Abstract
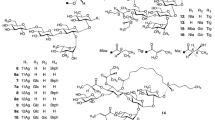
Alkaline hydrolysis of the ether-soluble resin glycoside (jalapin) fraction of the leaves and stems of Ipomoea digitata L. (Convolvulaceae) gave six organic acids, isobutyric, (S)-2-methylbutyric, tiglic, n-decanoic, n-dodecanoic, and cinnamic acids, and two glycosidic acids, quamoclinic acid A and operculinic acid A. Further, a new genuine resin glycoside, named digitatajalapin I, was isolated from the jalapin fraction, along with three known resin glycosides. Their structures have been determined on the basis of chemical and spectroscopic data.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shellard EJ (1961) The chemistry of some convolvulaceous resins. I. Vera Cruz jalap. Plant Med 9:102–116
Du X, Sun N, Nishi M, Kawasaki T, Guo Y, Miyahara K (1999) Components of ether-insoluble resin glycoside fraction from the seed of Cuscuta australis. J Nat Prod 62:722–725
Numba T (1980) Coloured illustrations of Wakan-Yaku (Vol. I). Hoikusya Publishing Co., Ltd., Japan, pp 142–144
Helmchen G, Volter H, Schuhle W (1977) Directed resolution of enantiomers via liquid chromatography of diastereomeric derivatives. III. a convenient method to determine the absolute configuration of carboxylic acids R1CHR2CO2H. Tetrahedron Lett 16:1417–1420
Ono M, Honda F, Karahashi A, Kawasaki T, Miyahara K (1997) Resin glycosides. XXV. Mutifidins I and II, new jalapins, from the seed of Quamoclit x multifida. Chem Pharm Bull 45:1955–1960
Ono M, Kawasaki T, Miyahara K (1989) Resin glycosides. V. Identification and characterization of the component organic and glycosidic acids of the ether-soluble crude resin glycosides (“jalapin”) from Rhizoma Jalapae Braziliensis (roots of Ipomoea operculata). Chem Pharm Bull 37:3209–3213
Chérigo L, Pereda-Miranda R, Fragoso-Serrano M, Jacobo-Herrera N, Kaatz GW, Gibbons S (2008) Inhibitors of bacterial multidrug efflux pumps from the resin glycosides of Ipomoea murucoides. J Nat Prod 71:1037–1045
Chérigo L, Pereda-Miranda R (2006) Resin glycosides from the flowers of Ipomoea murucoides. J Nat Prod 69:595–599
Ono M, Kuwabata K, Kawasaki T, Miyahara K (1992) Resin glycosides. XIV. Quamoclins I–IV, new ether-soluble resin glycosides (jalapin) from the seeds of Quamoclit pennata. Chem Pharm Bull 40:2674–2680
Ono M, Nishi M, Kawasaki T, Miyahara K (1990) Resin glycosides. IX. Operculins I, II, V, VII, and VIII, new ether-soluble resin glycosides of Rhizoma Jalapae Braziliensis (the roots of Ipomoea operculata. Chem Pharm Bull 38:2986–2991
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ono, M., Fukuda, H., Murata, H. et al. Resin glycosides from the leaves and stems of Ipomoea digitata . J Nat Med 63, 176–180 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-008-0309-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-008-0309-1