Summary
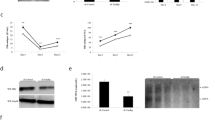
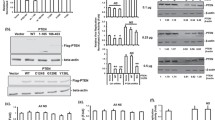
Protein-tyrosine phosphatase PTPN3 is a membrane-associated non-receptor protein-tyrosine phosphatase. PTPN3 contains a N-terminal FERM domain, a middle PDZ domain, and a C-terminal phosphatase domain. Upon co-expression of PTPN3, the level of human hepatitis B viral (HBV) RNAs, 3.5 kb, 2.4/2.1 kb, and 0.7 kb transcribed from a replicating HBV expression plasmid is significantly reduced in human hepatoma HuH-7 cells. When the expression of endogenous PTPN3 protein is diminished by specific small interfering RNA, the expression of HBV genes is enhanced, indicating that the endogenous PTPN3 indeed plays a suppressive role on HBV gene expression. PTPN3 can interact with HBV core protein. The interaction is mediated via the PDZ domain of PTPN3 and the carboxyl-terminal last four amino acids of core. Either deletion of PDZ domain of PTPN3 or substitution of PDZ ligand in core has no effect on PTPN3-mediated suppression. These results clearly show that the interaction of PTPN3 with core is not required for PTPN3 suppressive effect. Mutation of 359serine and 835serine of 14-3-3β binding sites to alanine, which slightly reduces the interaction with 14-3-3β, does not influence the PTPN3 effect. In contrast, mutation of the invariant 842cysteine residue in phosphatase domain to serine, which makes the phosphatase activity inactive, does not change its subcellular localization and interaction with core or 14-3-3β, but completely abolishes PTPN3-mediated suppression. Furthermore, deletion of FERM domain does not affect the phosphatase activity or interaction with 14-3-3β, but changes the subcellular localization from cytoskeleton-membrane interface to cytoplasm and nucleus, abolishes binding to core, and diminishes the PTPN3 effect on HBV gene expression. Taken together, these results demonstrate that the phosphatase activity and FERM domain of PTPN3 are essential for its suppression of HBV gene expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tautz L., Pellecchia M., Mustelin T. (2006) Targeting the PTPome in human disease. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 10: 157–177
Tonks N.K. (2005) Redox redux: revisiting PTPs and the control of cell signaling. Cell 121: 667–670
Stoker A.W. (2005) Protein tyrosine phosphatases and signaling. J. Endod. 185: 19–33
Mustelin T., Vang T., Bottini N. (2005) Protein tyrosine phosphatases and the immune response. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 5: 43–57
Ostman A., Hellberg C., Bohmer F.D. (2006) Protein-tyrosine phosphatases and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 6: 307–320
Sun C.X., Robb V.A., Gutmann D.H. (2002) Protein 4.1 tumor suppressors: getting a FERM grip on growth regulation. J. Cell Sci. 115: 3991–4000
Gjorioff-Wingren A., Saxena M., Han S., Wang X., Alonso A., Renedo M., Oh P., Williams S., Schnitzer J., Mustelin T. (2000) Subcellular localization of intracellular protein tyrosine phosphatases in T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 30: 2412–2421
Yang Q., Tonks N.K. (1991) Isolation of a cDNA clone encoding a human protein-tyrosine phosphatase with homology to the cytoskeletal-associated proteins band 4.1, ezrin, and talin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88: 5945–5953
Zhang S.H., Eckberg W.R., Yang Q., Samatar A.A., Tonks N.K. (1995) Biochemical characterization of a human band 4.1-related protein-tyrosine phosphatase, PTPH1. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 20067–20072
Harris B.Z., Lim W.A. (2001) Mechanism and role of PDZ domains in signaling complex assembly. J. Cell Sci. 114: 3219–3231
Nourry C., Grant S.G.N. and Borg J.P., PDZ domain proteins: plug and play. Sci. STKE 179: re7, 2003
van Ham M., Hendriks W. (2003) PDZ domains-glue and guide. Mol. Biol. Rep. 30: 69–82
Tonks N.K., Neel B.G. (2001) Combinatorial control of the specificity of protein tyrosine phosphatases. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 13: 182–195
Wang Z., Shen D., Parsons D.W., Bardelli A., Sager J., Szabo S., Ptak J., Silliman N., Peters B.A., van der Heijden M.S., Parmigiani G., Yan H., Wang T.L., Riggins G., Powell S.M., Willson J.K., Markowitz S., Kinzler K.W., Vogelstein B., Velculescu V.E. (2004) Mutational analysis of the tyrosine phosphatome in colorectal cancers. Science 304: 1164–1166
Block T.M., Mehta A.S., Fimmel C.J., Jordan R. (2003) Molecular viral oncology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 22: 5093–5107
Ganem D., Prince A.M. (2004) Hepatitis B virus infection-natural history and clinical consequences. N. Engl. J. Med. 350: 1118–1129
Yim H.J., Lok A.S. (2006) Natural history of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: what we knew in 1981 and what we know in 2005. Hepatology 43: S173–181
Seeger C., Mason W.S. (2000) Hepatitis B virus biology. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 64: 51–68
Hatton T., Zhou S., Standring D.N. (1992) RNA- and DNA-binding activities in hepatitis B virus capsid protein: a model for their roles in viral replication. J. Virol. 66: 5232–5241
Huang C.J., Chen Y.H., Ting L.P. (2000) Hepatitis B virus core protein interacts with the C-terminal region of actin-binding protein. J. Biomed. Sci. 7: 160–168
Yang C.Y., Kuo T.H., Ting L.P. (2006) Human hepatitis B viral e antigen interacts with cellular interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein and triggers interleukin-1 response. J. Biol. Chem. 281: 34525–34536
Yuh C.H., Chang Y.L., Ting L.P. (1992) Transcriptional regulation of precore and pregenomic RNAs of hepatitis B virus. J. Virol. 66: 4073–4084
Lai C.K., Ting L.P. (1999) Transcriptional repression of human hepatitis B viral genes by a bZIP family member, E4BP4. J. Virol. 73: 3197–3209
Zhang S.H., Kobayashi R., Graves P.R., Piwnica-Worms H., Tonks N.K. (1997) Serine phosphorylation-dependent association of the band 4.1-related protein-tyrosine phosphatase PTPH1 with 14-3-3β protein. J. Biol. Chem. 272: 27281–27287
Koschel M., Thomssen R., Bruss V. (1999) Extensive mutagenesis of the hepatitis B virus core gene and mapping of mutations that allow capsid formation. J. Virol. 73: 2153–2160
Zheng Y., Schlondorff J., Blobel C.P. (2002) Evidence for regulation of the tumor necrosis factor alpha-convertase (TACE) by protein-tyrosine phosphatase PTPH1. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 42463–42470
Jespersen T., Gavillet B., van Bemmelen M.X., Cordonier S., Thomas M.A., Staub O., Abriel H. (2006) Cardiac sodium channel Na(v)1.5 interacts with and is regulated by the protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPH1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 348: 1455–1462
Jing M., Bohl J., Brimer N., Kinter M., Vande Pol S.B. (2006) Degradation of tyrosine phosphatase PTPN3 (PTPH1) by association with oncogenic human papillomavirus E6 proteins. J. Virol. 81: 2231–2239
Bompard G., Martin M., Roy C., Vignon F., Freiss G. (2003) Membrane targeting of protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPL1 through its FERM domain via binding to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-biphosphate. J. Cell Sci. 116: 2519–2530
Han S., Williams S., Mustelin T. (2000) Cytoskeletal protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPH1 reduces T cell antigen receptor signaling. Eur. J. Immunol. 30: 1318–1325
Sozio M.S., Mathis M.A., Young J.A., Walchli S., Pitcher L.A., Wrage P.C., Bartók B., Campbell A., Watts J.D., Aebersold R., van Huijsduijnen R.H., van Oers N.S.C. (2004) PTPH1 is a predominant protein-tyrosine phosphatase capable of interacting with and dephosphorylating the T cell receptor ζ subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 279: 7760–7769
Rellahan B.L., Jensen J.P., Weissman A.M. (1994) Transcriptional regulation of the T cell antigen receptor zeta subunit: identification of a tissue-restricted promoter. J. Exp. Med. 180: 1529–1534
Rellahan B.L., Jensen J.P., Howcroft T.K., Singer D.S., Bonvini E., Weissman A.M. (1998) Elf-1 regulates basal expression from the T cell antigen receptor zeta-chain gene promoter. J. Immunol. 160: 2794–2801
Pasquali C., Curchod M.L., Walchli S., Espanel X., Guerrier M., Arigoni F., Strous G., van Huijsduijnen R.H. (2003) Identification of protein tyrosine phosphatases with specificity for the ligand-activated growth hormone receptor. Mol. Endocrinol. 17: 2228–2239
Flores-Morales A., Greenhalgh C.J., Norstedt G., Rico-Bautista E. (2006) Negative regulation of growth hormone receptor signaling. Mol. Endocrinol. 20: 241–253
Jeay S., Sonenshein G.E., Postel-Vinay M.C., Baixeras E. (2000) Growth hormone prevents apoptosis through activation of NF-κB in interleukin-3-dependent Ba/F3 cell line. Mol. Endocrinol. 14: 650–661
Zhang S.H., Liu J., Kobayashi R., Tonks N.K. (1999) Identification of the cell cycle regulator VCP (p97/CDC48) as a substrate of the band 4.1-related protein-tyrosine phosphatase PTPH1. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 17806–17812
Patel S., Latterich M. (1998) The AAA team: related ATPases with diverse functions. Trends Cell Biol. 8: 65–71
Dai R.M., Chen E., Longo D.L., Gorbea C.M., Li C.C.H. (1998) Involvement of valosin-containing protein, an ATPase co-purified with IκBα and 26S proteasome, in ubiquitin-proteasome-mediated degradation of IκBα. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 3562–3573
Dai R.M., Li C.C.H. (2001) Valosin-containing protein is a multi-ubiquitin chain-targeting factor required in ubiquitin-proteasome degradation. Nat. Cell Biol. 3: 740–744
Perkins N.D. (2006) Post-translational modifications regulating the activity and function of the nuclear factor kappa B pathway. Oncogene 25: 6717–6730
Hsu, E.C., Interaction between hepatitis B virus core protein and cellular protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPH1. Master thesis, National Yang-Ming University, 2004
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Research Grants NSC-92–2320-B-010–061, 93-2320-B-010-016, and 94-2320-B-010-003 from the National Science Council, R.O.C. We greatly appreciate the outstanding technical assistance of Imaging Core of the Instrumentation Resource Center of National Yang-Ming University for laser confocal microscopy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
En-Chi Hsu, Yen-Cheng Lin have equal contributions to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsu, EC., Lin, YC., Hung, CS. et al. Suppression of hepatitis B viral gene expression by protein-tyrosine phosphatase PTPN3. J Biomed Sci 14, 731–744 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11373-007-9187-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11373-007-9187-x