Abstract
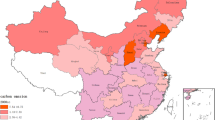
The government corruption and resource misallocation are important factors that inhibit economic transformation and environmental governance. Using a study sample of 30 provinces in China, this study employs the spatial econometric methods and threshold model to investigate the relationship between regional corruption, resource misallocation, and CO2 emission. The results show that there is a clear spatial dependence and correlation of CO2 emissions. Government corruption is a neglected contributor to carbon emissions, and this promotion effects are attributed to a promotion in resource misallocation. Moreover, the CO2 emissions are significantly promoted by local labor misallocation and capital misallocation, and the increasing effect is more pronounced in areas with high corruption. For spatial spillover effects, there is also no evidence that local CO2 emissions are significantly promoted by capital misallocation of surrounding areas. Additionally, the promoting effect of corruption on CO2 emissions is more pronounced in regions with weak environmental regulation, low marketization process, and the central and western of China. This work elucidates the mechanism of the impact of corruption on environmental pollution from the perspective of resource allocation, and provides an important reference for the effective management of environmental pollution.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Al-Mulali U, Ozturk I (2015) The effect of energy consumption, urbanization, trade openness, industrial output, and the political stability on the environmental degradation in the MENA (Middle East and North African) region. Energy 84:382–389
Aloi M, Tournemaine F (2011) Growth effects of environmental policy when pollution affects health. Econ Model 28(4):1683–1695
Bian Y, Song K, Bai J (2019) Market segmentation, resource misallocation and environmental pollution. J Clean Prod 228:376–387
Bilotkach V (2006) A tax evasion - bribery game: experimental evidence from ukraine. Eur J Comparative Econ 3(1):31–49
Bräutigam D, Tang X (2014) “Going global in groups”: structural transformation and China’s special economic zones overseas. World Dev 63:78–91
Cai Z, Wheale P (2009) Managing efficient capital allocation with emphasis on the Chinese experience. J Bus Ethics 87(1):111–135
Chang E, Golden MA (2010) Sources of corruption in authoritarian regimes. Soc Sci Q 91(1):1–20
Chen CJ, Li Z, Su X, Sun Z (2011) Rent-seeking incentives, corporate political connections, and the control structure of private firms: Chinese evidence. J Corp Finan 17(2):229–243
Chen H, Hao Y, Li J, Song X (2018) The impact of environmental regulation, shadow economy, and corruption on environmental quality: theory and empirical evidence from China. J Clean Prod 195:200–214
Chen S, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Liu Z (2019) The relationship between industrial restructuring and China’s regional haze pollution: a spatial spillover perspective. J Clean Prod 239:115808
Cheng W, Wu Y (2019) Bank finance for private firms in China: does political capital still pay off? The World Economy 42(1):242–267
Cui L, Duan H, Mo J, Song M (2021) Ecological compensation in air pollution governance: China’s efforts, challenges, and potential solutions. Int Rev Financ Anal 74:101701
Dechezleprêtre A, Nachtigall D, Venmans F (2022) The joint impact of the European Union emissions trading system on carbon emissions and economic performance. J Environ Econ Manag, 102758
Dreher A, Schneider F (2010) Corruption and the shadow economy: an empirical analysis. Public Choice 144(1):215–238
Du M, Hou Y, Zhou Q, Ren S (2022) Going green in China: how does digital finance affect environmental pollution? Mechanism discussion and empirical test. Environ Sci Pollut Res 7(1):1–15
Du W, Li M (2021) The impact of land resource mismatch and land marketization on pollution emissions of industrial enterprises in China. J Environ Manage 299:113565
Elhorst JP (2014) Spatial econometrics from cross-sectional data to spatial panels. Springer
Farhani S, Ozturk I (2015) Causal relationship between CO2 emissions, real GDP, energy consumption, financial development, trade openness, and urbanization in Tunisia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(20):15663–15676
Farzanegan MR, Mennel T (2012) Fiscal decentralization and pollution: institutions matter (No. 22–2012). MAGKS Joint Discussion Paper Series in Economics
Ferreira-Lopes A, Sequeira TN, Roseta-Palma C (2013) On the effect of technological progress on pollution: an overlooked distortion in endogenous growth. Oxf Econ Pap 65(2):394–416
Gao X, Wang S, Ahmad F, Chandio AA, Ahmad M, Xue D (2021) The nexus between misallocation of land resources and green technological innovation: a novel investigation of Chinese cities. Clean Technol Environ Policy 23(7):2101–2115
Gürlük S (2009) Economic growth, industrial pollution and human development in the Mediterranean Region. Ecol Econ 68(8):2327–2335
Hansen BE (1999) Threshold effects in non-dynamic panels: estimation, testing, and inference. Journal of Econometrics 93(2):345–368
Hao X, Li Y, Ren S, Wu H, Hao Y (2023) The role of digitalization on green economic growth: Does industrial structure optimization and green innovation matter? J Environ Manage 325:116504
Hao Y, Gai Z, Wu H (2020) How do resource misallocation and government corruption affect green total factor energy efficiency? Evidence from China. Energy Policy 143:111562
Hao Y, Huang J, Guo Y, Wu H, Ren S (2022) Does the legacy of state planning put pressure on ecological efficiency? Evidence from China. Bus Strateg Environ 31:403–424
Hassan ST, Zhu B, Lee CC, Ahmad P, Sadiq M (2021) Asymmetric impacts of public service “transportation” on the environmental pollution in China. Environ Impact Assess Rev 91:106660
He D, Zhang W, Shek J (2007) How efficient has been China’s investment? Empirical evidence from national and provincial data. Pac Econ Rev 12(5):597–617
Hsieh CT, Klenow PJ (2009) Misallocation and manufacturing TFP in China and India. Q J Econ 124(4):1403–1448
Khatibi SR, Karimi SM, Moradi-Lakeh M, Kermani M, Motevalian SA (2020) Fossil energy price and outdoor air pollution: predictions from a QUAIDS model. Biofuel Research Journal 7(3):1205
Lei T, Ding RJ (2008) Efficiency assessment of coal mine safety input by data envelopment analysis. J China Univ Min Technol 18(1):88–92
Li T, Long H, Zhang Y, Tu S, Ge D, Li Y, Hu B (2017) Analysis of the spatial mismatch of grain production and farmland resources in China based on the potential crop rotation system. Land Use Policy 60:26–36
Li Y, Long W, Ning X, Zhu Y, Guo Y, Huang Z, Hao Y (2022) How can China’s sustainable development be damaged in consequence of financial misallocation? Analysis from the perspective of regional innovation capability. Bus Strateg Environ 7(31):1–25
Lin T, Du M, Ren S (2022) How do green bonds affect green technology innovation? Firm Evidence from China Green Finance 4(4):492–511
Liu H, Lei H, Zhou Y (2022) How does green trade affect the environment? Evidence from China. J Econ Anal 1(1):1–27
Lovo S (2018) Effect of environmental decentralization on polluting firms in India. Econ Dev Cult Change 67(1):55–94
Netherlands S (2014) Corruption perception index. Springer, Netherlands
Pei Y, Zhu Y, Wang N (2021) How do corruption and energy efficiency affect the carbon emission performance of China’s industrial sectors? Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(24):31403–31420
Ponce P, Khan SAR (2021) A causal link between renewable energy, energy efficiency, property rights, and CO2 emissions in developed countries: a road map for environmental sustainability. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(28):37804–37817
Rehman A, Ma H, Ozturk I (2021) Do industrialization, energy importations, and economic progress influence carbon emission in Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(33):45840–45852
Ren S, Hao Y, Wu H (2021) Government corruption, market segmentation and renewable energy technology innovation: evidence from China. J Environ Manage 300:113686
Ren S, Hao Y, Wu H (2022a) How does green investment affect environmental pollution? Evidence from China. Environ Resource Econ 81(1):25–51
Ren S, Liu Z, Zhanbayev R, Du M (2022b) Does the internet development put pressure on energy-saving potential for environmental sustainability? Evidence from China. J Econ Anal 1(1):81–101
Roh T, Lee K, Yang JY (2021) How do intellectual property rights and government support drive a firm’s green innovation? The mediating role of open innovation. J Clean Prod 317:128422
Sharif A, Baris-Tuzemen O, Uzuner G, Ozturk I, Sinha A (2020) Revisiting the role of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on Turkey’s ecological footprint: Evidence from Quantile ARDL approach. Sustain Cities Soc 57:102138
Sharif A, Raza SA, Ozturk I, Afshan S (2019) The dynamic relationship of renewable and nonrenewable energy consumption with carbon emission: a global study with the application of heterogeneous panel estimations. Renewable Energy 133:685–691
Wang H, Ge Y, Shi L (2017) Technologies in deep and ultra-deep well drilling: present status, challenges and future trend in the 13th Five-Year Plan period (2016–2020). Natural Gas Industry B 4(5):319–326
Wang K, Wang C, Lu X, Chen J (2007) Scenario analysis on CO2 emissions reduction potential in China’s iron and steel industry. Energy Policy 35(4):2320–2335
Wang S, Yuan Y, Wang H (2019) Corruption, hidden economy and environmental pollution: A spatial econometric analysis based on China’s provincial panel data. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16(16):2871
Wang S, Zhao D, Chen H (2020) Government corruption, resource misallocation, and ecological efficiency. Energy Economics 85:104573
Wu H, Xia Y, Yang X, Hao Y, Ren S (2021a) Does environmental pollution promote China’s crime rate? A new perspective through government official corruption. Struct Chang Econ Dyn 57:292–307
Wu H, Xue Y, Hao Y, Ren S (2021b) How does internet development affect energy-saving and emission reduction? Evidence from China. Energy Economics 103:105577
Yang X, Wang W, Su X, Ren S, Ran Q, Wang J, Cao J (2022a) Analysis of the influence of land finance on haze pollution: an empirical study based on 269 prefecture-level cities in China. Growth Chang 4:1–24
Yang X, Wu H, Ren S, Ran Q, Zhang J (2021) Does the development of the internet contribute to air pollution control in China? Mechanism discussion and empirical test. Struct Chang Econ Dyn 56:207–224
Yang, Y., Wu, D., Xu, M., Yang, M., & Zou, W. (2022b). Capital misallocation, technological innovation, and green development efficiency: empirical analysis based on China provincial panel data. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 1–14.
Yao Y, Hu D, Yang C, Tan Y (2021) The impact and mechanism of fintech on green total factor productivity. Green Financ 3:198–221
Yian C (2019) Misallocation of human capital and productivity: evidence from China. Econ Res Ekonomska Istraživanja 32(1):3342–3359
Zhang M, Tan S, Pan Z, Hao D, Zhang X, Chen Z (2022) The spatial spillover effect and nonlinear relationship analysis between land resource misallocation and environmental pollution: evidence from China. J Environ Manage 321:115873
Zhang YJ, Da YB (2015) The decomposition of energy-related carbon emission and its decoupling with economic growth in China. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 41:1255–1266
Zheng C, Deng F, Zhuo C, Sun W (2022) Green credit policy, institution supply and enterprise green innovation. Journal of Economic Analysis 1(1):28–51
Zhou Q, Du M, Ren S (2022) How government corruption and market segmentation affect green total factor energy efficiency in the post-COVID-19 era: evidence from china. Front Energy Res 10:1–13
Zugravu-Soilita N (2017) How does foreign direct investment affect pollution? Toward a better understanding of the direct and conditional effects. Environ Resource Econ 66(2):293–338
Funding
The authors acknowledge financial support from the National natural science foundation of China (7206020101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Guo Xie: conceptualization, writing—review and editing. Zhanhong Cui: formal analysis, data handling, and methodology. Siyu Ren: writing—original draft variable construction. Kai Li: funding acquisition, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Nicholas Apergis.
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, G., Cui, Z., Ren, S. et al. Pathways to carbon neutrality: how do government corruption and resource misallocation affect carbon emissions?. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 40283–40297 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25179-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25179-2