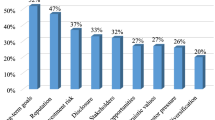
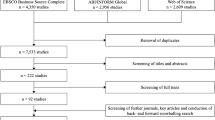
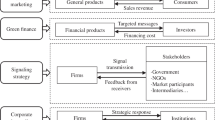
Abstract
Promoting green technology innovation through environmental tax is an important tool to achieve green development. Based on the data of Chinese listed companies from 2010 to 2020, this research examines the impact mechanisms of environmental tax policies on the quality and quantity of enterprise green technology innovation from the micro-enterprise perspective. The underlying mechanisms and heterogeneous effects were analyzed empirically using pooled OLS model and the mediated effects model. The results indicate that the environmental tax policy has an inhibitory effect on the quantity and quality of green patents, and the impact on the quantity is more significant. The mechanism analysis suggests that the environmental tax inhibits green technology innovation via accelerating capital renewal and environmental investment. Heterogeneity analysis shows that environmental tax has an inhibitory effect on green technology innovation behavior of large-scale enterprises and eastern region enterprises, while it has a boosting effect on green technology innovation of western region enterprises, and its effect on quantity of innovation is greater than that on quality. This study helps Chinese enterprises to better achieve green development from the perspective of green taxation and provides important empirical basis for achieving the win–win goal of economic growth and environmental development.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available on request.
References
Albrizio S, Kozluk T, Zipperer V (2017) Environmental policies and productivity growth: evidence across industries and firms. J Environ Econ Manage 81:209–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeem.2016.06.002
Awan U, Arnold MG, Gölgeci I (2021) Enhancing green product and process innovation: towards an integrative framework of knowledge acquisition and environmental investment. Bus Strateg Environ 30(2):1283–1295. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2684
Berrone P, Fosfuri A, Gelabert L, Gomez-Mejia LR (2013) Necessity as the mother of ‘green’ inventions: institutional pressures and environmental innovations. Strat Manag J 34(8):891–909. https://doi.org/10.1002/smj.2041
Boardman AE, Greenberg DH, Vining AR, Weimer DL (2017) Cost-benefit analysis: concepts and practice. Cambridge University Press
Cai X, Lu Y, Wu M, Yu L (2016) Does environmental regulation drive away inbound foreign direct investment? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. J Devel Econ 123:73–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdeveco.2016.08.003
Cai X, Zhu B, Zhang H, Li L, Xie M (2020) Can direct environmental regulation promote green technology innovation in heavily polluting industries? Evidence from Chinese listed companies. Sci Total Environ 746:140810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140810
Chen X, Zhan M (2022) Does environmental administrative penalty promote the quantity and quality of green technology innovation in China? Analysis based on the peer effect. Front Env Sci 10:2433. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.1070614
Chen Y, Zhang T, Ostic D (2022) Research on the green technology innovation cultivation path of manufacturing enterprises under the regulation of environmental protection tax law in China. Front Env Sci 448. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.874865.
Deng Y, You D, Wang J (2019) Optimal strategy for enterprises’ green technology innovation from the perspective of political competition. J Clean Prod 235:930–942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.06.248
Deng Y, You D, Wang J (2022) Research on the nonlinear mechanism underlying the effect of tax competition on green technology innovation-an analysis based on the dynamic spatial Durbin model and the threshold panel model. Resour Pol 76:102545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2021.102545
Endrikat J, Guenther E, Hoppe H (2014) Making sense of conflicting empirical findings: a meta-analytic review of the relationship between corporate environmental and financial performance. Eur Manag J 32(5):735–751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emj.2013.12.004
Fan X, Li X, Yin J (2019) Impact of environmental tax on green development: a nonlinear dynamical system analysis. Plos One 14(9):e0221264. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0221264
Fang J, Liu C, Gao C (2019) The impact of environmental regulation on firm exports: evidence from environmental information disclosure policy in China. Environ Sci Pollut R 26(36):37101–37113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06807-2
Goulder LH (1995) Environmental taxation and the double dividend: a reader’s guide. Int Tax Public Finan 2(2):157–183. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00877495
He Y, Wen C, He J (2020) The influence of China Environmental Protection Tax Law on firm performance–evidence from stock markets. Appl Econ Letters 27(13):1044–1047. https://doi.org/10.1080/13504851.2019.1659488
Hu G, Wang X, Wang Y (2021) Can the green credit policy stimulate green innovation in heavily polluting enterprises? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. Energy Econ 98:105134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105134
Huang L, Lei Z (2021) How environmental regulation affect corporate green investment: evidence from China. J Clean Prod 279:123560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123560
Huang X, Chang J (2021) Research on enterprise green transformation under environmental tax. Financ Eng Risk Manag 4(5):56–67. https://doi.org/10.23977/ferm.2021.040507
Jiang Z, Lyu P (2021) Stimulate or inhibit? Multiple environmental regulations and pollution-intensive industries’ transfer in China. J Clean Prod 328:129528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129528
Jiang Z, Xu C, Zhou J (2022) Government environmental protection subsidies, environmental tax collection, and green innovation: evidence from listed enterprises in China. Environ Sci Pollut R 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22538-3.
Lanoie P, Patry M, Lajeunesse R (2008) Environmental regulation and productivity: testing the porter hypothesis. J Productiv Anal 30(2):121–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11123-008-0108-4
Li G, Masui T (2019) Assessing the impacts of China’s environmental tax using a dynamic computable general equilibrium model. J Clean Prod 208:316–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.016
Li G, Zhang R, Masui T (2021) CGE modeling with disaggregated pollution treatment sectors for assessing China’s environmental tax policies. Sci Total Environ 761:143264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143264
Li J, Li S (2022) Environmental protection tax, corporate ESG performance, and green technological innovation. Front Env Sci 1512. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.982132.
Li P, Lin Z, Du H, Feng T, Zuo J (2021) Do environmental taxes reduce air pollution? Evidence from fossil-fuel power plants in China. J Environ Manage 295:113112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113112
Li X, Du K, Ouyang X, Liu L (2022) Does more stringent environmental regulation induce firms’ innovation? Evidence from the 11th Five-year plan in China. Energy Econ 106110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2022.106110
Li X, Hu Z, Zhang Q (2021c) Environmental regulation, economic policy uncertainty, and green technology innovation. Clean Technol Envir 23(10):2975–2988. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-021-02219-4
Lin B, Ma R (2022) Green technology innovations, urban innovation environment and CO2 emission reduction in China: fresh evidence from a partially linear functional-coefficient panel model. Technol Forecast Soc 176:121434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.121434
Liu G, Yang Z, Zhang F, Zhang N (2022) Environmental tax reform and environmental investment: a quasi-natural experiment based on China’s Environmental Protection Tax Law. Energy Econ 109:106000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2022.106000
Lu J (2022) Can environmental protection tax aggravate illegal pollution discharge of heavy polluting enterprises? Environ Sci Pollut R 29(22):33796–33808. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18002-3
Lv C, Shao C, Lee C-C (2021) Green technology innovation and financial development: do environmental regulation and innovation output matter? Energy Econ 98:105237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105237
MacKinnon DP, Krull JL, Lockwood CM (2000) Equivalence of the mediation, confounding and suppression effect. Prev Sci 1(4):173–181. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026595011371
Magat WA (1978) Pollution control and technological advance: a dynamic model of the firm. J Environ Econ Manage 5(1):1–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/0095-0696(78)90002-5
Montero JP (2002) Market structure and environmental innovation. J Appl Econ 5(2):293–325. https://doi.org/10.1080/15140326.2002.12040581
Ouyang X, Li Q, Du K (2020) How does environmental regulation promote technological innovations in the industrial sector? Evidence from Chinese provincial panel data. Energ Policy 139:111310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2020.111310
Pan X, Cheng W, Gao Y, Balezentis T, Shen Z (2021) Is environmental regulation effective in promoting the quantity and quality of green innovation? Environ Sci Pollut R 28(5):6232–6241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10984-w
Peng B, Zheng C, Wei G, Elahi E (2020) The cultivation mechanism of green technology innovation in manufacturing industry: from the perspective of ecological niche. J Clean Prod 252:119711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119711
Porter ME (1991) Towards a dynamic theory of strategy. Strat Manag J 12(S2):95–117. https://doi.org/10.1002/smj.4250121008
Shang S, Chen Z, Shen Z, Shabbir MS, Bokhari A, Han N, Klemeš JJ (2022) The effect of cleaner and sustainable sewage fee-to-tax on business innovation. J Clean Prod 132287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132287
Shao S, Hu Z, Cao J, Yang L, Guan D (2020) Environmental regulation and enterprise innovation: a review. Bus Strateg Environ 29(3):1465–1478. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2446
Shen F, Liu B, Luo F, Wu C, Chen H, Wei W (2021) The effect of economic growth target constraints on green technology innovation. J Environ Manage 292:112765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112765
Shi X, Xu Z (2018) Environmental regulation and firm exports: evidence from the eleventh Five-Year Plan in China. J Environ Econ Manage 89:187–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeem.2018.03.003
Song Y, Yang T, Zhang M (2019) Research on the impact of environmental regulation on enterprise technology innovation—an empirical analysis based on Chinese provincial panel data. Environ Sci Pollut R 26(21):21835–21848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05532-0
Tingbani I, Salia S, Hussain JG, Alhassan Y (2021) Environmental tax, SME financing constraint, and innovation: evidence from OECD countries. IEEE T Eng Manage https://doi.org/10.1109/TEM.2021.3110812
Tu Q, Wang Y (2021) New environmental protection taxes in China from the perspective of environmental economics. Dyn Nat Soc Discrete. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8622081
Wagner M (2007) On the relationship between environmental management, environmental innovation and patenting: evidence from German manufacturing firms. Res Pol 36(10):1587–1602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2007.08.004
Wang H, Qi S, Zhou C, Zhou J, Huang X (2022) Green credit policy, government behavior and green innovation quality of enterprises. J Clean Prod 331:129834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129834
Wang L, Long Y, Li C (2022) Research on the impact mechanism of heterogeneous environmental regulation on enterprise green technology innovation. J Environ Manage 322:116127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116127
Wang M, Li Y, Wang Z, Li J (2022c) The heterogeneous relationship between pollution charges and enterprise green technology innovation, based on the data of chinese industrial enterprises. Energies 15(5):1663. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15051663
Wang Y, Yu L (2021) Can the current environmental tax rate promote green technology innovation?-evidence from China’s resource-based industries. J Clean Prod 278:123443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123443
Wen H, Deng W, Guo Q (2021) The effects of the environmental protection tax law on heavily polluting firms in China. Plos One 16(12):e0261342. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0261342
Wen Z, Chang L, Hau K-T, Liu H (2004) Testing and application of the mediating effects. Acta Psychol Sin 36(5):614
Wen Z, Ye B (2014) Analyses of mediating effects: the development of methods and models. Adv Psychol Sci 22(5):731. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1042.2014.00731
Xie X, Huo J, Zou H (2019) Green process innovation, green product innovation, and corporate financial performance: a content analysis method. J Bus Res 101:697–706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.01.010
Xue Q, Bai C, Xiao W (2022) Fintech and corporate green technology innovation: Impacts and mechanisms. Manag Decis Econ 43(8):3898–3914. https://doi.org/10.1002/mde.3636
Yang L, Ouyang H, Fang K, Ye L, Zhang J (2015) Evaluation of regional environmental efficiencies in China based on super-efficiency-DEA. Ecol Indic 51:13–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.08.040
Yu H, Liao L, Qu S, Fang D, Luo L, Xiong G (2021) Environmental regulation and corporate tax avoidance: a quasi-natural experiments study based on China’s new environmental protection law. J Environ Manage 296:113160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113160
Yu Y, Cheng H (2021) Environmental taxes and innovation in Chinese textile enterprises: influence of mediating effects and heterogeneous factors. Sustain 13(8):4561. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13084561
Yuan B, Ren S, Chen X (2017) Can environmental regulation promote the coordinated development of economy and environment in China’s manufacturing industry? A panel data analysis of 28 sub-sectors. J Clean Prod 149:11–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.02.065
Yuan B, Xiang Q (2018) Environmental regulation, industrial innovation and green development of Chinese manufacturing: based on an extended CDM model. J Clean Prod 176:895–908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.034
Zhang F, Zhu L (2019) Enhancing corporate sustainable development: stakeholder pressures, organizational learning, and green innovation. Bus Strateg Environ 28(6):1012–1026. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2298
Zhang J, Liu Y, Zhou M, Chen B, Liu Y, Cheng B, Xue J, Zhang W (2022) Regulatory effect of improving environmental information disclosure under environmental tax in China: from the perspectives of temporal and industrial heterogeneity. Energ Policy 164:112760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2021.112760
Zhang W, Li G (2020) Environmental decentralization, environmental protection investment, and green technology innovation. Environ Sci Pollut R 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09849-z
Zhao A, Wang J, Sun Z, Guan H (2022) Environmental taxes, technology innovation quality and firm performance in China—a test of effects based on the Porter hypothesis. Econ Anal Policy 74:309–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eap.2022.02.009
Zhao X, Liu C, Yang M (2018) The effects of environmental regulation on China’s total factor productivity: an empirical study of carbon-intensive industries. J Clean Prod 179:325–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.100
Zheng D, Shi M (2017) Multiple environmental policies and pollution haven hypothesis: evidence from China’s polluting industries. J Clean Prod 141:295–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.09.091
Zhou D, Qiu Y, Wang M (2021) Does environmental regulation promote enterprise profitability? Evidence from the implementation of China’s newly revised environmental protection law. Econ Model 102:105585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2021.105585
Funding
This study is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 71772065, 72072056) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities at East China Normal University (No. 2021QKT007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Gang Du makes substantial contributions to conception and design, analysis, and interpretation of data. Yinuo Ma participates in drafting. Gang Du and Chuanmei Zhou analyzed the results and revised this paper. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Nicholas Apergis
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Du, G., Zhou, C. & Ma, Y. Impact mechanism of environmental protection tax policy on enterprises’ green technology innovation with quantity and quality from the micro-enterprise perspective. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 80713–80731 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28109-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28109-4