Abstract
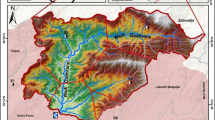
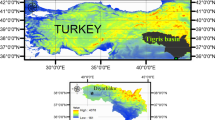
Accurate prediction of evapotranspiration values is important in planning agricultural irrigation, crop growth research, and hydrological modeling. This study is aimed at estimating monthly evapotranspiration (ET) values in Hakkâri province by combining support vector regression, bagged tree, and boosted tree methods with wavelet transform. For this purpose, precipitation, runoff, surface net solar radiation, air temperatures, and previous ET values were divided into sub-signals with various mother wavelets such as Daubechies 4, Meyer, and Symlet 2 and presented as input to machine learning (ML) algorithms. The study’s main contribution to the literature is to reveal which wavelet-based machine learning model, mother wavelet type, and combination of meteorological data show the most realistic results in ET estimation. While establishing the models, the data were divided into 80% training and 20% testing. The models’ performances were based on the widely used root mean square error, mean absolute error, determination coefficient, and Taylor diagrams. As a result of the study, it was revealed that the hybrid wavelet ML, which is established with input combinations separated into subcomponents by wavelet transform, generally produces more successful predictions than the stand-alone ML model. In addition, it was revealed that the optimum ET forecasting model was obtained with the wavelet bagged tree algorithm with Symlet 2 mother wavelet. Even though the best model established is based on the precipitation and temperature inputs, it was revealed that past ET, solar radiation, and runoff values are also effective inputs in ET prediction. The results can also be used in other regions of the world with semi-arid climates, such as Hakkâri. The study’s outputs provide essential resources to decision-makers and planners to manage water resources and plan agricultural irrigation.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data used in this study is available in a public repository, namely, the Climate Data Store.
References
Abbaszadeh P, Alipour A, Asadi S (2018) Development of a coupled wavelet transform and evolutionary Levenberg-Marquardt neural networks for hydrological process modeling. Comput Intell 34:175–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107081
Abrishami N, Sepaskhah AR, Shahrokhnia MH (2019) Estimating wheat and maize daily evapotranspiration using artificial neural network. Theoret Appl Climatol 135:945–958. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-018-2418-4
Agrawal Y, Kumar M, Ananthakrishnan S, Kumarapuram G (2022) Evapotranspiration modeling using different, tree-based ensembled machine learning algorithm. Water Resour Manag 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03067-7
Ahmadi F, Mehdizadeh S, Mohammadi B (2021) Development of bio-inspired-and wavelet-based hybrid models for reconnaissance drought index modeling. Water Resour Manage 35:4127–4147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02934-z
Alizamir M, Kisi O, Muhammad AR, Kuriqi A (2020) Modelling reference evapotranspiration by combining neuro-fuzzy and evolutionary strategies. Acta Geophys 68:1113–1126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-020-00446-9
Altunkaynak A, Jalilzadnezamabad A (2021) Extended lead time accurate forecasting of palmer drought severity index using hybrid wavelet-fuzzy and machine learning techniques. J Hydrol 601:126619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126619
Araghi A, Adamowski J, Martinez CJ (2020) Comparison of wavelet-based hybrid models for the estimation of daily reference evapotranspiration in different climates. J Water Clim Change 11:39–53. https://doi.org/10.2166/wcc.2018.113
Baatz R, Hendricks Franssen HJ, Euskirchen E, Sihi D, Dietze M, Ciavatta S, ... Vereecken H (2021) Reanalysis in Earth system science: toward terrestrial ecosystem reanalysis. Reviews of Geophysics 59: e2020RG000715. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020RG000715
Barzegar R, Fijani E, Moghaddam AA, Tziritis E (2017) Forecasting of groundwater level fluctuations using ensemble hybrid multi-wavelet neural network-based models. Sci Total Environ 599:20–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.04.189
Bateni SM, Khoshkam H, Karbasi M, Valipour M, Xu T, Heggy E (2020) Forecasting daily reference evapotranspiration using the wavelet-Gaussian Process Regression (GPR) approach, AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, pp. H166–0014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.04.189
Breiman L (1994) Bagging predictors (technical report 421). University of California, Berkeley
Chong KL, Lai SH, Yao Y, Ahmed AN, Jaafar WZW, El-Shafie A (2020) Performance enhancement model for rainfall forecasting utilizing integrated wavelet-convolutional neural network. Water Resour Manage 34:2371–2387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02554-z
Daubechies I (1990) The wavelet transform, time-frequency localization and signal analysis. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 36:961–1005. https://doi.org/10.1109/18.57199
Dawson CW, Wilby R (1998) An artificial neural network approach to rainfall-runoff modelling. Hydrol Sci J 43:47–66. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626669809492102
Ding R, Kang S, Li F, Zhang Y, Tong L, Sun Q (2010) Evaluating eddy covariance method by large-scale weighing lysimeter in a maize field of northwest China. Agric Water Manag 98:87–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2010.08.001
Efron B (1992) Bootstrap methods: another look at the jackknife, Breakthroughs in statistics. Springer, pp. 569–593. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-4380-9_41
Esmaeili-Gisavandani H, Farajpanah H, Adib A, Kisi O, Riyahi MM, Lotfirad M, Salehpoor J (2022) Evaluating ability of three types of discrete wavelet transforms for improving performance of different ML models in estimation of daily-suspended sediment load. Arab J Geosci 15:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-09282-7
Fan J, Guyot A, Ostergaard KT, Lockington DA (2018a) Effects of earlywood and latewood on sap flux density-based transpiration estimates in conifers. Agric for Meteorol 249:264–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2017.11.006
Fan J, Wang X, Wu L, Zhou H, Zhang F, Yu X, ... Xiang Y (2018b) Comparison of support vector machine and extreme gradient boosting for predicting daily global solar radiation using temperature and precipitation in humid subtropical climates: a case study in China. Energy conversion and management 164:102-111.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2018.02.087
Fan J, Yue W, Wu L, Zhang F, Cai H, Wang X, ... Xiang Y (2018c) Evaluation of SVM, ELM and four tree-based ensemble models for predicting daily reference evapotranspiration using limited meteorological data in different climates of China. Agricultural and forest meteorology 263:225–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2018.08.019
Feng Y, Cui N, Zhao L, Hu X, Gong D (2016) Comparison of ELM, GANN, WNN and empirical models for estimating reference evapotranspiration in humid region of Southwest China. J Hydrol 536:376–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.02.053
Fotovatikhah F, Herrera M, Shamshirband S, Chau KW, FaizollahzadehArdabili S, Piran MJ (2018) Survey of computational intelligence as basis to big flood management: challenges, research directions and future work. Eng Appl Comput Fluid Mech 12:411–437. https://doi.org/10.1080/19942060.2018.1448896
Fu T, Li X, Jia R, Feng L (2021) A novel integrated method based on a machine learning model for estimating evapotranspiration in dryland. J Hydrol 603:126881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126881
General Directorate of Meteorology (2017) Climate classifications. http://www.mgm.gov.tr/FILES/iklim/iklim_siniflandirmalari.pdf. (received:22.9.2022)
Ghazi B, Jeihouni E, Kalantari Z (2021) Predicting groundwater level fluctuations under climate change scenarios for Tasuj plain, Iran. Arab J Geosci 14:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-06508-6
Gocić M, Motamedi S, Shamshirband S, Petković D, Ch S, Hashim R, Arif M (2015) Soft computing approaches for forecasting reference evapotranspiration. Comput Electron Agric 113:164–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2015.02.010
Granata F (2019) Evapotranspiration evaluation models based on machine learning algorithms—a comparative study. Agric Water Manag 217:303–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2019.03.015
Hameed MM, AlOmar MK, Mohd Razali SF, Kareem Khalaf MA, Baniya WJ, Sharafati A, AlSaadi MA (2021) Application of artificial intelligence models for evapotranspiration prediction along the Southern Coast of Turkey. Complexity, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8850243
Hersbach H, Bell B, Berrisford P, Hirahara S, Horányi A, Muñoz-Sabater J, ... Thépaut JN (2020) The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q J R Meteorol Soc 146:1999–2049. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.3803
Huang Y, Lan Y, Thomson SJ, Fang A, Hoffmann WC, Lacey RE (2010) Development of soft computing and applications in agricultural and biological engineering. Comput Electron Agric 71:107–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2010.01.001
Huang G, Wu L, Ma X, Zhang W, Fan J Yu X, ... Zhou H (2019) Evaluation of CatBoost method for prediction of reference evapotranspiration in humid regions. J Hydrol 574:1029-1041.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.04.085
Jafari H, Rajaee T, Kisi O (2020) Improved water quality prediction with hybrid wavelet-genetic programming model and shannon entropy. Nat Resour Res 29:3819–3840. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-020-09702-7
Karbasi M, Karbasi M, Jamei M, Malik A, Azamathulla HM (2022) Development of a new wavelet-based hybrid model to forecast multi-scalar SPEI drought index (case study: Zanjan city, Iran). Theoret Appl Climatol 147:499–522. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-021-03825-4
Karthika B, Deka PC (2015) Prediction of air temperature by hybridized model (wavelet-ANFIS) using wavelet decomposed data. Aquatic Procedia 4:1155–1161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqpro.2015.02.147
Kisi O, Alizamir M (2018) Modelling reference evapotranspiration using a new wavelet conjunction heuristic method: wavelet extreme learning machine vs wavelet neural networks. Agric for Meteorol 263:41–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2018.08.007
Linh NTT, Ruigar H, Golian S, Bawoke GT, Gupta V, Rahman KU, ... Pham QB (2021) Flood prediction based on climatic signals using wavelet neural network. Acta Geophysica 69:1413–1426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-021-00620-7
Liu X, Yuan S, Li L (2012) Prediction of temperature time series based on wavelet transform and support vector machine. J Comput 7:1911–1918. https://doi.org/10.4304/jcp.7.8.1911-1918
Long X, Wang J, Gong S, Li G, Ju H (2022) Reference evapotranspiration estimation using long short-term memory network and wavelet-coupled long short-term memory network. Irrig Drain. https://doi.org/10.1002/ird.2699
Maheswaran R, Khosa R (2012) Comparative study of different wavelets for hydrologic forecasting. Comput Geosci 46:284–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2011.12.015
Mallat SG (1989) A theory for multi resolution signal decomposition: the wavelet representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Machine Intel 11(7):674–693
Mohammadi K, Shamshirband S, Tong CW, Arif M, Petković D, Ch S (2015) A new hybrid support vector machine–wavelet transform approach for estimation of horizontal global solar radiation. Energy Convers Manage 92:162–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2014.12.050
Mohammadrezapour O, Piri J, Kisi O (2019) Comparison of SVM, ANFIS and GEP in modeling monthly potential evapotranspiration in an arid region (case study: Sistan and Baluchestan Province, Iran). Water Supply 19:392–403. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2018.084
Morton F (1968) Evaporation and climate- a study in cause and effect. Sci. Set. J, Inland Waters Branch, Department of Energy, Mines, and Resources Ottawa, Canada
Musyimi PK, Sahbeni G, Timár G, Weidinger T, Székely B (2022) Actual evapotranspiration estimation using sentinel-1 SAR and sentinel-3 SLSTR data combined with a gradient boosting machine model in Busia county, Western Kenya. Atmosphere 13:1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111927
Nourani V, Alami MT, Aminfar MH (2009) A combined neural-wavelet model for prediction of Ligvanchai watershed precipitation. Eng Appl Artif Intell 22:466–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2008.09.003
Nourani V, Kisi Ö, Komasi M (2011) Two hybrid artificial intelligence approaches for modeling rainfall–runoff process. J Hydrol 402:41–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.03.002
Nourani V, Baghanam AH, Adamowski J, Kisi O (2014) Applications of hybrid wavelet–artificial intelligence models in hydrology: a review. J Hydrol 514:358–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.03.057
Partal T, Cigizoglu HK (2008) Estimation and forecasting of daily suspended sediment data using wavelet-neural networks. J Hydrol 358(3–4):317–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.06.013
Patil AP, Deka PC (2017) Performance evaluation of hybrid wavelet-ANN and wavelet-ANFIS models for estimating evapotranspiration in arid regions of India. Neural Comput Appl 28:275–285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-2055-0
Polikar R (2012) Ensemble learning. Ensemble machine learning. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, pp 1–34
Qasem SN, Samadianfard S, Kheshtgar S, Jarhan S, Kisi O, Shamshirband S, Chau KW (2019) Modeling monthly pan evaporation using wavelet support vector regression and wavelet artificial neural networks in arid and humid climates. Eng Appl Comput Fluid Mech 13:177–187. https://doi.org/10.1080/19942060.2018.1564702
Quilty J, Adamowski J (2021) A maximal overlap discrete wavelet packet transform integrated approach for rainfall forecasting–a case study in the Awash River Basin (Ethiopia). Environ Model Softw 144:105119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2021.105119
Rahman AS, Hosono T, Quilty JM, Das J, Basak A (2020) Multiscale groundwater level forecasting: coupling new machine learning approaches with wavelet transforms. Adv Water Resour 141:103595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2020.103595
Rathinasamy M, Adamowski J, Khosa R (2013) Multiscale streamflow forecasting using a new Bayesian Model Average based ensemble multi-wavelet Volterra non-linear method. J Hydrol 507:186–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.09.025
Ribeiro MHDM, dos Santos Coelho L (2020) Ensemble approach based on bagging, boosting and stacking for short-term prediction in agribusiness time series. Appl Soft Comput 86:105837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105837
Roy DK, Lal A, Sarker KK, Saha KK, Datta B (2021) Optimization algorithms as training approaches for prediction of reference evapotranspiration using adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system. Agric Water Manag 255:107003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2021.107003
Salam R, Islam ARMT (2020) Potential of RT, Bagging and RS ensemble learning algorithms for reference evapotranspiration prediction using climatic data-limited humid region in Bangladesh. J Hydrol 590:125241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125241
Sang YF (2013) A review on the applications of wavelet transform in hydrology time series analysis. Atmos Res 122:8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2012.11.003
Saraiva SV, de Oliveira Carvalho F, Santos CAG, Barreto LC, Freire PKDMM (2021) Daily streamflow forecasting in Sobradinho Reservoir using machine learning models coupled with wavelet transform and bootstrapping. Appl Soft Comput 102:107081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107081
Schapire RE (1990) The strength of weak learnability. Mach Learn 5:197–227. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00116037
Schneiders MGE (2001) Wavelets in control engineering. Master’s thesis, Eindhoven University of Technology, p 38
Seo Y, Kim S, Kisi O, Singh VP, Parasuraman K (2016) River stage forecasting using wavelet packet decomposition and machine learning models. Water Resour Manage 30:4011–4035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2016.07.439
Shiri J, Marti P, Nazemi AH, Sadraddini AA, Kisi O, Landeras G, FakheriFard A (2015) Local vs. external training of neuro-fuzzy and neural networks models for estimating reference evapotranspiration assessed through k-fold testing. Hydrol Res 46:72–88. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.2013.112
Sun Z, Chang C (2002) Structural damage assessment based on wavelet packet transform. J Struct Eng 128:1354–1361. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(2002)128:10(1354)
Tabari H, Kisi O, Ezani A, Talaee PH (2012) SVM, ANFIS, regression and climate based models for reference evapotranspiration modeling using limited climatic data in a semi-arid highland environment. J Hydrol 444:78–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.04.007
Taylor KE (2001) Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram. J Geophys Res: Atmospheres 106(D7):7183–7192. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000JD900719
Vapnik VN (1999) An overview of statistical learning theory. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 10:988–999. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8081286
Vicente-Serrano SM, Bidegain M, Tomas-Burguera M, Dominguez-Castro F, El Kenawy A, McVicar TR, ... Giménez A (2018) A comparison of temporal variability of observed and model-based pan evaporation over Uruguay (1973–2014). Int J Climatol 38:337-350.https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.517910.1002/joc.5179
Wang F, Yu Y, Zhang Z, Li J, Zhen Z, Li K (2018) Wavelet decomposition and convolutional LSTM networks based improved deep learning model for solar irradiance forecasting. Appl Sci 8:1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8081286
Wen X, Si J, He Z, Wu J, Shao H, Yu H (2015) Support-vector-machine-based models for modeling daily reference evapotranspiration with limited climatic data in extreme arid regions. Water Resour Manage 29:3195–3209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-015-0990-2
Wu L, Fan J (2019) Comparison of neuron-based, kernel-based, tree-based and curve-based machine learning models for predicting daily reference evapotranspiration. PloS one 14:e0217520. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0217520
Yeditha PK, Kasi V, Rathinasamy M, Agarwal A (2020) Forecasting of extreme flood events using different satellite precipitation products and wavelet-based machine learning methods. Chaos: An Interdiscip J Nonlinear Sci 30:063115. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0008195
Yu Y, Li Y, Li J, Gu X (2016) Self-adaptive step fruit fly algorithm optimized support vector regression model for dynamic response prediction of magnetorheological elastomer base isolator. Neurocomputing 211:41–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2016.02.074
Yu Y, Zhang C, Gu X, Cui Y (2019) Expansion prediction of alkali aggregate reactivity-affected concrete structures using a hybrid soft computing method. Neural Comput Appl 31:8641–8660. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3679-7
Zounemat-Kermani M, Batelaan O, Fadaee M, Hinkelmann R (2021) Ensemble machine learning paradigms in hydrology: a review. J Hydrol 598:126266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126266
Acknowledgements
The author thanks Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, for the ERA 5 data provided, the editor, and the anonymous reviewers for their contributions to the content and development of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The author completes the work independently.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The manuscript complies with all the ethical requirements.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Marcus Schulz
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The paper was not published in any journal. The authors confirm that the work described has not been published before, and it is not under consideration for publication elsewhere.
This study was presented orally at the II. International Joint Conference on Engineering, Science and Artificial Intelligence (IJCESAI 2022).
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Katipoğlu, O.M. Combining discrete wavelet decomposition with soft computing techniques to predict monthly evapotranspiration in semi-arid Hakkâri province, Türkiye. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 44043–44066 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25369-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25369-y