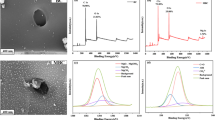
Abstract
Purpose
Co-composting of chicken manure and edible mushroom residue inoculated with oxytetracycline-degrading strain T4 was conducted to reduce the risk of residual oxytetracycline and tetracycline resistance genes (TRGs) to the ecological environment.
Materials and methods
Three treatments (CK: without bacteria agent T4 inoculated; AM: 1% bacteria agent T4 inoculated in mesophilic phase; AC: 1% bacteria agent T4 inoculated in cooling phase) were set to investigate dynamics of physicochemical properties, microbial composition, and antibiotic and antibiotic resistance genes.
Results and discussion
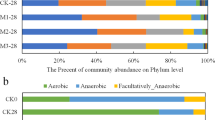
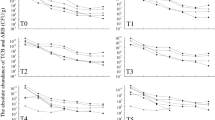
The bacteria agent T4 inoculated in the mesophilic phase was conductive to the reservation of nutrients and maturity of chicken manure and improved oxytetracycline degradation (t1/2 was 2.77 days, and the total degradation rate was 80.78%). Bacterial community dynamic analysis showed that strain T4 reduced microbial richness and diversity in composting. In addition, the bacteria agent T4 could reduce the relative abundance of encoding efflux pump (EFP) TRGs significantly, and inoculated in the mesophilic phase was better than the cooling phase while having little effect on ribosomal protection protein (RPP) TRGs and enzymatic inactivation (EI) TRG.
Conclusions
Inoculation of strain T4 in the initial stage of composting could be a promising technology to solve the problem of oxytetracycline residue and its resistance genes in chicken manure. It was also found that the abundance of TRGs was affected by bacterial composition and dynamic, which was affected by the physicochemical properties of composting and fates of oxytetracycline, and vice versa.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Abdellah Y, Luo Y, Sun S, Yang X, Ji H, Wang R (2023) Phytochemical and underlying mechanism of Mikania micrantha Kunth on antibiotic resistance genes, and pathogenic microbes during chicken manure composting. Biores Technol 367:128241
Alavi N, Sarmadi K, Goudarzi G, Babaei AA, Bakhshoodeh R, Paydary P (2019) Attenuation of tetracyclines during chicken manure and bagasse co-composting: degradation, kinetics, and artificial neural network modeling. J Environ Manage 231:1203–1210
Awasthi M, Liu H, Liu T, Awasthi S, Zhang Z (2022) Effect of biochar addition on the dynamics of antibiotic resistant bacteria during the pig manure composting. Sci Total Environ 814:152688
Ben Y, Fu C, Hu M, Liu L, Wong M, Zheng C (2019) Human health risk assessment of antibiotic resistance associated with antibiotic residues in the environment: a review. Environ Res 169:483–493
Bernal M, Alburquerque J, Moral R (2009) Composting of animal manures and chemical criteria for compost maturity assessment. a review. Biores Technol 100:5444–5453
Chang H, Zhu X, Wu J, Guo D, Zhang L, Feng Y (2021) Dynamics of microbial diversity during the composting of agricultural straw. J Integr Agric 20:1121–1136
Chen G, He W, Wang Y, Zou Y, Liang J, Liao X, Wu Y (2014) Effect of different oxytetracycline addition methods on its degradation behavior in soil. Sci Total Environ 479–480:241–246
Chen Z, Li Y, Ye C, He X, Zhang S (2021) Fate of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes during aerobic co-composting of food waste with sewage sludge. Sci Total Environ 784:146950
Cheng D, Feng Y, Liu Y, Xue J, Li Z (2019) Dynamics of oxytetracycline, sulfamerazine, and ciprofloxacin and related antibiotic resistance genes during swine manure composting. J Environ Manage 230:102–109
Cheng D, Liu Y, Shehata E, Feng Y, Lin H, Xue J, Li Z (2021) In-feed antibiotic use changed the behaviors of oxytetracycline, sulfamerazine, and ciprofloxacin and related antibiotic resistance genes during swine manure composting. J Hazard Mater 402:123710
Erickson B, Elkins C, Mullis L, Heinze T, Wagner R, Cerniglia C (2014) A metallo-β-lactamase is responsible for the degradation of ceftiofur by the bovine intestinal bacterium Bacillus cereus P41. Vet Microbiol 172:499–504
Feng Y, Wang G, Liu Y, Cheng D, Fan S, Zhao Q, Xue J, Zhang S, Li Z (2021) The impacts of oxytetracycline on humification during manure composting can be alleviated by adjusting initial moisture contents as illustrated by NMR. J Integr Agric 20:2277–2288
Feng Y, Wei C, Zhang W, Liu Y, Li Z, Hu H, Xue J, Davis M (2016) A simple and economic method for simultaneous determination of 11 antibiotics in manure by solid-phase extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography. J Soils Sediments 16:2242–2251
Fu Y, Zhu Y, Dong H, Li J, Zhang W, Shao Y, Shao Y (2022) Mechanisms of the effects of humic acid on antibiotic resistance genes and microbial communities in Cd-contaminated soils. Process Saf Environ Prot 160:62–69
Gong P, Liu H, Wang G, Yao J, Dai X (2021) Enhanced depletion of antibiotics and accelerated estabilization of dissolved organic matter by hydrothermal pretreatment during composting of oxytetracycline fermentation residue. Biores Technol 339:125618
Gou C, Wang Y, Zhang X, Lou Y, Gao Y (2017) Inoculation with a psychrotrophic-thermophilic complex microbial agent accelerates onset and promotes maturity of dairy manure-rice straw composting under cold climate conditions. Biores Technol 243:339–346
Gou C, Wang Y, Zhang X, Zhong R, Gao Y (2021) Effects of chlorotetracycline on antibiotic resistance genes and the bacterial community during cattle manure composting. Biores Technol 323:124517
Guan J, Wasty A, Grenier C, Chan M (2007) Influence of temperature on survival and conjugative transfer of multiple antibiotic-resistant plasmids in chicken manure and compost microcosms. Poult Sci 86:610–613
Hu X, Zhou Q, Luo Y (2010) Occurrence and source analysis of typical veterinary antibiotics in manure, soil, vegetables and groundwater from organic vegetable bases, northern China. Environ Pollut 158:2992–2998
Huang B, Jia H, Han X, Gou J, Huang C, Wang J, Wei J, Wang J, Zhang C (2021) Effects of biocontrol Bacillus and fermentation bacteria additions on the microbial community, functions and antibiotic resistance genes of prickly ash seed oil meal-biochar compost. Biores Technol 340:125668
Jiang J, Kang K, Chen D, Liu N (2018) Impacts of delayed addition of N-rich and acidic substrates on nitrogen loss and compost quality during pig manure composting. Waste Manage 72:161–167
Li C, Li H, Yao T, Su M, Ran F, Han B, Li J, Lan X, Zhang Y, Yang X, Gun S (2019a) Microbial inoculation influences bacterial community succession and physicochemical characteristics during pig manure composting with corn straw. Biores Technol 289:121653
Li H, Cheng W, Li B, Xu Y, Zheng X (2020) The fate of antibiotic resistance genes during co-composting of swine manure with cauliflower and corn straw. Biores Technol 300:122669
Li Y, Zhang X, Li W, Lu X, Liu B, Wang J (2013) The residues and environmental risks of multiple veterinary antibiotics in animal faeces. Environ Monit Assess 185:2211–2220
Li Z, Qi W, Feng Y, Liu Y, Ebrahim S, Long J (2019b) Degradation mechanisms of oxytetracycline in the environment. J Integr Agric 18:1953–1960
Lin H, Sun W, Yu Y, Ding Y, Yang Y, Zhang Z, Ma J (2021) Simultaneous reductions in antibiotics and heavy metal pollution during manure composting. Sci Total Environ 788:147830
Liu B, Yu K, Ahmed I, Gin K, Xi B, Wei Z, He Y, Zhang B (2021) Key factors driving the fate of antibiotic resistance genes and controlling strategies during aerobic composting of animal manure: a review. Sci Total Environ 791:148372
Liu Y, Cheng D, Xue J, Weaver L, Wakelin S, Feng Y, Li Z (2020) Changes in microbial community structure during pig manure composting and its relationship to the fate of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes. J Hazard Mater 389:122082
Liu Y, Feng Y, Cheng D, Xue J, Wakelin S, Li Z (2018) Dynamics of bacterial composition and the fate of antibiotic resistance genes and mobile genetic elements during the co-composting with gentamicin fermentation residue and lovastatin fermentation residue. Biores Technol 261:249–256
Liu Y, Feng Y, Cheng D, Xue J, Wakelin SA, Hu H, Li Z (2017) Gentamicin degradation and changes in fungal diversity and physicochemical properties during composting of gentamicin production residue. Biores Technol 244:905–912
Mcdonald D, Price M, Goodrich J, Nawrocki E, Desantis T, Probst A, Andersen G, Knight R, Hugenholtz P (2012) An improved green genes taxonomy with explicit ranks for ecological and evolutionary analyses of bacteria and archaea. Isme j 6:610–618
Qi W, Long J, Feng C, Feng Y, Cheng D, Liu Y, Xue J, Li Z (2019) Fe3+ enhanced degradation of oxytetracycline in water by pseudomonas. Water Res 160:361–370
Qian X, Sun W, Gu J, Wang X, Zhang Y, Duan M, Li H, Zhang R (2016) Reducing antibiotic resistance genes, integrons, and pathogens in dairy manure by continuous thermophilic composting. Biores Technol 220:425–432
Qiu X, Feng M, Zhou G, Wang H (2022) Effects of mineral additives on antibiotic resistance genes and related mechanisms during chicken manure composting. Biores Technol 346:126631
Ravindran B, Mnkeni P (2017) Identification and fate of antibiotic residue degradation during composting and vermicomposting of chicken manure. Int J Environ Sci Technol 14:263–270
Ren G, Xu X, Qu J, Zhu L, Wang T (2016) Evaluation of microbial population dynamics in the co-composting of cow manure and rice straw using high throughput sequencing analysis. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 32:101
Ren L, Yan B, Kumar A, Zhang J, Huang H, Zhang L, Luo L (2021) Accelerated humification and alteration of microbial communities by distillers’ grains addition during rice straw composting. Biores Technol 342:125937
Ren X, Wang Q, Awasthi M, Zhao J, Wang J, Liu T, Li R, Zhang Z (2019) Improvement of cleaner composting production by adding diatomite: from the nitrogen conservation and greenhouse gas emission. Biores Technol 286:121377
Sardar M, Zhu C, Geng B, Ahmad H, Song T, Li H (2021) The fate of antibiotic resistance genes in cow manure composting: shaped by temperature-controlled composting stages. Biores Technol 320:124403
Selvam A, Xu D, Zhao Z, Wong J (2012) Fate of tetracycline, sulfonamide and fluoroquinolone resistance genes and the changes in bacterial diversity during composting of swine manure. Biores Technol 126:383–390
Song T, Zhu C, Xue S, Li B, Ye J, Geng B, Li L, Fahad S, Li N, Feng S, Li H (2020) Comparative effects of different antibiotics on antibiotic resistance during swine manure composting. Biores Technol 315:123820
Song W, Wang X, Gu J, Zhang S, Yin Y, Li Y, Qian X, Sun W (2017) Effects of different swine manure to wheat straw ratios on antibiotic resistance genes and the microbial community structure during anaerobic digestion. Biores Technol 231:1–8
Soni K, Jyoti K, Chandra H, Chandra R (2022) Bacterial antibiotic resistance in municipal wastewater treatment plant; mechanism and its impacts on human health and economy. Bioresource Technology Reports 19:101080
Subirats J, Murray R, Scott A, Lau C, Topp E (2020) Composting of chicken litter from commercial broiler farms reduces the abundance of viable enteric bacteria, Firmicutes, and selected antibiotic resistance genes. Sci Total Environ 746:141113
Tang J, Li X, Cui P, Lin J, Zeng J, Lin H, Zhou S (2020) Nitrification plays a key role in N2O emission in electric-field assisted aerobic composting. Biores Technol 297:122470
Tang Y, Liang Z, Li G, Zhao H, An T (2021) Metagenomic profiles and health risks of pathogens and antibiotic resistance genes in various industrial wastewaters and the associated receiving surface water. Chemosphere 283:131224
Tian W, Sun Q, Xu D, Zhang Z, Chen D, Li C, Shen Q, Shen B (2013) Succession of bacterial communities during composting process as detected by 16S rRNA clone libraries analysis. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 78:58–66
Tong Z, Liu F, Sun B, Tian Y, Zhang J, Duan J, Bi W, Qin J, Xu S (2023) Effect of biochars with different particle sizes on fates of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes during composting of swine manure. Biores Technol 370:128542
Wang J, Ben W, Yang M, Zhang Y, Qiang Z (2016a) Dissemination of veterinary antibiotics and corresponding resistance genes from a concentrated swine feedlot along the waste treatment paths. Environ Int 92–93:317–323
Wang N, Zhao K, Li F, Peng H, Lu Y, Zhang L, Pan J, Jiang S, Chen A, Yan B, Luo L, Huang H, Li H, Wu G, Zhang J (2022) Characteristics of carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur cycling genes, microbial community metabolism and key influencing factors during composting process supplemented with biochar and biogas residue. Biores Technol 366:128224
Wang R, Zhang J, Sui Q, Wan H, Tong J, Chen M, Wei Y, Wei D (2016b) Effect of red mud addition on tetracycline and copper resistance genes and microbial community during the full scale swine manure composting. Biores Technol 216:1049–1057
Wu J, He S, Liang Y, Li G, Li S, Chen S, Nadeem F, Hu J (2017) Effect of phosphate additive on the nitrogen transformation during pig manure composting. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:17760–17768
Yang Y, Awasthi M, Du W, Ren X, Lei T, Lv J (2020) Compost supplementation with nitrogen loss and greenhouse gas emissions during pig manure composting. Biores Technol 297:122435
Zhang L, Gu J, Wang X, Sun W, Yin Y, Sun Y, Guo A, Tuo X (2017) Behavior of antibiotic resistance genes during co-composting of swine manure with Chinese medicinal herbal residues. Biores Technol 244:252–260
Zhang L, Jia Y, Zhang X, Feng X, Wu J, Wang L, Chen G (2016) Wheat straw: an inefficient substrate for rapid natural lignocellulosic composting. Biores Technol 209:402–406
Zhang R, Gu J, Wang X, Li Y, Zhang K, Yin Y, Zhang X (2018) Contributions of the microbial community and environmental variables to antibiotic resistance genes during co-composting with swine manure and cotton stalks. J Hazard Mater 358:82–91
Zhu L, Lian Y, Lin D, Huang D, Yao Y, Ju F, Wang M (2022) Insights into microbial contamination in multi-type manure-amended soils: the profile of human bacterial pathogens, virulence factor genes and antibiotic resistance genes. J Hazard Mater 437:129356
Zhang X, Cai T, Zhang S, Hou J, Cheng L, Chen W, Zhang Q (2024) Contamination distribution and non-biological removal pathways of typical tetracycline antibiotics in the environment: a review. J Hazard Mater 463:132862
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52370141) and the earmarked fund for CARS (China Agriculture Research System, No. CARS-29-zp-10).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qihang Wei: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, validation, data curation, visualization, and writing—original draft. Xiaoxing Wang: data curation, visualization, and formal analysis. Yao Feng: methodology, investigation, and validation. Yanfang Ren: formal analysis and writing—review and editing. Junyu He: formal analysis and writing—review and editing. Zhaojun Li: conceptualization, funding acquisition, project administration, resources, and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Hang-Wei Hu.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Q., Wang, X., Feng, Y. et al. Dynamics of physicochemical properties, microbial composition, and antibiotic and antibiotic resistance genes during chicken manure composting with strain T4. J Soils Sediments 24, 1750–1763 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-024-03755-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-024-03755-4