Abstract
Purpose
The herbicide diuron has the unfortunate property of being strongly adsorbed onto soil organic matter particles, and hence, is slowly degraded in the environment because of its reduced bioavailability. The aim of this work was to gain insight into the fate and behaviour of diuron in the soil–water system, and develop and test an environmentally friendly soil decontamination technique that could give rise to an enhancement of diuron mineralisation by sensitive soil endogenous microorganisms, by means of increasing the bioavailability of the pollutant employing cyclodextrin (CD) solutions what would represent an improvement from both economic and environmental standpoints.
Materials and methods
Selected soil colloidal components: montmorillonite, a synthetic humic acid and a synthetic acicular goethite, and two different soils were employed in this study to perform batch adsorption–desorption experiments. Desorption experiments were performed using a 0.01 M Ca(NO3)2 solution with and without hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPBCD) 50 mM. Assays to study the mineralisation of 14C-labelled diuron were performed in respirometers, into which 10 g of soil and 50 mL of mineral salts medium (MMK) were placed, obtaining a final concentration of 50 mg kg−1 and a radioactivity of approximately 900 Bq per flask.
Results and discussion
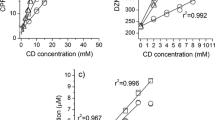
Humic acid could be clearly discerned as the major colloidal component responsible for adsorption. HPBCD was used in diuron desorption experiments from soil, showing a strong extracting power on its removal. The mineralisation of diuron in the presence and absence of HPBCD was tested in a soil managed with diuron for several years, involving therefore the presence of microorganisms that have some specificity for diuron. Natural soil attenuation for diuron was improved when a HPBCD solution was used in the presence of micronutrients as a bioavailability enhancer, obtaining 66 % of mineralisation in comparison to that obtained with only micronutrients addition (44 %).
Conclusions
The use of HPBCD solution at a very low concentration of only 10 times the diuron equimolar concentration in soil, acts as a bioavailability enhancer, accelerating the passage of the diuron-desorbing fraction from the soil particle surface to the soil solution, and hence, improving the accessibility of the microorganisms to the herbicide. Diuron mineralisation rate and the extent of its mineralisation were improved when the HPBCD solution was employed in the presence of micronutrients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander M (1999) Biodegradation and bioremediation, second edition. Academic Press
Allan IJ, Semple KT, Hare R, Reid BJ (2007) Cyclodextrin enhanced biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and phenols in contaminated soil slurries. Environ Sci Technol 41:5498–5504
Badr T, Brauer KH (2004) Enhanced solubilization and removal of naphthalene and phenanthrene by cyclodextrins from two contaminated soils. J Hazard Mater 215–223
Brinch UC, Ekelund F, Jacobsen CS (2002) Method for spiking soil samples with organic compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1808–1816
Cai BC, Gao SX, Lu GF (2006) Beta-cyclodextrin and its derivatives-enhanced solubility and biodegradation of 2-nitrobiphenyl. J Environ Sci 18:1157–1160
Delille D, Coulon F (2008) Comparative mesocosm study of biostimulation efficiency in two different oil-amended sub-antarctic soils. Microb Ecol 243–252
El Sebai T, Devers M, Lagacherie B, Rouard N, Soulasa G, Martin-Laurenta F (2009) Diuron mineralisation in a Mediterranean vineyard soil: impact of moisture content and temperature. Pest Manag Sci 66:988–995
Fava F, Di Gioia D, Marchetti L (1998) Cyclodextrin effects on the ex-situ bioremediation of a chronically polychlorobiphenyl-contaminated soil. Biotechnol Bioeng 58:345–355
Fenlon KA, Andreou K, Jones KC, Semple KT (2011) The extractability and mineralisation of cypermethrin aged in four UK soils. Chemosphere 82:187–192
Fenyvesi E, Gruiz K, Verstichel S, De Wilde B, Leitgib L, Csabai K, Szaniszlo N (2005) Biodegradation of cyclodextrins in soil. Chemosphere 60:1001–1008
Ginés JM, Pérez-Martínez JI, Arias MJ, Moyano JR, Morillo E, Ruiz-Conde A, Sánchez-Soto PJ (1996) Inclusion of the herbicide 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) with beta-cyclodextrin by different processing methods. Chemosphere 33:321–334
Gould S, Scott R (2005) 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HP-β-CD): a toxicology review. J Food Chem Toxicol 43:1451–1459
Guerin WF, Boyd SA (1992) Differential Bioavailability of soil- sorbed Naphthalene to two bacterial species. Am Soc Microbiol 58:1142–1152
Inoue MH, Olivera RS Jr, Constantin J, Alonso DG, Tormena CA (2009) Bioavailability of diuron, amazapic and isoxaflutole in soils of contrasting textures. J Environ Sci Health Part B 44:757–763
Jacobsen CS, Shapir N, Jensen LO, Jensen EH, Juhler RK, Streibig JC, Mandelbaum RT, Helweg A (2001) Bioavailability of triazine herbicides in a sandy soil profile. Biol Fer Soil 33:501–506
Kadian N, Malik A, Satya S, Dureja P (2012) Effect of organic amendments on microbial activity in chlorpyrifos contaminated soil. J Environ Manag 199–202
Kasozi GN, Nkedi-Kizza P, Agyin-Birikorang S, Zimmerman AR (2010) Characterization of adsorption and degradation of diuron in carbonatic and noncarbonatic soils. J Agric Food Chem 58:1055–1061
Katagi T (2008) Surfactant effects on environmental behaviour of pesticides. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 71–158
Mahedero MC, Muñoz De La Peña A, Bautista A, Aaron JJ (2002) An investigation of inclusion complexes of cyclodextrins with phenylurea herbicides by photochemically-induced fluorescence. Analytical applications. J Incl Phenom Macro Chem 42:61–70
Megharaj M, Ramakrishnan B, Venkateswarlu K, Sethunathan N, Naidu R (2011) Bioremediation approaches for organic pollutants: A critical perspective. Environ Inter 37:1362–1375
Morillo E, Pérez-Martínez JI, Ginés JM (2001) Leaching of 2,4-D from a soil in the presence of β-cyclodextrin: Laboratory columns experiments. Chemosphere 44:1065–1069
Morillo E, Maqueda C, Reinoso R, Undabeytia T (2002) Effect of two organic amendments on norflurazon retention and release by soils of different characteristics. Environ Sci Technol 36:4319–4325
Morillo E, Undabeytia T, Cabrera A, Villaverde J, Maqueda C (2004) Effect of soil type on adsorption-desorption, mobility, and activity of the herbicide Norflurazon. J Agric Food Chem 52:884–890
Morillo E, Sánchez-Trujillo MA, Moyano JR, Villaverde J, Gómez-Pantoja ME, Pérez-Martínez JI (2012) Enhanced solubilisation of six PAHs by three synthetic cyclodextrins for remediation applications. Molecular modelling of the inclusion complexes. PLoS ONE 7(9):e44137. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0044137
Pérez-Martínez JI, Ginés JM, Morillo E, González-Rodríguez ML, Moyano-Méndez JR (2000) Improvement of the desorption of the pesticide 2,4-D via complexation with HP-β-cyclodextrin. Pest Manag Sci 56:425–430
Posada-Baquero R, Niqui-Arroyo JL, Bueno-Montes M, Gutiérrez-Dabán A, Ortega-Calvo JJ (2008) Dual 14C/residue análisis method to assess the microbial accessibility of native phenanthrene in environmental simples. Environ Geochem Health 30:159–163
Qureshi A, Mohan M, Kanade GS, Kapley A, Purohit HJ (2008) In situ bioremediation of organochlorine-pesticide-contaminated microcosm soil and evaluation by gene probe. Pest Manag Sci 65:798–804
Reid B, Northcot TG, Jones KC, Semple K (1998) Evaluation of spiking procedures for the introduction of poorly water soluble contaminants into soil. Environ Sci Tecnol 32:3224–3227
Ross JA, Tweedy BG (1973) Degradation of four phenylurea herbicides by mixed populations from two soil types. Soil Biol Biochem 5:739–746
Rouchaud J, Neus O, Bulcke R, Cools K, Eelen H, Dekkers T (2000) Soil dissipation of diuron, chlorotoluron, simazine, propyzamide, and diflufenican herbicides after repeated applications in fruit tree orchards. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:60–65
Semple K, Doick KJ, Wick LY, Harms H (2007) Microbial interactions with organic contaminants in soil: definitions, processes and measurement. Environ Pollut 150:166–176
Shchegolikhina A, Schulz S (2012) Bernd Marschner Interacting effects of cation saturation and drying, freezing, or aging on the extractability of nonylphenol and phenanthrene from a sandy soil. J Soils Sediments 12:1280–1291
Sheng G, Johnston CT, Teppen BJ, Boyd SA (2011) Potential contributions of smectite clays and organic matter to pesticide retention in soils. J Agric Food Chem 49:2899–2907
Shin K-H, Kima K-W, Ahn Y (2006) Use of biosurfactant to remediate phenanthrene-contaminated soil by the combined solubilization–biodegradation process. J Hazard Mat 15:1831–1837
Song Y, Wang F, Yang X, Liu C, Kengara FO, Jin X, Jiang X (2011) Chemical extraction to assess the bioavailability of chlorobenzenes in soil with different aging periods. J Soils Sediments 11:1345–1354
Sorensen SR, Bending GD, Jacobsen CS, Walker A, Aamand J (2003) Microbial degradation of isoproturon and related phenylurea herbicides in and below agricultural fields. Microbiol Eco 45:1–11
Szejtli J (1992) The properties and potential uses of cyclodextrin derivates. J Incl Phenom Mol Recog Chem 14:25–36
Tomlin (2000) The pesticide manual. Twelfth Edition. British crop protection council
Undabeytia T, Sánchez-Verdejo T, Morillo E, Maqueda C (2004) Effect of organic anmendments on the retention and mobility of imazaquin in soils. J Agric Food Chem 52:4493–4500
Undabeytia T, Recio E, Maqueda C, Sánchez-Verdejo T, Balek V (2011) Slow diuron release formulations based on clay-phosphatidylcholine complexes. App Clay Sci 55:53–61
Villaverde J, Kah M, Brown CD (2003) Adsorption and degradation of four acidic herbicides in soils from southern. J Environ Qual 39:171–179
Villaverde J, Morillo E, Pérez-Martínez JI, Ginés JM, Maqueda C (2004) Preparation and characterization of inclusion complex of Norflurazon and β-cyclodextrin to improve herbicide formulations. J Agric Food Chem 52:864–869
Villaverde J, Pérez-Martínez JI, Maqueda C, Ginés JM, Morillo E (2005a) Inclusion complexes of α- and γ-cyclodextrins and the herbicide norflurazon: I. Preparation and characterisation. II. Enhanced solubilisation and removal from soils. Chemosphere 60:656–664
Villaverde J, Maqueda C, Morillo E (2005b) Improvement of the desorption of the herbicide norflurazon from soils via complexation with beta-cyclodextrin. J Agric Food Chem 53:5366–5372
Villaverde J, Maqueda C, Morillo E (2006) Effect of the simultaneous addition of β-cyclodextrin and the herbicide norflurazon on its adsorption and movement in soils. J Agric Food Chem 54:4766–4772
Villaverde J, Maqueda C, Undabeytia T, Morillo E (2007) Effect of various cyclodextrins on photodegradation of a hydrophobic herbicide in aqueous suspensions of different soil colloidal components. Chemosphere 69:575–584
Villaverde J, Posada-Baquero R, Rubio-Bellido M, Laiz L, Saiz-Jimenez C, Sanchez-Trujillo MA, Morillo E (2012) Enhanced mineralization of diuron using a cyclodextrin-based bioremediation technology. J Agric Food Chem 60:9941–9947
Wacker Chemie (2103) Cawasol W7 HP Material Safety data Sheet, http://www.wacker.com/cms/en/productsmarkets/products/product.jsp?product=8971
Wang PA, Keller A (2009) Sorption and desorption of atrazine and diuron onto water dispersible soil primary size fractions. Wat Res 43:1448–1456
Wang JM, Marlowe EM, Miller-Maier RM, Brusseau ML (1998) Cyclodextrin-enhanced biodegradation of phenanthrene. Environ Sci Technol 32:1907–1912
Wang JM, Maier RM, Brusseau ML (2005) Influence of hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin (HPCD) on the bioavailability and biodegradation of pyrene. Chemosphere 60:725–728
White JC, Alexander M, Pignatello JJ (1999) Enhancing the bioavailability of organic compounds sequestered in soil and aquifer solids. Environ Toxicol Chem 18:182–187
Acknowledgments
Marina Rubio thanks the Spanish Research Council (CSIC) for her Predoctoral Research grant (JAE-Pre). We are indebted to Presmar S.L. for providing the technical diuron. This work was supported by Spanish Ministry of Science Innovation (co-funded by Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional, FEDER), CTM2006-04626 and CTM2009-07335.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Jay Gan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Villaverde, J., Posada-Baquero, R., Rubio-Bellido, M. et al. Effect of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin on diuron desorption and mineralisation in soils. J Soils Sediments 13, 1075–1083 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-013-0677-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-013-0677-3