Abstract
Purpose
The effects of municipal sludge compost (MSC) as a soil amendment are often studied in agricultural soil or topsoil contaminated with heavy metals. However, little is known about the effects of MSC amendments on plant growth and heavy metal bioavailability in subsoil. This study was conducted to investigate the effects of MSC application on plant growth and the mobility and bioavailability of Cd, Cu, and Zn in an amended soil-plant system.
Materials and methods
A pot experiment was performed to evaluate the translocation of heavy metals to broad bean (Vicia faba L.) grown in loess subsoil previously amended with different application rates of MSC. The subsoil and MSC were homogeneously mixed to achieve six soil-amended treatments (total weight of 8 kg in each pot) in 0, 0.5, 2, 6, 15, and 30% mass ratios (MSC/total). Soil samples amended with MSC were aged for 60 days before sowing. Soil and plant samples were collected after 120 days of growth. Plant height was periodically measured until harvest. The total quantities of heavy metals and their different fractions were analyzed by using graphite furnace atomic absorption spectroscopy (GF-AAS).
Results and discussion
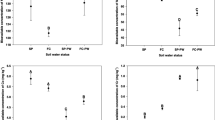
Compared with the control soil (0% treatment), the average biomass growth rates from the 0.5 to 30% treatments ranged from 14.5 to 170.4% (increasing order), respectively. Cd (0.42–1.85 mg kg−1) and Cu (14.95–23.01 mg kg−1) mainly concentrated in the plant roots, and Zn (22.06–36.48 mg kg−1) mainly concentrated in the plant stems and leaves. Fortunately, the metal concentrations in the edible plant parts (0.03–0.1 mg kg−1) remained below the Chinese national standard thresholds (0.2 mg kg−1), possibly because of the alkaline soil pH (8.60–7.74), organic matter (7.4–65.9 g kg−1) bound to metals, and translocation of less metal to the edible plant parts by biochemical modulation.
Conclusions
MSC can enhance subsoil fertility and promote plant development, especially in the 30% treatment. The mobility and bioavailability of heavy metals suggest that Cd is the element needing to be monitored during MSC application. High organic matter content and alkaline pH are the most important factors for controlling Cd levels. More work is required to determine the long-term impacts of sludge amendment on the soil and environment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdu N, Agbenin JO, Buerkert A (2011) Phytoavailability, human risk assessment and transfer characteristics of cadmium and zinc contamination from urban gardens in Kano, Nigeria. J Sci Food Agric 91:2722–2730
Alvarenga P et al (2015) Sewage sludge, compost and other representative organic wastes as agricultural soil amendments: benefits versus limiting factors. Waste Manag 40:44–52
Amir S, Hafidi M, Merlina G, Revel JC (2005) Sequential extraction of heavy metals during composting of sewage sludge. Chemosphere 59:801–810
Autier V, White D (2004) Examination of cadmium sorption characteristics for a boreal soil near Fairbanks, Alaska. J Hazard Mater 106:149–155
Baldantoni D, Bellino A, Alfani A (2016) Soil compost amendment enhances tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) quality. J Sci Food Agric 96:4082–4088
Bishop J, Potts SG, Jones HE (2016) Susceptibility of faba bean (Vicia faba L.) to heat stress during floral development and anthesis. J Agron Crop Sci 202:508–517
Borgese L et al (2013) Metal fractionation in soils and assessment of environmental contamination in Vallecamonica, Italy. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 20:5067–5075
Cai QY, Mo CH, Wu QT, Zeng QY, Katsoyiannis A (2007) Concentration and speciation of heavy metals in six different sewage sludge-composts. J Hazard Mater 147:1063–1072
Carbonell G, de Imperial RM, Torrijos M, Delgado M, Rodriguez JA (2011) Effects of municipal solid waste compost and mineral fertilizer amendments on soil properties and heavy metals distribution in maize plants (Zea mays L.) Chemosphere 85:1614–1623
Centofanti T, Chaney RL, Beyer WN, McConnell LL, Davis AP, Jackson D (2016) Assessment of trace element accumulation by earthworms in an orchard soil remediation study using soil amendments. Water Air Soil Pollut. doi:10.1007/s11270-016-3055-0
Chojnacka K, Chojnacki A, Gorecka H, Gorecki H (2005) Bioavailability of heavy metals from polluted soils to plants. Sci Total Environ 337:175–182
Deepesh V, Verma VK, Suma K, Ajay S, Gnanavelu A, Madhusudanan M (2016) Evaluation of an organic soil amendment generated from municipal solid waste seeded with activated sewage sludge. J Mater Cycles Waste Manage 18:273–286
Diacono M, Montemurro F (2010) Long-term effects of organic amendments on soil fertility. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 30:401–422
Elloumi N, Belhaj D, Jerbi B, Zouari M, Kallel M (2016) Effects of sewage sludge on bio-accumulation of heavy metals in tomato seedlings. Span J Agric Res 14:1–13
Flores F et al (2013) Adaptation of spring faba bean types across European climates. Field Crops Res 145:1–9
Garrido S, Del Campo GM, Esteller MV, Vaca R, Lugo J (2005) Heavy metals in soil treated with sewage sludge composting, their effect on yield and uptake of broad bean seeds (Vicia faba L.) Water Air Soil Pollut 166:303–319
Grace JB (2001) The roles of community biomass and species pools in the regulation of plant diversity. Oikos 92:193–207
Green CE, Chaney RL, Bouwkamp J (2003) Interactions between cadmium uptake and phytotoxic levels of zinc in hard red spring wheat. J Plant Nutr 26:417–430
Hattab N, Motelica-Heino M, Faure O, Bouchardon JL (2015) Effect of fresh and mature organic amendments on the phytoremediation of technosols contaminated with high concentrations of trace elements. J Environ Manag 159:37–47
Huang M, Zhu Y, Li Z, Huang B, Luo N, Liu C, Zeng G (2016) Compost as a soil amendment to remediate heavy metal-contaminated agricultural soil: mechanisms, efficacy, problems, and strategies. Water Air Soil Pollut 227:359
Jensen ES, Peoples MB, Hauggaard-Nielsen H (2010) Faba bean in cropping systems. Field Crops Res 115:203–216
Kasthuri H, Shanthi K, Sivakumar S, Rajakumar S, Son HK, Song YC (2011) Influence of municipal solid waste compost (MSWC) on the growth and yield of green gram (Vigna Radiate (L) Wilczek), fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) and on soil quality. Iran J Environ Health Sci 8:285–294
Kidd PS, Dominguez-Rodriguez MJ, Diez J, Monterroso C (2007) Bioavailability and plant accumulation of heavy metals and phosphorus in agricultural soils amended by long-term application of sewage sludge. Chemosphere 66:1458–1467
Kirkham MB (2006) Cadmium in plants on polluted soils: effects of soil factors hyperaccumulation and amendments. Geoderma 137:19–32
Kumpiene J, Lagerkvist A, Maurice C (2008) Stabilization of As, Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn in soil using amendments—a review. Waste Manag 28:215–225
Liu HT (2016) Relationship between organic matter humification and bioavailability of sludge-borne copper and cadmium during long-term sludge amendment to soil. Sci Total Environ 566:8–14
Liu HT, Wang YW, Huang WD, Lei M (2016) Response of wine grape growth, development and the transfer of copper, lead, and cadmium in soil-fruit system to sludge compost amendment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:24230–24236
López R, Burgos P, Madrid F, Camuna I (2015) Source separate collection of recyclables reduces chromium and nickel content in municipal solid waste compost. Clean: Soil Air Water 43:427–433
López-Rayo S, Laursen KH, Lekfeldt JDS, Delle Grazie F, Magid J (2016) Long-term amendment of urban and animal wastes equivalent to more than 100 years of application had minimal effect on plant uptake of potentially toxic elements. Agric Ecosyst Environ 231:44–53
Menon M, Hermle S, Abbaspour KC, Gunthardt-Georg MS, Oswald SE, Schulin R (2005) Water regime of metal-contaminated soil under juvenile forest vegetation. Plant Soil 271:227–241
Moynahan OS, Zabinski CA, Gannon JE (2002) Microbial community structure and carbon-utilization diversity in a mine tailings revegetation study. Restor Ecol 10:77–87
Nasernejad B, Zadeh TE, Pour BB, Bygi ME, Zamani A (2005) Camparison for biosorption modeling of heavy metals (Cr (III), Cu (II), Zn (II)) adsorption from wastewater by carrot residues. Process Biochem 40:1319–1322
Nötzold R, Blossey B, Newton E (1998) The influence of below ground herbivory and plant competition on growth and biomass allocation of purple loosestrife. Oecologia 113:82–93
Pardo R, Barrado E, Perez L, Vega M (1990) Determination and speciation of heavy metals in sediments of the Pisuerga river. Water Res 24:373–379
Park JH, Lamb D, Paneerselvam P, Choppala G, Bolan N, Chung J-W (2011) Role of organic amendments on enhanced bioremediation of heavy metal(loid) contaminated soils. J Hazard Mater 185:549–574
Parraga-Aguado I, Alvarez-Rogel J, Gonzalez-Alcaraz MN, Conesa HM (2017) Metal mobility assessment for the application of an urban organic waste amendment in two degraded semiarid soils. J Geochem Explor 173:92–98
Pedra F, Domingues H, Ribeiro AB, Polo A, Monteiro O (2006) Relationship between Cu and Zn extractable foliar contents and BCR sequential extraction in soil treated with organic amendments. Environ Technol 27:1357–1367
Peyton DP et al (2016) Nutrient, metal and microbial loss in surface runoff following treated sludge and dairy cattle slurry application to an Irish grassland soil. Sci Total Environ 541:218–229
Pritchard DL, Penney N, McLaughlin MJ, Rigby H, Schwarz K (2010) Land application of sewage sludge (biosolids) in Australia: risks to the environment and food crops. Water Sci Technol 62:48–57
Przywitowski M, Mikulski D, Zdunczyk Z, Rogiewicz A, Jankowski J (2016) The effect of dietary high-tannin and low-tannin faba bean (Vicia faba L.) on the growth performance, carcass traits and breast meat characteristics of finisher turkeys. Anim Feed Sci Technol 221:124–136
Pulkkinen M, Zhou X, Lampi AM, Piironen V (2016) Determination and stability of divicine and isouramil produced by enzymatic hydrolysis of vicine and convicine of faba bean. Food Chem 212:10–19
Qiu JR, Guo XF, Cai QY, Liu W, Zhang MW, Wei ZB, Wu QT (2014) Phytotreatment of sewage sludge contaminated by heavy metals and PAHs by co-planting sedum alfredii and Alocasia marorrhiza. Int J Phytoremediation 16:1–13
Rahoui S, Chaoui A, El Ferjani E (2010) Reserve mobilization disorder in germinating seeds of Vicia faba L. Exposed to Cadmium J Plant Nutr 33:809–817
Reddy GB, Faza A, Bennett R (1987) Activity of enzymes in rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soils amended with sludge. Soil Biol Biochem 19:203–205
Reichman SM (2002) The responses of plants to metal toxicity: a review focusing on copper, manganese and zinc. Australian Minerals & Energy Environment Foundation, Melbourne
Salomons W, Förstner U (1980) Trace metal analysis on polluted sediments. Part II: evaluation of environmental impact. Environ Technol Lett 1:506–517
Santos S, Costa CA, Duarte AC, Scherer HW, Schneider RJ, Esteves VI, Santos EB (2010) Influence of different organic amendments on the potential availability of metals from soil: a study on metal fractionation and extraction kinetics by EDTA. Chemosphere 78:389–396
Sevilla-Perea A, Romero-Puertas MC, Mingorance MD (2016) Optimizing the combined application of amendments to allow plant growth in a multielement-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 148:220–226
Shukla P, Singh AK (2015) Nitric oxide mitigates arsenic-induced oxidative stress and genotoxicity in Vicia faba L. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:13881–13891
Siddiqui MH, Al-Whaibi MH, Sakran AM, Basalah MO, Ali HM (2012) Effect of calcium and potassium on antioxidant system of Vicia faba L. under cadmium stress. Int J Mol Sci 13:6604–6619
Singh J, Kalamdhad AS (2013) Effects of lime on bioavailability and leachability of heavy metals during agitated pile composting of water hyacinth. Bioresour Technol 138:148–155
Singh KP, Mohan D, Singh VK, Malik A (2005) Studies on distribution and fractionation of heavy metals in Gomti river sediments—a tributary of the Ganges, India. J Hydrol 312:14–27
Smiri M, Elarbaoui S, Missaoui T, Ben Dekhil A (2015) Micropollutants in sewage sludge: elemental composition and heavy metals uptake by Phaseolus vulgaris and Vicia faba seedlings. Arabian J Sci Eng 40:1837–1847
Smith SR (2009) A critical review of the bioavailability and impacts of heavy metals in municipal solid waste composts compared to sewage sludge. Environ Int 35:142–156
Tessier A, Campbell PGC, Bisson M (1979) Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal Chem 51:844–851
Tytla M, Widziewicz K, Zielewicz E (2016) Heavy metals and its chemical speciation in sewage sludge at different stages of processing. Environ Technol 37:899–908
Venegas A, Rigol A, Vidal M (2016) Changes in heavy metal extractability from contaminated soils remediated with organic waste or biochar. Geoderma 279:132–140
Wang X, Ding WG, Nan ZR, Liao Q, Wu WF (2013) Fraction of Cd in oasis soil and its bioavailability to commonly grown crops in Northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 70:471–479
Yang H, Li ZJ, Lu L, Long J, Liang YC (2013) Cross-species extrapolation of prediction models for cadmium transfer from soil to corn grain. PLoS One 8:e80855
Yue Y, Yao Y, Lin QM, Li GT, Zhao XR (2016) The change of heavy metals fractions during hydrochar decomposition in soils amended with different municipal sewage sludge hydrochars. J Soils Sed
Zeng ZZ, Lei XJ, Gou JF, Gao DX, Wang HC, Nan ZR (2015) Leaching-induced migration and compositional form change of Cu, Zn, and Cd from sludge to loess. Toxicol Environ Chem 97:439–453
Zhou SQ, Lu WD, Zhou X (2010) Effects of heavy metals on planting watercress in kailyard soil amended by adding compost of sewage sludge. Process Saf Environ Prot 88:263–268
Zhu B, Alva AK (1993) Differential adsorption of trace metals by soils as influenced by exchangeable cations and ionic strength. Soil Sci 155:61–66
Acknowledgements
This work was jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51178209, 41501337) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (lzujbky-2015-214, nwunjbky-31920150069). We also thank the graduate students Wenfei Wu, Jian Zhou, Xiaolin Li, and Xun Yao at Lanzhou University for preparing the pot experiments. The constructive criticisms provided by anonymous referees are greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Jean Paul Schwitzguébel
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 22 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, C., Nan, Z., Wang, H. et al. Plant growth and heavy metal bioavailability changes in a loess subsoil amended with municipal sludge compost. J Soils Sediments 17, 2797–2809 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-017-1698-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-017-1698-0