Abstract
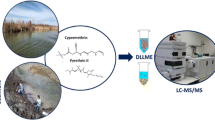
3-Phenoxybenzoic acid (3-PBA) and 4-hydroxy-3-phenoxybenzoic acid (OH-PBA) are the two common metabolites for most pyrethroid insecticides. A rapid, sensitive, and eco-friendly method has been developed based on ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (DLLME) coupled to large volume injection–gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry for the simultaneous determination of pyrethroid metabolites in rat brain treated with cypermethrin (CYP). Brain samples were homogenized in methanol (disperser solvent) followed by derivatization with methyl chloroformate (MCF) and extraction using DLLME. Factors that influence the extraction and derivatization efficiency such as type and volume of extraction and disperser solvent, sonication time, pH, ionic strength, and volumes of MCF and pyridine were optimized. Under optimized conditions, the limits of detection were 1 and 4 ng/g for 3-PBA and OH-PBA, respectively. Mean recoveries of pyrethroid metabolites in rat brain were in the range of 83–95 %. The developed method was successfully applied for determination of 3-PBA and OH-PBA in brain samples of CYP-treated rats. The developed method can be adopted for rapid and sensitive analysis of pyrethroid metabolites in toxicological and forensic laboratories.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 3-PBA:
-
3-Phenoxybenzoic acid
- ACFs:
-
Alkyl chloroformates
- CB:
-
Chlorobenzene
- CSIR-IITR:
-
Council of Industrial Research-Indian Institute of Toxicology Research
- CYP:
-
Cypermethrin
- DCM:
-
Dichloromethane
- DLLME:
-
Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- GC–ECD:
-
Gas chromatography–electron capture detection
- GC–MS:
-
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry
- GC–MS/MS:
-
Gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- LLE:
-
Liquid–liquid extraction
- LOD:
-
Limit of detection
- LOQ:
-
Limit of quantification
- LVI:
-
Large volume injection
- MCF:
-
Methyl chloroformate
- NIST:
-
National Institute of Standards and Technology
- OH-PBA:
-
4-Hydroxy-3-phenoxybenzoic acid
- PFBBr:
-
Pentafluorobenzyl bromide
- PTV–LVI:
-
Programmable temperature vaporization–large volume injection
- PYRs:
-
Pyrethroids
- RSD:
-
Relative standard deviation
- SPE:
-
Solid-phase extraction
- SPME:
-
Solid-phase microextraction
- SRM:
-
Selected reaction monitoring
- TCE:
-
Trichloroethylene
- UA:
-
Ultrasound-assisted
References
Feo ML, Eljarrat E, Barcelo D (2010) Determination of pyrethroid insecticides in environmental samples. Trends Anal Chem 29:692–706
Lin CH, Yan CT, Kumar PV, Li HP, Jen JF (2011) Determination of pyrethroid metabolites in human urine using liquid phase microextraction coupled in-syringe derivatization followed by gas chromatography/electron capture detection. Anal Bioanal Chem 401:927–937
Grand RL, Dulaurent S, Gaulier JM, Marcoux FS, Moesh C, Lachatre G (2012) Simultaneous determination of five synthetic pyrethroid metabolites in urine by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry: application to 39 persons without known exposure to pyrethroids. Toxicol Lett 210:248–253
Shrivastava A, Peshin SS, Kaleekal T, Gupta SK (2005) An epidemiological study of poisoning cases to the National Poison Information Centre, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi. Hum Exp Toxicol 24:6279–6285
Ch SR, Venkateswarlu V, Surender T, Eddleston M, Buckley NA (2005) Pesticide poisoning in south India: opportunities for prevention and improved medical management. Trop Med Int Health 6:581–588
Mudiam MKR, Jain R, Mourya SK, Khan HA, Bandyopadhyay S, Murthy RC (2012) Low density solvent based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction with gas chromatography-electron capture detection for the determination of cypermethrin in tissue and blood of cypermethrin treated rats. J Chromatogr B 895–896:65–70
Mishra S, Sharma CB (1997) Metabolism and bioaccumulation of fenvalerate and its metabolites in rat organs. Biomed Chromatogr 11:50–53
Marei AEM, Ruzo LO, Casida JE (1982) Analysis and persistence of permethrin, cypermethrin, deltamethrin, and fenvalerate in the fat and brain of treated rats. J Agric Food Chem 30:558–562
Barr DB, Olsson AO, Wong LY, Udunka S, Baker SE, Whitehead RD, Magsumbol MS, Williams BL, Needham LL (2010) Urinary concentration of metabolites of pyrethroid insecticides in the general U.S. population: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999–2002. Environ Health Perspect 118:742–748
Maloney SE, Maule A, Smith AR (1988) Microbial transformation of the pyrethroid insecticides: permethrin, deltamethrin, fastac, fenvalerate and fluvalinate. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:2874–2876
Woolen BH, Marsh JR, Laird WJD, Lesser JE (1999) The metabolism of cypermethrin in man: differences in urinary metabolite profiles following oral and dermal administration. Xenobiotica 22:983–991
Wang D, Kamijima M, Imai R, Suzuki T, Kameda Y, Asai K, Okamura A, Naito H, Ueyama J, Saito I, Nakajima T, Goto M, Shibata E, Kondo T, Takagi K, Takaji K, Wakusawa S (2007) Biological monitoring of pyrethroid exposure of pest control workers in Japan. J Occup Health 49:509–514
Aziz MH, Agrawal AK, Adhami VM, Shukla Y, Seth PK (2001) Neurodevelopmental consequences of gestational exposure (GD14–GD20) to low dose deltamethrin in rats. Neurosci Lett 300:161–165
Ding Y, White CA, Muralidhara S, Bruckner JV, Bartlett MG (2004) Determination of deltamethrin and its metabolite 3-phenoxybenzoic acid in male rat plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr B 810:221–227
Ahn KC, Gee SJ, Kim HJ, Aronov PA, Vega H, Krieger RI, Hammock BD (2011) Immunochemical analysis of 3-phenoxybenzoic acid, a biomarker of forestry worker exposure to pyrethroid insecticides. Anal Bioanal Chem 401:1285–1293
Hardt J (2001) Ibuprofen interference in the determination of 3-phenoxybenzoic acid in urine. Fresenius J Anal Chem 371:787–790
Husek P (1998) Chloroformates in gas chromatography as general purpose derivatizing agents. J Chromatogr B 717:57–91
Sams C, Jones K (2011) Biological monitoring for exposure to deltamethrin: a human oral dosing study and background levels in the UK general population. Toxicol Lett 213:35–38
Mudiam MKR, Jain R, Dua VK, Singh AK, Sharma VP, Murthy RC (2011) Application of ethyl chloroformate derivatization for solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometric determination of bisphenol-A in water and milk samples. Anal Bional Chem 401:1695–1701
Pusvaskiene E, Januskevic B, Prichodko A, Vickackaite V (2009) Simultaneous derivatization and dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for fatty acids GC determination in water. Chromatographia 69:271–276
Leggio A, Belsito EL, Marco RD, Liguori A, Siciliano C, Spinella M (2012) Simultaneous extraction and derivatization of amino acids and free fatty acids in meat products. J Chromatogr A 1241:96–102
Luo S, Fang L, Wang X, Liu H, Ouynag G, Lan C, Luan T (2010) Determination of octylphenol and nonylphenol sample using simultaneous derivatization and dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1217:6762–6768
Yonamine M, Tawil N, Moreau RLDM, Silva OA (2003) Solid-phase micro-extraction-gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and headspace-gas chromatography of tetrahydrocannabinol, amphetamine, methamphetamine, cocaine and ethanol in saliva samples. J Chromatogr B 789:73–78
Saito T, Miura N, Namara A, Oikawa H, Miyazaki S, Nakamoto A, Inokuchi S (2012) Mixed-mode C-C18 monolithic spin-column extraction and GC–MS for simultaneous assay of organophosphorous compounds, glyphosate, and glufosinate in human serum and urine. Forensic Toxicol 30:1–10
Namera A, Saito T, Miyazaki S, Ohta S, Oikawa H, Torikoshi A, Shiraishi H, Nagao M (2013) Sequential extraction of amphetamines, opiates, and 11-nor-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol-9-carboxylic acid from a limited volume of urine using a monolithic silica spin column coupled with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Forensic Toxicol 31:312–321
Hayashi D, Kumazawa T, Hasegawa C, Lee X-P, Marumo A, Uchigasaki S, Kawamura M, Sato K (2012) A simple and reliable method for quantifying plasma concentrations of tetracyclic antidepressants using monolithic silica solid-phase extraction tips. Forensic Toxicol 30:98–105
Menck RA, de Oliveira CDR, de Lima DS, Goes LE, Leyton V, Pasqualucci CA, Munoz DR, Yonamine M (2013) Hollow fiber-liquid phase microextraction of barbiturates in liver samples. Forensic Toxicol 31:31–36
Rezaee M, Assadi Y, Hosseini MRM, Aghaee E, Ahmadi F, Berijani S (2006) Determination of organic compounds in water using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. J Chromatogr A 1116:1–9
Cortada C, Vidal L, Canals A (2011) Determination of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol in water and wine samples by ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction coupled to gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1218:17–22
Mudiam MKR, Chauhan A, Jain R, Ch R, Fatima G, Malhotra E, Murthy RC (2012) Development, validation and comparison of two microextraction technique for the rapid and sensitive determination of pregabalin in urine and pharmaceutical formulations after ethyl chloroformate derivatization followed by gas chromatography–mass spectrometric analysis. J Pharm Biomed Anal 70:310–319
Rezaee M, Yamini Y, Faraji M (2010) Evaluation of dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction method. J Chromatogr A 1217:2342–2357
Shafer TJ, Meyer DA, Crofton KM (2005) Developmental neurotoxicity of pyrethroid insecticides: critical review and future research needs. Environ Health Prespect 113:123–136
Singh A, Yadav S, Shrivastava V, Kumar R, Singh D, Sethumadhavan R, Parmar D (2013) Imprinting of cerebral and hepatic cytochrome P450 in rat offsprings exposed to low dose of cypermethrin. Mol Neurobiol. doi:10.1007/s12035-013-8419-5
Peters FT, Drummer OH, Musshoff F (2007) Validation of new methods. Forensic Sci Int 165:216
Kvitvang HFN, Andreassen T, Adam T, Boas SGV, Bruhein P (2011) Highly sensitive GC/MS/MS method for quantitation of amino and nonamino organic acids. Anal Chem 83:2705–2711
Husek P (1990) Fast esterification of fatty acids with alkyl chloroformates. J High Res Chrom 13:633–638
Zampolli MG, Basaglia G, Dondi F, Sternberg R, Szopa C, Pietrogrande MC (2007) Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis of amino acid enantiomers as methyl chloroformate derivatives: application to space analysis. J Chromatogr A 1150:162–172
Wu Q, Li Z, Wu C, Wang C, Wang Z (2010) Application of ultrasound-assisted emulsification microextraction for the determination of triazine herbicides in soil samples by high performance liquid chromatography. Microchim Acta 170:59–65
Cartiser N, Bevalot F, Le Meur C, Gaillard Y, Malicier D, Hubert N, Guitton J (2011) Gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry assay for the quantification of four benzodiazepines and citalopram in eleven postmortem rabbit fluid and tissues, with application to animal and human samples. J Chroamtogr B 879:2909–2918
Zaitsu K, Miyagawa H, Sakamoto Y, Matsuta S, Tsuboi K, Nishioka H, Katai M, Sato T, Tatsuno M, Tsuchihashi H, Suzuki K, Ishii A (2013) Mass spectrometric differentiation of the isomers of mono-methoxyethylamphetamines and mono-methoxydimethylamphetamines by GC–EI–MS–MS. Forensic Toxicol 31:292–300
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. K. C. Gupta, Director, CSIR-IITR, for support in providing the necessary facilities to carry out this work. RJ is thankful to UGC for providing a research fellowship to carry out this research work. AS is thankful to CSIR for providing a research fellowship. All authors are indebted to CSIR, New Delhi, for financial support through the INDEPTH (BSC0111) scheme.
Conflict of interest
There are no financial or other relations that could lead to a conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
M. K. R. Mudiam and R. Jain contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mudiam, M.K.R., Jain, R., Singh, A. et al. Development of ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction–large volume injection–gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method for determination of pyrethroid metabolites in brain of cypermethrin-treated rats. Forensic Toxicol 32, 19–29 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-013-0196-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-013-0196-3