Abstract
Purpose
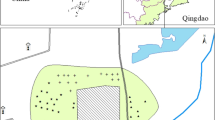
The distribution and characteristics of heavy metals around an electric arc furnace (EAF) plant in Taichung City, Taiwan, were investigated. The aim of this research was to predict the main steelmaking processes causing contamination of As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Ni, Pb, and Zn in the environment.
Materials and methods
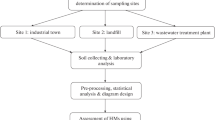
Food crop, surface water, sediments, and soils were collected from a total of 65 and 53 sampling sites during November 2011 and June 2012, thus establishing the basic environmental information. The heavy metals in samples were assessed by potential ecological risk indices. The correlation between the source and receptors of contamination was evaluated through the statistical significance of isotope approach and hierarchical cluster analysis.
Results and discussion
The heavy metal contamination was mainly from the storage facility of waste iron and the discharging device of fly ash in the EAF plant. Surface runoff and rainwash were the two potential routes distributing the metallurgical Cd and Pb to the surrounding environment. Based on the mathematical simulation of dispersion modeling, the impact of heavy metals through the two specific flue gases on the farmland was insignificant; the particulate matter (PM), SO2, and NOx were concentrated southward in the atmosphere, and they were 1.71 μg—PM/Nm3, 2.80 ppb—SO2, and 1.87 ppb—NOx, respectively.
Conclusions
Because of topographical features, the contaminated sediment produced by steelmaking activities is washed into downstream via surface runoff, which is supposed to be the major source of long-term accumulation of heavy metals in the environments, although the contamination with heavy metals was graded as low.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida SM, Lage J, Fernández B, Garcia S, Reis MA, Chaves PC (2015) Chemical characterization of atmospheric particles and source apportionment in the vicinity of a steelmaking industry. Sci Total Environ 521–522:411–420
Bi C, Zhou Y, Chen Z, Jia J, Bao X (2018) Heavy metals and lead isotopes in soils, road dust and leafy vegetables and health risks via vegetable consumption in the industrial areas of Shanghai, China. Sci Total Environ 619–620:1349–1357
Bridgestock L, van de Flierdt T, Rehkamper M, Paul M, Middag R, Milne A, Lohan MC, Baker AR, Chance, Khondoker R, Strekopytov S, Humphreys-Williams E, Achterberg EP, Rijkenberg MJA, Gerringa LJA, de Baar HJW (2016) Return of naturally sourced Pb to Atlantic surface waters. Nat Commun 7:12921:1–13
Carolin CF, Kumar PS, Saravanan A, Joshiba GJ, Nausha M (2017) Efficient techniques for the removal of toxic heavy metals from aquatic environment: a review. J Environ Chem Eng 5:2782–2799
Chen MH (2002) Baseline metal concentrations in sediments and fish, and the determination of bioindicators in the subtropical Chi-ku Lagoon, S W Taiwan. Mar Pollut Bull 44(7):703–714
Conway TM, Rosenberg AD, Adkins JF, John SG (2013) A new method for precise determination of iron, zinc and cadmium stable isotope ratios in seawater by double-spike mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 793:44–52
Djukic A, Lekic B, Rajakovic-Ognjanovic V, Veljovic D, Vulic T, Djolic M, Naunovic Z, Despotovic J, Prodanovic D (2016) Further insight into the mechanism of heavy metals partitioning in stormwater runoff. J Environ Manag 168:104–110
EIPPCB (2012) Best Available Techniques (BAT) reference document for iron and steel production
European Union (2002) Heavy metals in wastes, European Commission on Environment
Fouedjio F (2016) A hierarchical clustering method for multivariate geostatistical data. Spat Stat 18:333–351
Gao B, Zhou H, Liang X, Tu X (2013) Cd isotopes as a potential source tracer of metal pollution in river sediments. Environ Poll 181:340–343
Gołdyn B, Chudzińska M, Barałkiewicz D, Celewicz-Gołdyn S (2015) Heavy metal contents in the sediments of astatic ponds: influence of geomorphology, hydroperiod, water chemistry and vegetation. Ecotoxic Environ Saf 118:103–111
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Hosseini B, Stockie JM (2017) Estimating airborne particulate emissions using a finite-volume forward solver coupled with a Bayesian inversion approach. Comp Flu 154:27–43
Hu Y, Liu X, Bai J, Shih K, Zeng EY, Cheng H (2013) Assessing heavy metal pollution in the surface soils of a region that had undergone three decades of intense industrialization and urbanization. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:6150–6159
Hu Y, Cheng H, Tao S (2016) The challenges and solutions for cadmium-contaminated rice in China: a critical review. Environ Int 92–93:515–532
Karunanidhi K, Rajendran R, Pandurangan D, Arumugam G (2017) First report on distribution of heavy metals and proximate analysis in marine edible puffer fishes collected from Gulf of Mannar Marine Biosphere Reserve, south India. Toxicol Report 4:319–327
Khan MU, Malik RN, Muhammad S (2013) Human health risk from heavy metal via food crops consumption with wastewater irrigation practices in Pakistan. Chemosphere 93:2230–2238
Kroukamp EM, Wondimu T, Forbes PBC (2016) Metal and metalloid speciation in plants: overview, instrumentation, approaches and commonly assessed elements. Trend Anal Chem 77:87–99
Lee HD, Yoo JW, Kang MK, Kang JS, Jung JH, Oh KJ (2014) Evaluation of concentrations and source contribution of PM10 and SO2 emitted from industrial complexes in Ulsan, Korea: interfacing of the WRF–CALPUFF modeling tools. Atmosph Poll Res 5:664–676
Li Y, Zhang H, Shao LM, He PJ (2017) Tracing source and migration of Pb during waste incineration using stable Pb isotopes. J Hazard Mater 327:28–34
Ma D, Zhang Z (2016) Contaminant dispersion prediction and source estimation with integrated Gaussian-machine learning network model for point source emission in atmosphere. J Hazard Mater 311:237–245
Ma HW, Matsubae K, Nakajima K, Tsai MS, Shao KH, Chen PC, Lee CH, Nagasaka T (2011) Substance flow analysis of zinc cycle and current status of electric arc furnace dust management for zinc recovery in Taiwan. Resour Conserv Recy 56:134–140
Mohiuddin K, Strezov V, Nelson PF, Stelcer E, Evans T (2014) Mass and elemental distributions of atmospheric particles nearby blast furnace and electric arc furnace operated industrial areas in Australia. Sci Total Environ 487:323–334
Moreno-Jiménez E, Meharg AA, Smolders E, Manzano R, Becerra D, Sánchez-Llerena J, Albarrán Á, López-Piñero A (2014) Sprinkler irrigation of rice fields reduces grain arsenic but enhances cadmium. Sci Total Environ 485–486:468–473
Ogundele LT, Owoade OK, Hopke PK, Olise FS (2017) Heavy metals in industrially emitted particulate matter in Ile-Ife, Nigeria. Environ Re 156:320–325
Palma P, Ledo L, Soares S, Barbosa IR, Alvarenga P (2014) Spatial and temporal variability of the water and sediments quality in the Alqueva reservoir (Guadiana Basin; southern Portugal). Sci Total Environ 470–471:780–790
Praveena SM, Omar NA (2017) Heavy metal exposure from cooked rice grain ingestion and its potential health risks to humans from total and bioavailable forms analysis. Food Chem 235:203–211
Rai PK (2016) Impacts of particulate matter pollution on plants: implications for environmental biomonitoring. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 129:120–136
Soliman NF, Nasr SM, Okbah MA (2015) Potential ecological risk of heavy metals in sediments from the Mediterranean coast, Egypt. J Environ Health Sci Eng 13(70):1–12
Strezov V, Chaudhary C (2017) Impacts of iron and steelmaking facilities on soil quality. J Environ Manag 203:1158–1162
Sun GX, Wang XJ, Hu QH (2011) Using stable lead isotopes to trace heavy metal contamination sources in sediments of Xiangjiang and Lishui Rivers in China. Environ Poll 159:3406–3410
Wang JHC, Tsai CT, Chiang CF (2015) Screening procedure for airborne pollutants emitted from a high-tech industrial complex in Taiwan. Chemosphere 139:268–275
Yang GCC, Chuang TN, Huang CW (2017) Achieving zero waste of municipal incinerator fly ash by melting in electric arc furnaces while steelmaking. Waste Manag 62:160–168
Yu R, Hu G, Lin C, Yang Q, Zhang C, Wang X (2017) Contamination of heavy metals and isotopic tracing of Pb in intertidal surface sediments of Jinjiang River Estuary, SE China. Appl Geochem 83:41–49
Zafra C, Temprano J, Suárez J (2017) A simplified method for determining potential heavy metal loads washed-off by stormwater runoff from road-deposited sediments. Sci Total Environ 601–602:260–270
Zhang X, Yang H, Cui Z (2018) Evaluation and analysis of soil migration and distribution characteristics of heavy metals in iron tailings. J Clean Prod 172:475–480
Zhou Q, Wu Y, Xiong X (1994) Compound pollution of Cd and Zn and its ecological effect on rice plant. Chin J Appl Ecol 5:428–441
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Dong-Mei Zhou
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 181 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, YC., Lee, WJ., Shih, YJ. et al. Levels and sources of heavy metals in soil, sediment, and food crop in the vicinity of electric arc furnace (EAF) steelmaking plant: a case study from Taiwan. J Soils Sediments 18, 2562–2572 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-1963-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-1963-x