Abstract
Purpose
Fe-Mn nodules are the common feature of tropical and subtropical soils and contain abundant information of pedogenic processes, palaeoenvironmental changes, and element geochemistry. The main aim of the present study was to determine the internal structure and spatial distribution of elements in the Fe-Mn nodules to better understand the 3D internal structure, enrichment, and dynamics of heavy metals in nodules and to provide more aspects to explore the possible heavy metal sequestration and pedoenvironmental implications of Fe-Mn nodules in soils.
Materials and methods
The studied Typic Plinthudult was developed on Quaternary red earths in Èastern China. The Fe-Mn nodules in the Bs horizon of soil were separated and classified into four size fractions (5–8, 3–5, 2–3, and 1–2 mm). The 3D microstructure of Fe-Mn nodules was examined by means of synchrotron radiation-based X-ray microcomputed tomography (SR-mCT), and the spatial distribution of Fe and Mn in nodules was studied by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) equipped with an energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer (EDS). The association of heavy metals with Fe and Mn oxides in nodules was described by selective chemical dissolution, SEM/EDS, and principal component analysis.
Results and discussion
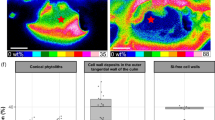
The SR-mCT images indicated that the 5–8, 3–5, and 2–3 mm nodules exhibited well-defined ring structures, while the 1–2 mm nodule exhibited homogeneous fabric. The internal microstructures of nodules could be divided into four parts: Fe-rich ring, Mn-rich ring, Fe and Mn overlapped ring, and the gap between ring structures. The Fe-Mn nodules were significantly enriched in Mn, Pb, Ni, Cu, and Zn relative to the soil matrix. In particular, the concentrations of Mn and Pb in the nodules were 150 and 90 times greater than those in the soil matrix, respectively. A clear partitioning of heavy metals between Mn and Fe oxide phases was observed in the nodules, indicating that Pb was mainly present in Fe oxides, while Ni, Cu, and Zn were mainly associated with Mn oxide phases.
Conclusions
The SR-mCT and SEM-EDS revealed the detailed internal microstructure of the Fe-Mn nodules and geochemical dynamics of heavy metals in the soil system. The Fe-Mn nodules have very high scavenging ability in sequestrating toxic heavy metals in soils, such as Pb and Ni. The microstructure and spatial distribution of Fe and Mn in nodules reflected the cycle of alternating drying and wetting conditions and served as an important basis for inferring the pedogenic processes and pedoenvironmental conditions.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aide M (2005) Elemental composition of soil nodules from two alfisols on an alluvial terrace in Missouri. Soil Sci 170:1022–1033
Arocena JM, Pawluk S (1991) The nature and origin of nodules in podzolic soils from Alberta. Can J Soil Sci 71:411–426
Bao S (2004) Soil and agricultural analysis. China Agricultural Press, Beijing
Childs CW, Leslie DM (1977) Interelement relationships in iron-manganese concretions from a catenary sequence of yellow-grey earth soils in loess. Soil Sci 123:369–376
Cornu S, Deschatrettes V, Salvador-Blanes S, Clozel B, Hardy M, Branchut S, Forestier L (2005) Trace element accumulation in Mn-Fe-oxide nodules of a planosolic horizon. Geoderma 125:11–24
Dawson BSW, Fergusson JE, Campbell AS, Cutler EJB (1985) Distribution of elements in some Fe-Mn nodules and an iron-pan in gley soils of New Zealand. Geoderma 35:127–143
Dixon JB, White GN (2002) Manganese oxides. In: Dixon JB, Schulze DG (eds) Soil mineralogy with environmental applications, vol 7, SSSA Book Ser. SSSA, Madison, pp 367–388
Gasparatos D (2012) Fe-Mn concretions and nodules to sequester heavy metals in soils. In: Lichtfouse E (eds) Environmental Chemistry for a Sustainable World, Vol 2: Remediation of Air and Water Pollution. Springer Science + Business Media B.V., pp 443–474
Gasparatos D (2013) Sequestration of heavy metals from soil with Fe-Mn concretions and nodules. Environ Chem Lett 11:1–9
Gasparatos D, Tarenidis D, Haidouti C, Oikonomou G (2005) Microscopic structure of soil Fe-Mn nodules: environmental implication. Environ Chem Lett 2:175–178
Hu XF, Wei J, Xu LF, Zhang GL, Zhang WG (2009) Magnetic susceptibility of the Quaternary red clay in subtropical China and its paleoenvironmental implications. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 279:216–232
Latrille C, Elsass F, van Oort F, Denaix L (2001) Physical speciation of trace metals in Fe-Mn concretions from a rendzic lithosol developed on Sinemurian limestones (France). Geoderma 100:127–146
Lindbo DL, Rhoton FE, Hudnall WH, Smeck NE, Bigham JM, Tyler DD (2000) Fragipan degradation and nodule formation in Glossic Fragiudalfs of the Lower Mississippi River Valley. Soil Sci Soc Am J 64:1713–1722
Liu F, Colombo C, Adamo P, He JZ, Violante A (2002) Trace elements in manganese-iron nodules from a Chinese Alfisol. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66:661–670
Liu C, Deng CL, Liu QS (2012) Mineral magnetic studies of the vermiculated red soils in southeast China and their paleoclimatic significance. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 329–330:173–183
Löhr SC, Grigorescu M, Cox ME (2013) Iron nodules in ferric soils of the Fraser Coast, Australia: relicts of laterisation or features of contemporary weathering and pedogenesis? Soil Res 51:77–93
Manceau A, Tamura N, Celestre RS, Macdowell AA, Geoffroy N, Sposito G, Padmore HA (2003) Molecular-scale speciation of Zn and Ni in soil ferromanganese nodules from loess soils of the Mississippi basin. Environ Sci Technol 37:75–80
Mehra OP, Jackson ML (1960) Iron oxide removal from soils and clays by dithionite-citrate system buffered with sodium bicarbonate. Clays Clay Miner 7:317–327
Neaman A, Waller B, Mouele F, Trolard F, Bourrie G (2004) Improved methods for selective dissolution of manganese oxides from soils and rocks. Eur J Soil Sci 55:47–54
Neaman A, Martinez CE, Trolard F, Bourrie G (2008) Trace element associations with Fe- and Mn-oxides in soil nodules: comparison of selective dissolution with electron probe microanalysis. Appl Geochem 23:778–782
Palumbo B, Bellanca A, Neri R, Roe MJ (2001) Trace metal partitioning in Fe-Mn nodules from Sicilian soils, Italy. Chem Geol 173:257–269
Rhoton FE, Bigham JM, Schulze DG (1993) Properties of iron-manganese nodules from a sequence of eroded fragipan soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 57:1386–1392
Sanz A, Garcia-Gonzalez MT, Vizcayno C, Rodriguez R (1996) Iron-manganese nodules in a semi-arid environment. Aust J Soil Res 34:623–634
Stiles CA, More CI, Driese SG (2001) Pedogenic iron-manganese nodules in Vertisols: a new proxy for paleoprecipitation? Geology 29:943–946
Szymański W, Skiba M (2013) Distribution, morphology, and chemical composition of Fe-Mn nodules in Albeluvisols of the Carpathian Foothills, Poland. Pedosphere 23:445–454
Szymański W, Skiba M, Błachowski A (2014) Mineralogy of Fe-Mn nodules in Albeluvisols in the Carpathian Foothills, Poland. Geoderma 217–218:102–110
Tan WF, Liu F, Li YH, Hu HQ, Huang QY (2006) Eelemental composition and geochemical characteristics of iron-manganese nodules in main soils of china. Pedosphere 16:72–81
Tripathi JK, Rajamani V (2007) Geochemistry and origin of ferruginous nodules in weathered granodioritic gneisses, Mysore Plateau, Southern India. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 71:1674–1688
Trolard F, Bourrié G, Jeanroy E, Herbillon A, Martin H (1995) Trace metals in natural iron oxides from laterites: a study using selective kinetic extraction. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59:1285–1297
Uzochukwu GA, Dixon JB (1986) Manganese oxides minerals in nodules of two soils of Texas and Alabama. Soil Sci Soc Am J 50:1358–1363
Wang SY, Lin S, Lu SG (2013) Rock magnetism, iron oxide mineralogy and geochemistry of Quaternary red earth in central China and their paleopedogenic implication. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 379–380:95–103
White GN, Dixon JB (1996) Iron and manganese distribution in nodules from a young Texas Vertisol. Soil Sci Soc Am J 60:1254–1262
Zhang M, Karathanasis AD (1997) Characterization of iron-manganese concretions in Kentucky Alfisols with perched water table. Clays Clay Min 45:428–439
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41171182) and the Ph.D. Program Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (20130101110130). We also thank all the staff of beamline BL13W1 in Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (SSRF) for support for CT data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Richard K. Shaw
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, X., Lu, S. Micrometer-scale internal structure and element distribution of Fe-Mn nodules in Quaternary red earth of Eastern China. J Soils Sediments 16, 621–633 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1212-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1212-5