Abstract
Purpose
Herein is reported an application of life cycle analysis (LCA), using the Methodology for the Ecodesign of Energy Using Products (MEEUP), in order to assess the influence of some design parameters in the environmental impact of three-phase induction motors. A motor design procedure to minimize the total environmental impact, based on data obtained from commercial motors, is presented. This procedure is specially intended for the low power range due to the greater potential for energy savings in motors having an output power of 0.75 to 4 kW.
Methods
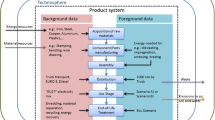
A procedure has been developed, based on previously acquired data, to determine the parameters required for application of the MEEUP methodology. These comprise the quantity of each of the motor's main constituent materials used in the production phase, and the two operating variables that directly influence the LCA results: output power and efficiency.
Results and discussion
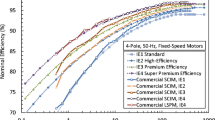
The procedure was applied to two 1.5 kW induction motors of different efficiency (according to standard IEC60034-2-1). The calculation results were compared satisfactorily with the laboratory test results. The total environmental impact of the two real motors and of the proposed motor was determined in the production, service life, and end-of-life phases.
Conclusions
Given the potential for energy savings in electric motors, LCA-based environmental impact assessment should be incorporated into motor design.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
ABB Environmental product declaration (2005) 1MRK590 011-BEN, Issued December 2005
Andrada P, Blanqué B, Martínez E, Perat JI, Sánchez JA, Torrent M (2009) comparison of environmental and life cycle impact of a switched reluctance motor drive and inverter-fed induction motor drives. International Conference on Renewable Energies and Power Quality, ICREPQ'09. Valencia (Spain), 15–17 April 2009
Boldea I, Nasar S (2002) The Induction Machine Handbook. CRC Press LLC, New York
Croezen HJ, Bello OSF (2003) Environmental profiles of motors and transformers. Delft, March 2003
De Almeida AT, Ferreira FJTE, Fong JAC, Fonseca P (2008) EUP Lot 11 Motors: Final
De Almeida AT, Ferreira FJTE, Fong JAC (2011) Standards for efficiency of electric motors. IEEE Ind Appl Mag 17(1):12–19
De Keulenaer H, Herrmann C, Parasiliti F (2006) Eco-sheet: 22 kW induction motors with increasing efficiency. May 2006. www.leonardo-energy.org
Deprez W, Pardon L, De Keulenaer H, Herrmann C, Driesen J (2006) Ecodesign toolbox for electrical equipment. 13th CIRP International Conference on Life Cycle Engineering. Leuven (Belgium)
European Directive (2005) European Directive 2005/32/CE on the eco-design of Energy-using Products
European Directive (2009) European Directive 2009/125/EC establishing a framework for the setting of ecodesign requirements for energy-related products
European Commission (2009)Regulation 640/2009 implementing Directive 2005/32/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council with regard to ecodesign requirements for electric motors
Hamdi ES (1994) Design of small electrical machines. John Wiley & Sons
IEC 60034-2-1 (2007) Rotating electrical machines. Part 2–1: standard methods for determining losses and efficiency from tests
IEC 60034–30 (2007) Rotating electrical machines - Part 30: efficiency classes of single-speed three-phase cage induction motors
Jardot D, Eichhammer W, Fleiter T (2010) Effects of economies of scale and experience on the costs of energy-efficient technologies—case study of electric motors in Germany. Energy Efficiency 3:331–346
Martínez E, Sanz F, Pellegrini S, Jiménez E, Blanco J (2009) Life-cycle assessment of a 2-MW rated power wind turbine: CML method. Int J Life Cycle Assess 14:52–63
MEEUP Methodology Report, final (2005) VHK for European Commission
Pyrhönen J, Jokinen T, Hrabovcová V (2008) Design of rotating electrical machines. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zbigniew Stanislaw Klos
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Torrent, M., Martínez, E. & Andrada, P. Life cycle analysis on the design of induction motors. Int J Life Cycle Assess 17, 1–8 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-011-0332-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-011-0332-4