Abstract
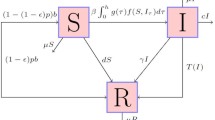
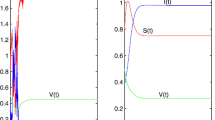
We study the application of a pulse vaccination strategy to eradicate the slowly progressing diseases that have infectiousness in latent period. We derive the condition in which eradication solution is a global attractor, this condition depends on pulse vaccination proportion p. We also obtain the condition of the global asymptotic stability of the solution. The condition shows that large enough pulse vaccination proportion and relatively small interpulse time lead to the eradication of the diseases. Moreover the results of the theoretical study might be instructive to the epidemiology of HIV.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. M. Ander and R. M. May, Infectious Diseases of Humans, Oxford University Press, 1991.
M.Martcheva and H. R. Thieme, Progression age enhanced backward bifurcation in an epidemic model with super-infection, J. Math. Biol., 2003, 46: 385–424.
Z. Feng, M. Iannelli, and F. A. Milner, A two-strain tuberculosis model with age of infection, SIAM. Appl. Math., 2002, 62 (5): 1634–1656.
Z. Agur, L. Cojocaru, R. M. Anderson, and Y. L. Danon, Pulse mass measles vaccination across age cohorts, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (USA), 1993, 90: 11698–11702.
B. Shulgin, L. Ston, and Z. Agur, Theoretical examination of pulse vaccination policy in the SIR epidemic model, Math. Comput. Modelling, 2000, 31(4–5): 207–215.
A. D’Onofri, Stability properties of pulse vaccination strategy in SEIR epidemic model, Math. Biosci., 2002, 179: 57–72.
Y. Zhou and H. Liu, Stability of periodic solutions for an SIS model with pulse vaccination, Math. Comput. Modelling, 2003, 38: 229–308.
B. Shulgin, L. Stone, and Z. Agur, Pulse vaccination strategy in the SIR epidemic model, Bull. Math. Biol., 1998, 60: 1123–1148.
A. D’Onofri, Pulse vaccination strategy in the SIR epidemic model: Global asymptotic stable eradication in presence of vaccine failures, Math. Comput. Modelling, 2002, 36: 473–489.
C. A. de Quadros, J. K. Andrus, and J. M. Olive, Eradication of poliomyelitis: progress in the Americas, Pediat. Inf. Dis. J., 1991, 10(3): 222–229.
A. B. Sabin, Measlles: Killer of millions in developing countries: strategies of elimination and continuing control, Eur. J. Epid., 1991, 7: 1–022.
M. Ramsay and E. Miller, The epidemiology of measles in England and Wales Rationale for 1994 national vaccination campaign, Eur. J. Epid., 1991, 7: 1–22.
S. Busenberg and P. van der Driessche, Analysis of a disease transmission model in a population with varying size, J. Math. Biol., 1990, 28: 257–270.
M. Y. Li, J. R. Graef, L. Wang, and J. Karsai, Global dynamics of an SEIR model with varying population size, Math. Biosc., 1999, 160: 191–213.
L. Esteva and C. Vargas, A model for Dengue disease with variable human population, J. Math. Biol., 1999, 38: 220–240.
G. F. Webb, Theory of Nonlinear Age-dependent Population Dynamics, Marcel Dekker, New York, 1985.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The research is supported by the National Science Foundation of Henan Province (No. 0611051800).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Yu, J. & Zhu, G. Global Asymptotic Stable Eradication for the Siv Epidemic Model with Impulsive Vaccination and Infection-Age. Jrl Syst Sci & Complex 19, 393–402 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-006-0393-9
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-006-0393-9