Abstract
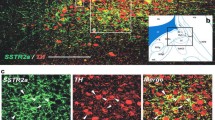
Serotonin receptor 1A and 2A positive cells in postmortem brainstems were demonstrated via immunohistochemistry in eight control age-matched elderly individuals and eight Alzheimer patients. The 5-HT1A positive cells were found in substantia nigra, pontile nucleus, and vagal as well as dorsal raphe nucleus, while 5-HT2A receptor positive cells were found in motor, sensory and spinal trigeminal nuclei, pontile nucleus, substantia nigra, and nucleus solitarius. A comparison in density of positive cells per unit area was made between control age-matched and Alzheimer individuals. Statistically significant differences (p ≤ 0.01) in density were observed in 5-HT1A cells in pontile, dorsal raphe, and vagal nuclei between control age-matched and Alzheimer, and in 5-HT2A positive cells in the sensory trigeminal nucleus, between control and Alzheimer. This de novo study indicated the presence of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A receptor positive cells in the above nuclei of human brainstem and revealed differences in density between control age-matched and Alzheimer, indicating possible functional derangements in Alzheimer patients in these areas. In addition, colocalization studies indicated that 5-HT1A receptors were in cholinergic cells and gamma-aminobutyric acid positive fibers were linked to 5-HT2A receptor positive cells. It is hoped that understanding these two important 5-HT receptors and their localization might lead to advances in future therapeutic development.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe K, Kato G, Katafuchi T, Tamae A, Furue H, Yoshimura M (2009) Responses to 5-HT in morphologically identified neurons in the rat substantia gelatinosa in vitro. Neuroscience 159:316–324
Arango V, Underwood MD, Mann JJ (2002) Serotonin brain circuits involved in major depression and suicide. Prog Brain Res 136:443–453
Banerjee P, Mehta M, Kanjilal B (2007) The 5-HT receptor: a signaling 1A hub linked to emotional balance. In: Chattopadhyay A (ed) Serotonin receptors in neurobiology. CRC, Boca Raton, pp 133–156
Bibancos T, Jardim DL, Aneas I, Chiavegatto S (2007) Social isolation and expression of serotonergic neurotransmission-related genes in several brain areas of male mice. Genes Brain Behav 6:529–539
Brodal A (1981) Neurological anatomy, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1053pp
Burnet PW, Eastwood SL, Lacey K, Harrison PJ (1995) The distribution of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A receptor mRNA in human brain. Brain Res 676:157–168
Costall B, Barnes JM, Hamon M, Müller WE, Briley M (1990) Biochemical models for cognition enhancers. Pharmacopsychiatry 23(Suppl 2):85–88
Curran AK, Leiter JC (2007) Baroreceptor-mediated inhibition of respiration after peripheral and central administration of a 5-HT1A receptor agonist in neonatal piglets. Exp Physiol 92:757–767
Delgado M, Caicoya AG, Greciano V, Benhamú B, López-Rodríguez ML, Fernández-Alfonso MS, Pozo MA, Manzanares J, Fuentes JA (2005) Anxiolytic-like effect of a serotonergic ligand with high affinity for 5-HT1A, 5-HT2A and 5-HT3 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 511:9–19
Frazer A, Hensler JG (1999) Serotonin receptors. In: Siegel GJ, Agranoff BW, Albers RW, Fisher SK, Uhler MD (eds) Basic neurochemistry: molecular, cellular, and medical aspects. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia, pp 263–292
Freitas RL, Bassi GS, de Oliveira AM, Coimbra NC (2008) Serotonergic neurotransmission in the dorsal raphe nucleus recruits in situ 5-HT(2A/2C) receptors to modulate the post-ictal antinociception. Exp Neurol 213:410–418
Hall H, Lundkvist C, Halldin C, Farde L, Pike VW, McCarron JA, Fletcher A, Cliffe IA, Barf T, Wikström H, Sedvall G (1997) Autoradiographic localization of 5-HT1A receptors in the post-mortem human brain using [3H]WAY-100635 and [11C]way-100635. Brain Res 745:96–108
Hoyer D, Clarke DE, Fozard JR, Hartig PR, Martin GR, Mylecharane EJ, Saxena PR, Humphrey PP (1994) International Union of Pharmacology classification of receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine (Serotonin). Pharmacol Rev 46:157–203
Jordan D (2005) Vagal control of the heart: central serotonergic (5-HT) mechanisms. Exp Physiol 90:175–181
Kennett GA, Dourish CT, Curzon G (1987) Antidepressant-like action of 5-HT1A agonists and conventional antidepressants in an animal model of depression. Eur J Pharmacol 134:265–274
Kroeze WK, Kristiansen K, Roth BL (2002) Molecular biology of serotonin receptors structure and function at the molecular level. Curr Top Med Chem 2:507–528
Lazarov NE (2002) Comparative analysis of the chemical neuroanatomy of the mammalian trigeminal ganglion and mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus. Prog Neurobiol 66:19–59
Li WP, Chan WY, Lai HW, Yew DT (1997) Terminal dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) positive cells in the different regions of the brain in normal aging and Alzheimer patients. J Mol Neurosci 8:75–82
Li Q, Lu G, Antonio GE, Mak YT, Rudd JA, Fan M, Yew DT (2007) The usefulness of the spontaneously hypertensive rat to model attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) may be explained by the differential expression of dopamine-related genes in the brain. Neurochem Int 50:848–857
Lira A, Zhou M, Castanon N, Ansorge MS, Gordon JA, Francis JH, Bradley-Moore M, Lira J, Underwood MD, Arango V, Kung HF, Hofer MA, Hen R, Gingrich JA (2003) Altered depression-related behaviors and functional changes in the dorsal raphe nucleus of serotonin transporter-deficient mice. Biol Psychiatry 54:960–971
Liu Q, Wong-Riley MT (2010) Postnatal changes in the expressions of serotonin 1A, 1B, and 2A receptors in ten brain stem nuclei of the rat: implication for a sensitive period. Neuroscience 165:61–78
Lorke DE, Kwong WH, Chan WY, Yew DT (2003) Development of catecholaminergic neurons in the human medulla oblongata. Life Sci 73(10):1315–1331
Lorke DE, Lu G, Cho E, Yew DT (2006) Serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT6 receptors in the prefrontal cortex of Alzheimer and normal aging patients. BMC Neurosci 7:36
Lundberg J, Borg J, Halldin C, Farde L (2007) A PET study on regional coexpression of 5-HT1A receptors and 5-HTT in the human brain. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 195:425–433
Meyer LC, Fuller A, Mitchell D (2006) Zacopride and 8-OH-DPAT reverse opioid-induced respiratory depression and hypoxia but not catatonic immobilization in goats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 290:R405–R413
Müller CP, Carey RJ, Huston JP, De Souza Silva MA (2007) Serotonin and psychostimulant addiction: focus on 5-HT1A-receptors. Prog Neurobiol 81:133–178
Nalivaiko E, Ootsuka Y, Blessing WW (2005) Activation of 5-HT1A receptors in the medullary raphe reduces cardiovascular changes elicited by acute psychological and inflammatory stresses in rabbits. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 289:R596–R604
Ogren SO, Eriksson TM, Elvander-Tottie E, D'Addario C, Ekström JC, Svenningsson P, Meister B, Kehr J, Stiedl O (2008) The role of 5-HT(1A) receptors in learning and memory. Behav Brain Res 195:54–77
Ozawa Y, Okado N (2002) Alteration of serotonergic receptors in the brain stems of human patients with respiratory disorders. Neuropediatrics 33:142–149
Popa D, Léna C, Fabre V, Prenat C, Gingrich J, Escourrou P, Hamon M, Adrien J (2005) Contribution of 5-HT2 receptor subtypes to sleep-wakefulness and respiratory control, and functional adaptations in knock-out mice lacking 5-HT2A receptors. J Neurosci 25:11231–11238
Ramanathan S, Glatt SJ (2009) Serotonergic system genes in psychosis of Alzheimer dementia: meta-analysis. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 17:839–846
Raote I, Bhattacharya A, Panicker MM (2007) Serotonin 2A (5-HT2A) receptor function: ligand-dependent mechanisms and pathways. In: Chattopadhyay A (ed) Serotonin receptors in neurobiology. CRC, Boca Raton, pp 105–132
Raul L (2003) Serotonin2 receptors in the nucleus tractus solitarius: characterization and role in the baroreceptor reflex arc. Cell Mol Neurobiol 23:709–726
Rocchi A, Micheli D, Ceravolo R, Manca ML, Tognoni G, Siciliano G, Murri L (2003) Serotoninergic polymorphisms (5-HTTLPR and 5-HT2A): association studies with psychosis in Alzheimer disease. Genet Test 7:309–314
Salmon E (2007) A review of the literature on neuroimaging of serotoninergic function in Alzheimer's disease and related disorders. J Neural Transm 114:1179–1185
Sawaguchi T, Ozawa Y, Patricia F, Kadhim H, Groswasser J, Sottiaux M, Takashima S, Nishida H, Kahn A (2003) Serotonergic receptors in the midbrain correlated with physiological data on sleep apnea in SIDS victims. Early Hum Dev 75(Suppl):S65–S74
Saxena PR (1995) Serotonin receptors: subtypes, functional responses and therapeutic relevance. Pharmacol Ther 66:339–368
Schreiber R, Melon C, De Vry J (1998) The role of 5-HT receptor subtypes in the anxiolytic effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in the rat ultrasonic vocalization test. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 135:383–391
Shelton RC, Sanders-Bush E, Manier DH, Lewis DA (2009) Elevated 5-HT 2A receptors in postmortem prefrontal cortex in major depression is associated with reduced activity of protein kinase A. Neuroscience 158:1406–1415
Shen WZ, Luo ZB, Zheng DR, Yew DT (1989) Immunohistochemical studies on the development of 5-HT (serotonin) neurons in the nuclei of the reticular formations of human fetuses. Pediatr Neurosci 15:291–295
Sumiyoshi T, Bubenikova-Valesova V, Horacek J, Bert B (2008) Serotonin1A receptors in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia: development of novel cognition-enhancing therapeutics. Adv Ther 25:1037–1056
Tiu SC, Li WY, Luo CB, Yew DT (1993) Habenulo-interpeduncular descending pathways and their relationship to enkephalin- and somatostatin-immunoreactive neurons in the interpeduncular nucleus of human fetuses. Neuroscience 53:489–493
Ulak G, Mutlu O, Tanyeri P, Komsuoglu FI, Akar FY, Erden BF (2010) Involvement of serotonin receptor subtypes in the antidepressant-like effect of trim in the rat forced swimming test. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 95:308–314
Wai SM, Kindler PM, Lam ET, Zhang A, Yew DT (2004) Distribution of neuropeptide Y-immunoreactive neurons in the human brainstem, cerebellum, and cortex during development. Cell Mol Neurobiol 24:667–684
Wai MS, Shi C, Kwong WH, Zhang L, Lam WP, Yew DT (2008) Development of the human insular cortex: differentiation, proliferation, cell death, and appearance of 5HT-2A receptors. Histochem Cell Biol 130:1199–1204
Wesołowska A (2002) In the search for selective ligands of 5-HT5, 5-HT6 and 5-HT7 serotonin receptors. Pol J Pharmacol 54:327–341
Yan Z (2002) Regulation of GABAergic inhibition by serotonin signaling in prefrontal cortex: molecular mechanisms and functional implications. Mol Neurobiol 26:203–216
Yew DT, Chan WY (1999) Early appearance of acetylcholinergic, serotoninergic, and peptidergic neurons and fibers in the developing human central nervous system. Microsc Res Tech 45:389–400
Yew DT, Luo CB, Zheng DR, Guan YL, Lin YQ, Chen WZ (1990) Development and localization of enkephalin and substance P in the nucleus of tractus solitarius in the medulla oblongata of human fetuses. Neuroscience 34:491–498
Yew DT, Pang KM, Mok YC (1991) Immunohistochemical and ultrastructural studies of the various nuclei of the trigeminal complex in the human newborn. Neuroscience 45:23–35
Yew DT, Luo CB, Shen WZ (1992) Immunohistochemical localization of enkephalin and substance P in the nucleus caudalis of the spinal trigeminal V in the medulla oblongata of the human fetus. Neuroscience 51:185–190
Yew DT, Webb SE, Lam ET (1996) Neurotransmitters and peptides in the developing human facial nucleus. Neurosci Lett 206:65–68
Yew DT, Li WP, Webb SE, Lai HW, Zhang L (1999a) Neurotransmitters, peptides, and neural cell adhesion molecules in the cortices of normal elderly humans and Alzheimer patients: a comparison. Exp Gerontol 34:117–133
Yew DT, Wong HW, Li WP, Lai HW, Yu WH (1999b) Nitric oxide synthase neurons in different areas of normal aged and Alzheimer's brains. Neuroscience 89:675–686
Yew DT, Chan WY, Luo CB, Zheng DR, Yu MC (1999c) Neurotransmitters and neuropeptides in the developing human central nervous system. A review. Biol Signals Recept 8:149–159
Yuen EY, Jiang Q, Chen P, Feng J, Yan Z (2008) Activation of 5-HT2A/C receptors counteracts 5-HT1A regulation of n-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channels in pyramidal neurons of prefrontal cortex. J Biol Chem 283:17194–17204
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Yeung, L.Y., Kung, H.F. & Yew, D.T. Localization of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A positive cells in the brainstems of control age-matched and Alzheimer individuals. AGE 32, 483–495 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-010-9152-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-010-9152-x