Abstract
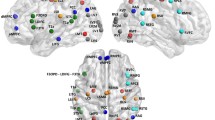
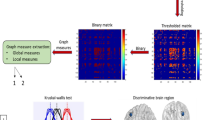
Moving from the hypothesis that aging processes modulate brain connectivity networks, 170 healthy elderly volunteers were submitted to EEG recordings in order to define age-related normative limits. Graph theory functions were applied to exact low-resolution electromagnetic tomography on cortical sources in order to evaluate the small-world parameter as a representative model of network architecture. The analyses were carried out in the whole brain—as well as for the left and the right hemispheres separately—and in three specific resting state subnetworks defined as follows: attentional network (AN), frontal network (FN), and default mode network (DMN) in the EEG frequency bands (delta, theta, alpha 1, alpha 2, beta 1, beta 2, gamma). To evaluate the stability of the investigated parameters, a subgroup of 32 subjects underwent three separate EEG recording sessions in identical environmental conditions after a few days interval. Results showed that the whole right/left hemispheric evaluation did not present side differences, but when individual subnetworks were considered, AN and DMN presented in general higher SW in low (delta and/or theta) and high (gamma) frequency bands in the left hemisphere, while for FN, the alpha 1 band was lower in the left with respect to the right hemisphere. It was also evident the test-retest reliability and reproducibility of the present methodology when carried out in clinically stable subjects.
Evidences from the present study suggest that graph theory represents a reliable method to address brain connectivity patterns from EEG data and is particularly suitable to study the physiological impact of aging on brain functional connectivity networks.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen EA, Erhardt EB, Damaraju E, Gruner W, Segall JM, Silva RF, et al. A baseline for the multivariate comparison of resting-state networks. Front Syst Neurosci. 2011;5:2.
Allen JJB, Keune PM, Schönenberg M and Nusslock R, 2018, Frontal EEG alpha asymmetry and emotion: from neural underpinnings and methodological considerations to psychopathology and social cognition. Psychophysiology, 55.
Antonenko D, Meinzer M, Lindenberg R, Witte AV, Flöel A. Grammar learning in older adults is linked to white matter microstructure and functional connectivity. Neuroimage. 2012;62:1667–74.
Antonenko D, Brauer J, Meinzer M, Fengler A, Kerti L, Friederici AD, et al. Functional and structural syntax networks in aging. Neuroimage. 2013;83:513–23.
Bartolomei F, Bosma I, Klein M, Baayen JC, Reijneveld JC, Postma TJ, et al. Disturbed functional connectivity in brain tumour patients: evaluation by graph analysis of synchronization matrices. Clin Neurophysiol. 2006;117:2039–49.
Bassett DS, Bullmore E. Small-world brain networks. Neuroscientist. 2006;12:512–23.
Bassett DS, Meyer-Lindenberg A, Achard S, Duke T, Bullmore E. Adaptive reconfiguration of fractal small-world human brain functional networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:19518–23.
Bazanova OM, Vernon D. Interpreting EEG alpha activity. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2014;44:94–110.
Bell AJ, Sejnowski TJ. An information-maximization approach to blind separation and blind deconvolution. Neural Comput. 1995;7:1129–59.
Buckner RL, Snyder AZ, Shannon BJ, LaRossa G, Sachs R, Fotenos AF, et al. Molecular, structural, and functional characterization of Alzheimer’s disease: evidence for a relationship between default activity, amyloid, and memory. J Neurosci. 2005;25:7709–17.
Bullmore E, Sporns O. Complex brain networks: graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009;10:186–98.
Cao C, Slobounov S. Alteration of cortical functional connectivity as a result of traumatic brain injury revealed by graph theory, ICA, and sLORETA analyses of EEG signals. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2010;18:11–9.
Coan JA, Allen JJ. Frontal EEG asymmetry and the behavioral activation and inhibition systems. Psychophysiology. 2003;40:106–14.
Ferreri F, Vecchio F, Ponzo D, Pasqualetti P, Rossini PM. Time-varying coupling of EEG oscillations predicts excitability fluctuations in the primary motor cortex as reflected by motor evoked potentials amplitude: an EEG-TMS study. Hum Brain Mapp. 2014;35:1969–80.
Gong G, He Y, Concha L, Lebel C, Gross DW, Evans AC, et al. Mapping anatomical connectivity patterns of human cerebral cortex using in vivo diffusion tensor imaging tractography. Cereb Cortex. 2009;19:524–36.
Greicius MD, Krasnow B, Reiss AL, Menon V. Functional connectivity in the resting brain: a network analysis of the default mode hypothesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:253–8.
Hoffmann S, Falkenstein M. The correction of eye blink artefacts in the EEG: a comparison of two prominent methods. PLoS One. 2008;3:e3004.
Horwitz B. The elusive concept of brain connectivity. Neuroimage. 2003;19:466–70.
Iriarte J, Urrestarazu E, Valencia M, Alegre M, Malanda A, Viteri C, et al. Independent component analysis as a tool to eliminate artifacts in EEG: a quantitative study. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2003;20:249–57.
Jung TP, Makeig S, Humphries C, Lee TW, McKeown MJ, Iragui V, et al. Removing electroencephalographic artifacts by blind source separation. Psychophysiology. 2000;37:163–78.
Keehn B, Müller RA, Townsend J. Atypical attentional networks and the emergence of autism. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2013;37:164–83.
Kubicki S, Herrmann WM, Fichte K, Freund G. Reflections on the topics: EEG frequency bands and regulation of vigilance. Pharmakopsychiatr Neuropsychopharmakol. 1979;12:237–45.
Lehmann D, Faber PL, Tei S, Pascual-Marqui RD, Milz P, Kochi K. Reduced functional connectivity between cortical sources in five meditation traditions detected with lagged coherence using EEG tomography. Neuroimage. 2012;60:1574–86.
Mazaheri A, van Schouwenburg MR, Dimitrijevic A, Denys D, Cools R, Jensen O. Region-specific modulations in oscillatory alpha activity serve to facilitate processing in the visual and auditory modalities. Neuroimage. 2014;87:356–62.
Meinzer M, Antonenko D, Lindenberg R, Hetzer S, Ulm L, Avirame K, et al. Electrical brain stimulation improves cognitive performance by modulating functional connectivity and task-specific activation. J Neurosci. 2012;32:1859–66.
Micheloyannis S, Pachou E, Stam CJ, Breakspear M, Bitsios P, Vourkas M, et al. Small-world networks and disturbed functional connectivity in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2006;87:60–6.
Miraglia F, Vecchio F, Bramanti P, Rossini PM. Small-worldness characteristics and its gender relation in specific hemispheric networks. Neuroscience. 2015;310:1–11.
Miraglia F, Vecchio F, Bramanti P, Rossini PM. EEG characteristics in “eyes-open” versus “eyes-closed” conditions: small-world network architecture in healthy aging and age-related brain degeneration. Clin Neurophysiol. 2016;127:1261–8.
Miraglia F, Vecchio F, Rossini PM. Searching for signs of aging and dementia in EEG through network analysis. Behav Brain Res. 2017;317:292–300.
Miraglia F, Vecchio F, Rossini PM. Brain electroencephalographic segregation as a biomarker of learning. Neural Netw. 2018;106:168–74.
Miraglia F, Vecchio F, Marra C, Quaranta D, Alù F, Peroni B, et al. Small world index in default mode network predicts progression from mild cognitive impairment to dementia. Int J Neural Syst. 2020;30:2050004.
Nolte G, Bai O, Wheaton L, Mari Z, Vorbach S, Hallett M. Identifying true brain interaction from EEG data using the imaginary part of coherency. Clin Neurophysiol. 2004;115:2292–307.
Ocklenburg S, Friedrich P, Schmitz J, Schlüter C, Genc E, Güntürkün O, et al. Beyond frontal alpha: investigating hemispheric asymmetries over the EEG frequency spectrum as a function of sex and handedness. Laterality. 2019;24:505–24.
Pascual-Marqui RD. Instantaneous and lagged measurements of linear and nonlinear dependence between groups of multivariate time series: frequency decomposition. eprint arXiv:07111455. 2007;arXiv:0711.1455.
Pascual-Marqui RD, Lehmann D, Koukkou M, Kochi K, Anderer P, Saletu B, et al. Assessing interactions in the brain with exact low-resolution electromagnetic tomography. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2011;369:3768–84.
Petersen SE, Posner MI. The attention system of the human brain: 20 years after. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2012;35:73–89.
Pizzagalli DA, Sherwood RJ, Henriques JB, Davidson RJ. Frontal brain asymmetry and reward responsiveness: a source-localization study. Psychol Sci. 2005;16:805–13.
Ponten SC, Bartolomei F, Stam CJ. Small-world networks and epilepsy: graph theoretical analysis of intracerebrally recorded mesial temporal lobe seizures. Clin Neurophysiol. 2007;118:918–27.
Posner MI, Petersen SE. The attention system of the human brain. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1990;13:25–42.
Raichle ME, MacLeod AM, Snyder AZ, Powers WJ, Gusnard DA, Shulman GL. A default mode of brain function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:676–82.
Rossini PM, Di Iorio R, Granata G, Miraglia F, Vecchio F. From mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease: a new perspective in the “land” of human brain reactivity and connectivity. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016;53:1389–93.
Rubinov M, Sporns O. Complex network measures of brain connectivity: uses and interpretations. Neuroimage. 2010;52:1059–69.
Salmaso D, Longoni AM. Problems in the assessment of hand preference. Cortex. 1985;21:533–49.
Smit DJ, Stam CJ, Posthuma D, Boomsma DI, de Geus EJ. Heritability of “small-world” networks in the brain: a graph theoretical analysis of resting-state EEG functional connectivity. Hum Brain Mapp. 2008;29:1368–78.
Smith EE, Cavanagh JF and Allen JJB, 2018, Intracranial source activity (eLORETA) related to scalp-level asymmetry scores and depression status. Psychophysiology, 55.
Sporns O, Zwi JD. The small world of the cerebral cortex. Neuroinformatics. 2004;2:145–62.
Stam CJ, Jones BF, Nolte G, Breakspear M, Scheltens P. Small-world networks and functional connectivity in Alzheimer’s disease. Cereb Cortex. 2007;17:92–9.
Stam CJ, Reijneveld JC. Graph theoretical analysis of complex networks in the brain. Nonlinear Biomed Phys. 2007;1:3.
Vecchio F, Miraglia F, Bramanti P, Rossini PM. Human brain networks in physiological aging: a graph theoretical analysis of cortical connectivity from EEG data. J Alzheimers Dis. 2014a;41:1239–49.
Vecchio F, Miraglia F, Marra C, Quaranta D, Vita MG, Bramanti P, et al. Human brain networks in cognitive decline: a graph theoretical analysis of cortical connectivity from EEG data. J Alzheimers Dis. 2014b;41:113–27.
Vecchio F, Miraglia F, Curcio G, Della Marca G, Vollono C, Mazzucchi E, et al. Cortical connectivity in fronto-temporal focal epilepsy from EEG analysis: a study via graph theory. Clin Neurophysiol. 2015;126:1108–16.
Vecchio F, Miraglia F, Quaranta D, Granata G, Romanello R, Marra C, et al. Cortical connectivity and memory performance in cognitive decline: a study via graph theory from EEG data. Neuroscience. 2016;316:143–50.
Vecchio F, Miraglia F, Maria Rossini P. Connectome: graph theory application in functional brain network architecture. Clin Neurophysiol Pract. 2017a;2:206–13.
Vecchio F, Miraglia F, Piludu F, Granata G, Romanello R, Caulo M, et al. “Small world” architecture in brain connectivity and hippocampal volume in Alzheimer’s disease: a study via graph theory from EEG data. Brain Imaging Behav. 2017b;11:473–85.
Vecchio F, Miraglia F, Romano A, Bramanti P, Rossini PM. Small world brain network characteristics during EEG Holter recording of a stroke event. Clin Neurophysiol. 2017c;128:1–3.
Vecchio F, Miraglia F, Iberite F, Lacidogna G, Guglielmi V, Marra C, et al. Sustainable method for Alzheimer dementia prediction in mild cognitive impairment: electroencephalographic connectivity and graph theory combined with apolipoprotein E. Ann Neurol. 2018a;84:302–14.
Vecchio F, Miraglia F, Quaranta D, Lacidogna G, Marra C, Rossini PM. Learning processes and brain connectivity in a cognitive-motor task in neurodegeneration: evidence from EEG network analysis. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018b;66:471–81.
Vecchio F, Caliandro P, Reale G, Miraglia F, Piludu F, Masi G, et al. Acute cerebellar stroke and middle cerebral artery stroke exert distinctive modifications on functional cortical connectivity: a comparative study via EEG graph theory. Clin Neurophysiol. 2019a;130:997–1007.
Vecchio F, Tomino C, Miraglia F, Iodice F, Erra C, Di Iorio R, et al. Cortical connectivity from EEG data in acute stroke: a study via graph theory as a potential biomarker for functional recovery. Int J Psychophysiol. 2019b;146:133–8.
Watts DJ, Strogatz SH. Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature. 1998;393:440–2.
Zaidel E, 2001, Brain Asymmetry. 1321-1329.
Zar JH. Biostatistical analysis. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall; 1984.
Funding
This work was partially supported by the Italian Ministry of Health for Institutional Research (Ricerca corrente) and for the project GR-2013-02358430.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Vecchio, F., Miraglia, F., Judica, E. et al. Human brain networks: a graph theoretical analysis of cortical connectivity normative database from EEG data in healthy elderly subjects. GeroScience 42, 575–584 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-020-00176-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-020-00176-2