Abstract
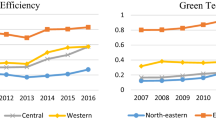
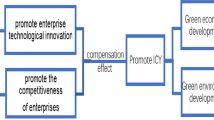
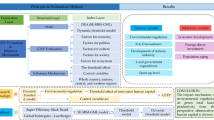
Following a consensus among world leaders at COP26 and COP27, every country is trying to deal with environmental issues. In this context, the role of green innovation efficiency is crucial, as it can positively drive the environmental efforts of a country. However, past research has ignored the methods through which a country can drive green innovation efficiency. To address this research gap, this work selected data from 2007 to 2021 in China, measured the green innovation efficiency (GIE) of each province, and constructed a systematic GMM model to analyze the role of environmental regulation policy and human capital on GIE. The findings of the study are as follows. (1) The overall GIE in China is 0.537, which is still at a low efficiency level, and high efficiency is mainly concentrated in the eastern region, while the western region has the lowest level of GIE. (2) The relationship between environmental regulations and GIE in the whole country and in the eastern, central, and western regions is shown to be “U” shaped. The regression coefficient of human capital on GIE is found to be positive, but there is regional variation, which is not significant in the western region and shows a significant positive correlation in other regions. (3) There is regional heterogeneity in FDI’s impact on GIE; the results in the eastern region are consistent with the national results, which can promote GIE, but not significantly in the central and western regions; marketization can improve GIE in the national and eastern regions, but is not significant in the central and western regions; scientific and technological innovation can promote GIE except in the central region; and economic development can improve GIE in all regions. Studying the impact of environmental regulation and human capital development on the efficiency of green innovation and realizing the coordinated development of the environment and economy under institutional innovation and human capital innovation is of great significance for the development of China’s low-carbon economy and has important reference value for accelerating sustainable economic development.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data is publicly available and proper sources have been cited in the text.
References
Aboelmaged M, Hashem G (2019) Absorptive capacity and green innovation adoption in SMEs: The mediating effects of sustainable organisational capabilities. J Clean Prod 220:853–863
Arellano M, Bover O (1995) Another look at the instrumental variable estimation of error-components models. J Econ 68(1):29–51
Asadi S, Pourhashemi SOS, Nilashi M (2020) Investigating influence of green innovation on sustainability performance: a case on Malaysian hotel industry. J Clean Prod 258:120860
Benhabib J, Spiegel MM (2005) Human capital and technology diffusion. Handb Econ Growth 1:935–966
Bergek A, Berggren C (2014) The impact of environmental policy instruments on innovation: a review ofenergy and automotive industry studies. Ecol Econ 106(10):112–123
Berrone P, Fosfuri A, Gelabert L (2013) Necessity as the mother of ‘green’ inventions: institutional pressures and environmental innovations. Strateg Manag J 34(8):891–909
Bilgaev A, Sadykova E, Mikheeva A (2022) Green economy development progress in the Republic of Buryatia (Russia). Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(13):7928
Binh An N, Kuo YL, Mabrouk F (2022) Ecological innovation for environmental sustainability and human capital development: the role of environmental regulations and renewable energy in advanced economies. Econ Res-Ekonomska Istraživanja 36(1):243–263
Blundell R, Bond S (2000) GMM estimation with persistent panel data: an application to production functions. Economet Rev 19(3):321–340
Cai X, Zhu BZ, Zhang HJ, Li L, Xie MY (2020) Can direct environmental regulation promote green technology innovation in heavily polluting industries? Evidence from Chinese listed companies. Sci Total Environ 746:140810
Chang L, Gan X, Mohsin M (2022) Studying corporate liquidity and regulatory responses for economic recovery in COVID-19 crises. Econ Anal Policy 76:211–225
Chang L, Taghizadeh-Hesary F, Chen H, Mohsin M (2022) Do green bonds have environmental benefits? Energy Econ 115:106356
Dension EF (1981) Accouting for slower economic growth: the United States in the 1970s. South Econ J 47(4):1191–1193
Du K, Cheng YY, Yao X (2021) Environmental regulation, green technology innovation, and industrial structure upgrading: the road to the green transformation of Chinese cities. Energy Econ 98:105274
Frondel M, Horbach J, Rennings K (2007) End-of-pipe or cleaner production? An empirical comparison of environmental innovation decisions across OECD countries. Bus Strateg Environ 16(8):571–584
Harlan T (2021) Green development or greenwashing? A political ecology perspective on China’s green Belt and Road. Eurasian Geogr Econ 62(2):202–226
Herrmann FF, Barbosa-Povoa AP, Butturi MA, Marinelli S, Sellitto MA (2021) Green supply chain management: conceptual framework and models for analysis. Sustainability 13(15):8127
Hsu CC, Quang-Thanh N, Chien FS (2021) Evaluating green innovation and performance of financial development: mediating concerns of environmental regulation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(40):57386–57397
Jefferson GH, Tanaka S, Yin W (2013) Environmental regulation and industrial performance: evidence from unexpected externalities in China. Soc Sci Electron Publ 111(12):108–142
Khan MT (2014) Effects of education and training on “human capital and effects of human capital on economic activity a literature based research. Int J Inf Bus Manag 6(3):108–116
Kurtz MJ, Brooks SM (2011) Conditioning the “resource curse”: globalization, human capital, and growth in oil-rich nations. Comp Polit Stud 44(6):747–770
Lazear EP (2004) Balanced skills and entrepreneurship. Am Econ Rev 94(2):208–211
Levine R, Loayza N, Beck T (2000) Financial intermediation and growth: causality and causes. J Monet Econ 46(1):31–77
Li CS (2020) Evaluation of GIE of industrial enterprises in China–an analysis based on panel time-varying stochastic frontier model. Technol Econ 39(9):119–125
Li WH, Cao WL (2020) FDI, environmental regulation and regional GIE. Stat Decis Making 36(19):118–122
Li JR, Li C, Li ZY (2017) Evaluation of urban GIE and analysis of its influencing factors. Stat Decis Making 20:116–120
Liu F, Meng Y (2020) How the marketization process affects the innovation performance of regional industrial agglomerations - empirical evidence from China’s high-tech industries. Econ Econ 1:105–113
Liu PZ, Zhang LY, Yan ZY (2021) Analysis on spatio-temporal characteristics and influencing factors of industrial GIE—from the perspective of innovation value chain. Sustainability 14(1):342
Ma DL, Zhao N, Li QS (2022) Study on the spatial and temporal evolution of industrial GIE in Yangtze River Economic Zone and its influencing factors. Ecol Econ 38(2):43–50+58
Mohd S, Kaushal VK (2018) Green finance: a step towards sustainable development. J Field Actions 5(1):59–74
Mohsin M, Orynbassarov D, Anser MK, Oskenbayev Y (2023) Does hydropower energy help to reduce CO2 emissions in European Union countries? Evid Quantile Estimation Environ Dev 45:100794
Munawar S, Yousaf HQ, Ahmed M (2022) Effects of green human resource management on green innovation through green human capital, environmental knowledge, and managerial environmental concern. J Hosp Tour Manag 52:141–150
Peng GH (2007) Regional total factor productivity and human capital composition in China. China Ind Econ 2:52–59
Peng WB, Cheng FF, Lu JL (2017) Research on the threshold effect of environmental regulation on provincial GIE. South Econ 36(9):73–84
Porter ME, van der L (1995) Toward a new conception of the environment-competitiveness relationship. J Econ Perspect 9(4):97–118
Rauch JE (1993) Productivity gains from geographic concentration of human capital: evidence from the cities. J Urban Econ 34(3):380–400
Rehman SU, Kraus S, Shah SA (2021) Analyzing the relationship between green innovation and environmental performance in large manufacturing firms. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 163:120481
Sellitto MA, Camfield CG, Buzuku S (2020) Green innovation and competitive advantages in a furniture industrial cluster: a survey and structural model. Sustain Prod Consum 23:94–104
Seman NAA, Govindan K, Mardani A (2019) The mediating effect of green innovation on the relationship between green supply chain management and environmental performance. J Clean Prod 229:115–127
Singh CD (2021) MCDM based model for sustainable green development through modern production techniques. Int J Compet 2(1):62–90
Song W, Han X (2022) The bilateral effects of foreign direct investment on GIE: evidence from 30 Chinese provinces]. Energy 261:125332
Soo C, Tian AW, Teo STT (2017) Intellectual capital-enhancing HR, absorptive capacity, and innovation. Hum Resour Manage 56(3):431–454
Sun XT, Gao JH, Fan D (2018) Analysis of regional differences and efficiency improvement of green technology innovation in China. Sci Technol Dev 14(11):1092–1098
Tolliver C, Fujii H, Keeley AR (2021) Green innovation and finance in Asia. Asian Econ Policy Rev 16(1):67–87
Tone KM (2001) A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur J Oper Res 30(3):498–509
Tone K (2002) A strange case of the cost and allocative efficiencies in DEA. J Oper Res Soc 53(11):1225–1231
Wang CM, Li J (2019) Evaluation of regional green innovation performance in China and analysis of its spatial and temporal differences–based on inter-provincial industrial enterprises panel data from 2005–2015. Sci Res Manag 6:29–42
Wang FH, Wang YS (2021) The threshold effect of high-tech service industry agglomeration on regional innovation efficiency. Stat Policy 37(04):91–95
Wang H, Miao Z, Wang SQ (2015) Spatial spillover, industrial agglomeration effect and industrial GIE. China Sci Technol Forum 2:33–38
Wang L, Zhao YL, Wang SH (2022) Study on the impact of clustering pattern of high-tech industries on GIE in China. Manag Modern 1:17–23
Wei X, Mohsin M, Zhang Q (2022) Role of foreign direct investment and economic growth in renewable energy development. Renew Energy 192:828–837
Wu YR (2008) The contribution of productivity to China’s economic growth: new estimates. Econ (quarterly) 2,827–842
Xiao L, Gao JF, Han B (2018) Spatial spillover effects of inter-provincial GIE in China - a test of homogeneity and heterogeneity. Ind Technol Econ 37(4):30–38
Xu H, Li GY (2018) Research on the impact of environmental regulation on GIE. Res Finance Econ 9:52–58
Yan CL, Zhu ML (2016) Analysis of the impact of China’s R&D investment on economic growth and its transmission mechanism. Ind Econ Rev 1:20–29
Yang QY, Chen QH (2017) Environmental regulation and GIE of industrial enterprises: an empirical study of 2SLS based on panel data. Ningxia Soc Sci 5:60–67
Yang SW, Wu T, Li ZB (2018) Research on the spatial and temporal divergence of GIE in Yangtze River Economic Zone and the influencing factors. Macroecon Econ Res 6,107–117+132
Zeng J, Škare M, Lafont J (2021) The co-integration identification of GIE in Yangtze River Delta region. J Bus Res 134:252–262
Zhang D, Mohsin M, Taghizadeh-Hesary F (2022) Does green finance counteract the climate change mitigation: asymmetric effect of renewable energy investment and R&D. Energy Econ 113:106183
Zhao LD, Zhang L, Xu L (2016) Mechanism of the role of human capital, industrial restructuring and green development efficiency. China Popul - Resour Environ 26(11):106–114
Zhao PJ (2020) Manufacturing agglomeration, environmental regulation and GIE. Southwest University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wei Song: conceptualization, methodology, software, data curation, writing—original draft preparation; Lei Meng: writing—reviewing and editing, software; Dexia Zang:visualization, investigation, validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors listed agreed to publish this work.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Song, W., Meng, L. & Zang, D. Exploring the impact of human capital development and environmental regulations on green innovation efficiency. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 67525–67538 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27199-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27199-4