Abstract
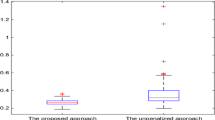
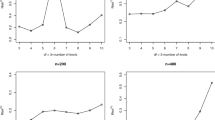
The varying-coefficient single-index model (VCSIM) is widely used in economics, statistics and biology. A model averaging method for VCSIM based on a Mallows-type criterion is proposed to improve prodictive capacity, which allows the number of candidate models to diverge with sample size. Under model misspecification, the asymptotic optimality is derived in the sense of achieving the lowest possible squared errors. The authors compare the proposed model averaging method with several other classical model selection methods by simulations and the corresponding results show that the model averaging estimation has a outstanding performance. The authors also apply the method to a real dataset.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xia Y and Li W K, On single-index coefficient regression models, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1999, 94(448): 1275–1285.
Härdle W, Müller M, Sperlich S, et al., Nonparametric and Semiparametric Models, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 2004.
Wong H, Wai C I, and Zhang R, Varying-coefficient single-index model, Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 2008, 52(3): 1458–1476.
Zhao Y, Xüe L, and Feng S, Semiparametric estimation of the single-index varying-coefficient model, Communications in Statistics — Theory and Methods, 2016, 46(9): 4311–4326.
Ichimura H, Semiparametric least squares and weighted sls estimation of single-index models, Journal of Econometrics, 1993, 58(1): 71–120.
Härdle W, Hall P, and Ichimura H, Optimal smoothing in single-index models, The Annals of Statistics, 1993, 21(1): 157–178.
Stoker T M, Consistent estimation of scaled coefficients, Econometrica, 1986, 54(6): 1461–1481.
Härdle W and Stoker T M, Investigating smooth multiple regression by the method of average derivatives, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1989, 84(408): 986–995.
Li K C, Sliced inverse regression for dimension reduction, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1991, 86(414): 316–327.
Wahba G, Smoothing noisy data with spline function, Numerische Mathematik, 1975, 24: 383–393.
Wahba G, Bayesian confidence-intervals for the cross-validated smoothing spline, Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B, 1983, 45(1): 133–150.
Wahba G, A comparison of gcv and gml for choosing the smoothing parameter in the generalized spline smoothing problem, The Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 1985, 13(4): 1378–1402.
Nadaraya E A, On estimating regression, Theory Probability and Its Application, 1964, 9(1): 141–142.
Watson G S, Smooth regression analysis, Sankhya: The Indian Journal of Statistics, Series A, 1964, 26(4): 359–372.
Fan J, Design adaptive nonparametric regression, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1991, 87(420): 998–1004.
Fan J, Local linear regression smoothers and their minimax efficiency, The Annals of Statistics, 1993, 21(1): 196–216.
Fan J and Gijbels I, Local Polynomial Modeling and Its Application, Chapman and Hall, London, 1996.
Yu Y and Ruppert D, Penalized spline estimation for partially linear single-index models, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 2002, 97(460): 1042–1054.
Zhou Z H, When semi-supervised learning meets ensemble learning, Frontiers of Electrical & Electronic Engineering in China, 2011, 6(1): 6–16.
Fersini E, Messina E, and Pozzi F A, Sentiment analysis: Bayesian ensemble learning, Decision Support Systems, 2014, 68: 26–38.
Liu B, Wang S, Ren L, et al., irspot-el: Identify recombination spots with an ensemble learning approach, Bioinformatics, 2017, 33(1): 35–41.
Hansen B E, Least squares model averaging, Econometrica, 2007, 75(4): 1175–1189.
Zhang X, Yu D, Zou G, et al., Optimal model averaging estimation for generalized linear models and generalized linear mixed-effects models, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 2016, 111(516): 1775–1790.
Akaike H, Information theory and an extension of the maximum likelihood principle, Breakthroughs in Statistics, 1973, 1: 610–624.
Schwarz G, Estimating the dimension of a model, The Annals of Statistics, 1978, 6(2): 461–464.
Mallows C L, Some comments on cp, Technometrics, 1973, 42(1): 87–94.
Wan A T K, Zhang X, and Zou G, Least squares model averaging by mallows criterion, Journal of Econometrics, 2010, 156(2): 277–283.
Zhu R, Wan A T K, Zhang X, et al., A mallows-type model averaging estimator for the varying-coefficient partially linear model, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 2019, 114(526): 882–892.
Hoeting J A, Madigan D, Raftery A E, et al., Bayesian model averaging: A tutorial, Statistical Science, 1999, 14: 382–417.
Wang H, Zhang X, and Zou G, Frequentist model averaging estimation: A review, Journal of Systems Science and Complexity, 2009, 22(4): 732–748.
Buckland S T, Burnham K P, and Augustin N H, Model selection: An integral part of inference, Biometrics, 1997, 53: 603–618.
Claeskens G, Croux C, and van K J, Variable selection for logistic regression using a prediction-focused information criterion, Biometrics, 2006, 62: 972–979.
Liang H, Zou G, Wan A T K, et al., Optimal weight choice for frequentist model average estimators, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 2011, 106: 1053–1066.
Zhao Z H and Zou G H, Average estimation of semiparametric models for high-dimensional longitudinal data, Journal of Systems Science and Complexity, 2020, 33(6): 2013–2047.
Zhang X, Zheng Y, and Wang S, A demand forecasting method based on stochastic frontier analysis and model average: An application in air travel demand forecasting, Journal of Systems Science and Complexity, 2019, 32(4): 615–633.
Yuan Z and Yang Y, Combining linear regression models: When and how. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 2005, 100: 1202–1214.
Zhang X, Lu Z, and Zou G, Adaptively combined forecasting for discrete response time series, Journal of Econometrics, 2013, 176: 80–91.
Liu C, Distribution theory of the least squares averaging estimator, Journal of Econometrics, 2015, 186: 142–159.
Yin S, Liu C, and Lin C, Focused information criterion and model averaging for large panels with a multifactor error structure, Journal of Business & Economic Statistics, 2019, forthcoming.
Li D, Linton O, and Lu Z, A flexible semiparametric forecasting model for time series, Journal of Econometrics, 2015, 187: 345–357.
Hristache M, Juditsky A, and Spokoiny V, Direct estimation of the index coefficient in a single-index model, The Annals of Statistics, 2001, 29(3): 595–623.
Fan J and Zhang W, Statistical estimation in varying coefficient models, The Annals of Statistics, 1999, 27(5): 1491–1518.
Hansen B E and Racine J S, Jackknife model averaging, Journal of Econometrics, 2012, 167(1): 38–46.
Zhang X, Wan A T K, and Zou G, Model averaging by jackknife criterion in models with dependent data, Journal of Econometrics, 2013, 174(2): 82–94.
Hjort N L and Claeskens G, Frequentist model average estimators, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 2003, 98(464): 879–899.
Hjort N L and Claeskens G, Rejoinder to the discussion of “frequentist model average estimators” and “focused information criterion”, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 2003, 98(464): 938–945.
Hjort N L and Claeskens G, Focused information criteria and model averaging for the cox hazard regression model, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 2006, 101(476): 1449–1464.
Li K C, Asymptotic optimality for cp, cl, cross-validation and generalized cross-validation: Discrete dindex set, The Annals of Statistics, 1987, 15(3): 958–975.
Li C, Li Q, Racine J S, et al., Optimal model averaging of varying coefficient models, Statistica Sinica, 2018, 28(4): 2795–2809.
Yu Z, He B, and Chen M, Empirical likelihood for generalized partially linear single-index models, Communications in Statistics, 2014, 43: 4156–4163.
Xie S, Wan A T K, and Zhou Y, Quantile regression methods with varying-coefficient models for censored data, Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 2015, 88: 154–172.
Gao Y, Zhang X, Wang S, et al., Frequentist model averaging for threshold models, Annals of the Institute of Statistical Mathematics, 2018, 71(2): 275–306.
Zhang X, Model averaging and its applications, PhD thesis, Academy of Mathematics and Systems Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China, under Grant Nos. 12001559 and 11971324 and the Ministry of Education of Humanities and Social Science project, under Grant No. 19YJC910008.
This paper was recommended for publication by Editor ZHANG Xinyu.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Zou, J., Zhao, S. et al. Model Averaging Estimation for Varying-Coefficient Single-Index Models. J Syst Sci Complex 35, 264–282 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-021-0158-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-021-0158-5