Abstract
Purpose
We report a more reliable method for determination of the herbicide diquat (DQ) in human biological samples using stable isotope dilution liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS). DQ-d8, a newly synthesized stable isotope was used as the internal standard (IS) for quantification of DQ instead of DQ-d4 typically used so far. The use of DQ-d8 could completely prevent errors like the misdetection of DQ and inaccurate quantification probably caused by using DQ-d4. Additionally, we developed a method for simultaneous determination of DQ and the similar herbicide paraquat (PQ) in urine, serum and whole blood by stable isotope dilution LC–MS/MS after solid-phase extraction.
Methods
The stable isotopes DQ-d8 and PQ-d6 were synthesized and used as ISs. The DQ and PQ in the samples were extracted by solid-phase extraction using an EVOLUTE® WCX. The extracted DQ and PQ were separated and detected by LC–MSMS using a ZIC®-pHILIC column.
Results
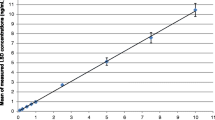
The recovery rates ranged from 82.0 to 99.7%. Calibration curves showed good linearity in the 0.01–2 μg/mL. The intraday accuracy and intraday precision [% relative standard deviation (RSD)] ranged from 92.1 to 106% and from 0.4 to 4.7%, respectively. The interday precision (%RSD) ranged between 0.8 and 6.7%.
Conclusions
The stable isotopes DQ-d8 and PQ-d6 allowed for accurate and precise quantification. Especially for analysis of DQ, the use of DQ-d8 could completely prevent errors caused by using DQ-d4. Therefore, the proposed method would be of great use in criminal investigations and emergency medicine.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Almeida RM, Yonamine M (2007) Gas chromatographic–mass spectrometric method for the determination of the herbicides paraquat and diquat in plasma and urine samples. J Chromatogr B 853:260–264
Moreira PN, de Pinho PG, Baltazar MT, Bastos ML, Carvalho F, Dinis-Oliveira RJ (2012) Quantification of paraquat in postmortem samples by gas chromatography–ion trap mass spectrometry and review of the literature. Biomed Chromatogr 26:338–349
Saito T, Fukushima T, Yui Y, Miyazaki S, Nakamoto A, Namera A, Inokuchi S (2011) Monolithic spin column extraction and GC–MS for the simultaneous assay of diquat, paraquat, and fenitrothion in human serum and urine. Anal Bioanal Chem 400:25–31
Gao L, Liu J, Wang C, Liu G, Niu X, Shu C, Zhu J (2014) Fast determination of paraquat in plasma and urine samples by solid–phase microextraction and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 944:136–140
Tomita M, Okuyama T, Nigo Y (1992) Simultaneous determination of paraquat and diquat in serum using capillary electrophoresis. Biomed Chromatogr 6:91–94
Wu W-S, Tsai J-L (1998) Simultaneous determination of paraquat and diquat in urine by capillary electrophoresis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 14:76–80
Vinner E, Stievenart M, Humbert L, Mathieu D, Lhermitte M (2001) Separation and quantification of paraquat and diquat in serum and urine by capillary electrophoresis. Biomed Chromatogr 15:342–347
Ishiwata T, Onuki S, Okada H, Ohashi K (2002) Determination of paraquat and diquat in human blood by capillary electrophoresis after solid-phase extraction using an OASIS MCX® cartridge. Jpn J Forensic Toxicol 20:284–294
Narita Y, Tomioka N, Iida H, Yanagi Y, Minagawa T (2005) Analysis of paraquat and diquat in human blood by capillary electrophoresis (in Japanese with English abstract). Jpn J Forensic Sci Tech 10:171–178
Lanaro R, Costa JL, Fernandes LCR, Resende RR, Tavares MFM (2011) Detection of paraquat in oral fluid, plasma, and urine by capillary electrophoresis for diagnosis of acute poisoning. J Anal Toxicol 35:274–279
Fuke C, Arao T, Morinaga Y, Takaesu H, Ameno K, Miyazaki T (2002) Analysis of paraquat, diquat and two metabolites in biological materials by high-performance liquid chromatography. Leg Med 4:156–163
Paixão P, Costa P, Bugalho T, Fidalgo C, Pereira LM (2002) Simple method for determination of paraquat in plasma and serum of human patients by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr B 775:109–113
Brunetto MR, Morales AR, Gallignani M, Burguera JL, Burguera M (2003) Determination of paraquat in human blood plasma using reversed-phase ion-pair high-performance liquid chromatography with direct sample injection. Talanta 59:913–921
Ito M, Hori Y, Fujisawa M, Oda A, Katsuyama S, Hirose Y, Yoshioka T (2005) Rapid analysis method for paraquat and diquat in the serum using ion-pair high-performance liquid chromatography. Biol Pharm Bull 28:725–728
Hara S, Sasaki N, Takase D, Shiotsuka S, Ogata K, Futagami K, Tamura K (2007) Rapid and sensitive HPLC method for the simultaneous determination of paraquat and diquat in human serum. Anal Sci 23:523–526
Zou Y, Shi Y, Bai Y, Tang J, Chen Y, Wang L (2011) An improved approach for extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography analysis of paraquat in human plasma. J Chromatogr B 879:1809–1812
Shindo K, Kishikawa N, Ohyama K, Kuroda N (2015) Simultaneous determination of paraquat and diquat in human plasma using HPLC with chemiluminescence detection (in Japanese with English abstract). Bunseki Kagaku 64:581–587
Sun B, Chen Y (2015) A simple and rapid method for detection of paraquat in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:17067–17071 (PMCID:PMC4694198)
Lee X-P, Kumazawa T, Fujishiro M, Hasegawa C, Arinobu T, Seno H, Ishii A, Sato K (2004) Determination of paraquat and diquat in human body fluids by high-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrum 39:1147–1152
Ariffin MM, Anderson RA (2006) LC/MS/MS analysis of quaternary ammonium drugs and herbicides in whole blood. J Chromatogr B 842:91–97
Wang K-C, Chen S-M, Hsu J-F, Cheng S-G, Lee C-K (2008) Simultaneous detection and quantitation of highly water-soluble herbicides in serum using ion-pair liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 876:211–218
Whitehead RD Jr, Montesano MA, Jayatilaka NK, Buckley B, Winnik B, Needham LL, Barr DB (2010) Method for measurement of the quaternary amine compounds paraquat and diquat in human urine using high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 878:2548–2553
Wang Z, Wang Z, Xing J (2011) The quantitative analysis of paraquat in biological samples by liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization–mass spectrometry. J Anal Toxicol 35:23–27
Wunnapuk K, Medley GA, Liu X, Grice JE, Jayasinghe S, Gawarammana I, Buckey NA, Roberts MS (2011) Simple and sensitive liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry methods for quantification of paraquat in plasma and urine: application to experimental and clinical toxicological studies. J Chromatogr B 879:3047–3052
Yoshioka N, Asano M, Kuse A, Matsuoka T, Akiyama Y, Mitsuhashi T, Nagasaki Y, Ueno Y (2012) Rapid and sensitive quantification of paraquat and diquat in human serum by liquid chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry using atmospheric pressure photoionization. Forensic Toxicol 30:135–141
Ruan X-L, Qiu J-J, Wu C, Huang T, Meng R-B, Lai Y-Q (2014) Magnetic single-walled carbon nanotubes-dispersive solid phase extraction method combined with liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of paraquat in urine. J Chromatogr B 965:85–90
Suzuki Y, Kaneko T (2016) Determination of paraquat and diquat in human body fluid by oxidation method-liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (in Japanese with English abstract). Jpn J Forensic Sci Tech 21:57–65
Lu H, Yu J, Wu L, Xing J, Wang J, Huang P, Zhang J, Xiao H, Gao R (2016) Optimized ultra performance liquid chromatography tandem high resolution mass spectrometry method for the quantification of paraquat in plasma and urine. J Chromatogr B 1027:96–102
Tsao Y-C, Lai Y-C, Liu H-C, Liu R-H, Lin D-L (2016) Simultaneous determination and quantitation of paraquat, diquat, glufosinate and glyphosate in postmortem blood and urine by LC–MS–MS. J Anal Toxicol 40:427–436
The pharmaceutical Society of Japan (2017) Standard methods of analysis in poisoning with commentary 2017 (in Japanese). Tokyo Kagaku Dojin, Tokyo, pp 332–336
Tomlin CDS (2003) The pesticide manual: a world compendium, 13th edn. British Crop Protection Council, Alton, pp 341–342 and 742–743
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no financial or other relations that could lead to a conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuki, Y., Kaneko, T. & Saito, K. The internal standard diquat-d4 causes errors in diquat analysis by LC–MS/MS. Forensic Toxicol 36, 458–466 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-018-0423-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-018-0423-z