Abstract
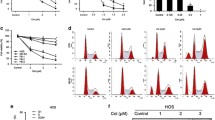
Pachymic acid (PA) is a lanostane type triterpenoid isolated from Poria cocos, which possesses an anti-tumor effect in breast cancer, prostate cancer, lung cancer, and bladder cancer cells. In this study, we investigated the effect of PA on the growth and apoptosis of human immortalized cell line (HOS) and primary osteosarcoma cells by a Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) and Annexin V and propidium iodide (PI) staining, respectively. Western blot was used to measure the expression of cleaved Caspase 3, PTEN, and AKT, as well as the AKT phosphorylation. The Caspase 3 activity was determined using the Caspase-3 Colorimetric Assay Kit. From the results, PA significantly reduced cell proliferation in a concentration- and time-dependent manner. PA also induced cell apoptosis in a dose-dependent fashion. PA treatment led to increased Caspase 3 activation and PTEN expression, as well as reduced AKT phosphorylation. Moreover, Ac-DEVD-CHO (a Caspase 3/7 inhibitor) pre-treatment or PTEN knockdown partially blocked the effects of PA on cell proliferation and apoptosis. Caspase 3/7 inhibitor had an additive effect with PTEN knockdown. Collectively, our results suggested that induction of apoptosis by PA was mediated in part by PTEN/AKT signaling and Caspase 3/7 activity. This study provides evidence that PA might be useful in the treatment of human osteosarcoma.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu H, Tang J, Tang M, Cai H (2013) Upregulation of SOX9 in osteosarcoma and its association with tumor progression and patients’ prognosis. Diagn Pathol 8:183. doi:10.1186/1746-1596-8-183
Jaffe N (2009) Osteosarcoma: review of the past, impact on the future. The American experience. Cancer Treat Res 152:239–262. doi:10.1007/978-1-4419-0284-9_12
Budihardjo I, Oliver H, Lutter M, Luo X, Wang X (1999) Biochemical pathways of caspase activation during apoptosis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 15(1):269–290
Ríos J-L (2011) Chemical constituents and pharmacological properties of Poria cocos. Planta Med 77(07):681–691
Tai T, Akahori A, Shingu T (1991) Triterpenoids from Poria cocos. Phytochemistry 30(8):2796–2797
Kaminaga T, Yasukawa K, Kanno H, Tai T, Nunoura Y, Takido M (1996) Inhibitory effects of lanostane-type triterpene acids, the components of Poria cocos, on tumor promotion by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate in two-stage carcinogenesis in mouse skin. Oncology 53(5):382–385
Ling H, Zhang Y, Ng K-Y, Chew E-H (2011) Pachymic acid impairs breast cancer cell invasion by suppressing nuclear factor-κB-dependent matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression. Breast Cancer Res Treat 126(3):609–620
Hong R, Shen M-H, Xie X-H, Ruan S-M (2012) Inhibition of breast cancer metastasis via PITPNM3 by pachymic acid. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 13(5):1877–1880
Gapter L, Wang Z, Glinski J, Ng K-y (2005) Induction of apoptosis in prostate cancer cells by pachymic acid from Poria cocos. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 332(4):1153–1161
Ling H, Jia X, Zhang Y, Gapter LA, Lim Y-s, Agarwal R, Ng K-y (2010) Pachymic acid inhibits cell growth and modulates arachidonic acid metabolism in nonsmall cell lung cancer A549 cells. Mol Carcinog 49(3):271–282
Jeong JW, Lee WS, Go S-i, Nagappan A, Baek JY, Lee JD, Lee SJ, Park C, Kim GY, Kim HJ (2015) Pachymic acid induces apoptosis of EJ bladder cancer cells by DR5 up-regulation, ROS generation, modulation of Bcl-2 and IAP family members. Phytother Res 29(10):1516–1524
Cuéllar MJ, Giner RM, Recio MC, Just MJ, Máñez S, Ríos JL (1996) Two fungal lanostane derivatives as phospholipase A2 inhibitors. J Nat Prod 59(10):977–979
Park D-W, Kim J-R, Kim S-Y, Sonn J-K, Bang O-S, Kang S-S, Kim J-H, Baek S-H (2003) Akt as a mediator of secretory phospholipase A2 receptor-involved inducible nitric oxide synthase expression. J Immunol 170(4):2093–2099
Díaz-Montero CM, Wygant JN, Mcintyre BW (2006) PI3-K/Akt-mediated anoikis resistance of human osteosarcoma cells requires Src activation. Eur J Cancer 42(10):1491–1500
Miwa S, Sugimoto N, Shirai T, Hayashi K, Nishida H, Ohnari I, Takeuchi A, Yachie A, Tsuchiya H (2011) Caffeine activates tumor suppressor PTEN in sarcoma cells. Int J Oncol 39(2):465–472
Cantley LC, Neel BG (1999) New insights into tumor suppression: PTEN suppresses tumor formation by restraining the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(8):4240–4245
Soldani C, Scovassi AI (2002) Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 cleavage during apoptosis: an update. Apoptosis 7(4):321–328
Steelman LS, Chappell WH, Abrams SL, Kempf CR, Long J, Laidler P, Mijatovic S, Maksimovic-Ivanic D, Stivala F, Mazzarino MC, Donia M (2011) Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR pathways in controlling growth and sensitivity to therapy-implications for cancer and aging. Aging (Albany NY) 3(3):192
Yang G, Sun X, Wang R (2004) Hydrogen sulfide-induced apoptosis of human aorta smooth muscle cells via the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and caspase-3. FASEB J 18(14):1782–1784
Porter AG, Jänicke RU (1999) Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 6(2):99–104
Morgensztern D, McLeod HL (2005) PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway as a target for cancer therapy. Anticancer Drugs 16(8):797–803
Simpson L, Parsons R (2001) PTEN: life as a tumor suppressor. Exp Cell Res 264(1):29–41
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, H., Wu, Z., Hu, H. et al. The anti-tumor effect of pachymic acid on osteosarcoma cells by inducing PTEN and Caspase 3/7-dependent apoptosis. J Nat Med 72, 57–63 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-017-1117-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-017-1117-2