blend films. Biomacromolecules, 2007, 8(5): 1505–1510
Zhou D, Mei X, Ouyang J. Ionic conductivity enhancement of polyethylene oxide-LiClO4 electrolyte by adding functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J Phys Chem C, 2011, 115(33): 16688–16694
Fan L, Nan CW, Dang Z. Effect of modified montmorillonites on the ionic conductivity of (PEO)16LiClO4 electrolytes. Electrochim Acta, 2002, 47(21): 3541–3544
Katsaros G, Stergiopoulos T, Arabatzis IM, Papadokostaki KG, Falaras P. A solvent-free composite polymer/inorganic oxide electrolyte for high efficiency solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells. J Photoch Photobio A, 2002, 149(1–3): 191–198
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Y., Jiang, P., Wang, F. et al. Composite electrolytes based on poly(ethylene oxide) and binary ionic liquids for dye-sensitized solar cells. Sci. China Chem. 55, 1608–1613 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-012-4635-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-012-4635-5