Abstract
This study examines long-term connection and short-term dynamics concerning ecological footprint and six independent variables, named fossil fuel consumption, energy consumption, financial depth, trade, GDP, and ICT for Pakistan’s duration from 1960 to 2019. The “QARDL-quantile autoregressive distributed lag” technique is used for time series and panel estimation. The QARDL model exhibits the connection between variables over the quantiles range, reflecting varying stages of Pakistan’s ecological footprint. The results exhibit noticeable quantile-varying co-integration connection among ecological footprint and six independent variables. The results accentuate the significant influence of energy consumption, strong financial position, economic growth, and ICT technologies on ecological well-being, which assists in understanding short and long-term impact on the environment in Pakistan.

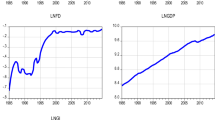
Source: authors’ estimation



Source: authors’ estimation
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Notes
“LI-low income; LMI- lower-middle-income countries”.
References
Abbasi KR, Hussain K, Radulescu M, Ozturk I (2022) Asymmetric impact of renewable and non-renewable energy on the industrial sector in Pakistan: fresh evidence from Bayesian and non-linear ARDL. Renewable Energy 187:944–957
AhAtil A, Bouheni,FB, Lahiani A, Shahbaz M (2019) Factors influencing CO2 emission in China: a non-linear autoregressive distributed lags investigation
Ahmad M, Khan Z, Ur Rahman Z, Khan S (2018) Does financial development asymmetrically affect CO2 emissions in China? An application of the non-linear autoregressive distributed lag (NARDL) model. Carbon Management 9(6):631–644
Ahmed Z, Nathaniel SP, Shahbaz M (2021) The criticality of information and communication technology and human capital in environmental sustainability: evidence from Latin American and Caribbean countries. J Clean Prod 286:125529
Ahmed K, Long W (2013) An empirical analysis of CO2 emission in Pakistan using EKC hypothesis. J Int Trade Law Policy
Akbostancı E, Türüt-Aşık S, Tunç Gİ (2009) The relationship between income and environment in Turkey: is there an environmental Kuznets curve? Energy Policy 37(3):861–867
Al-Mulali U, Tang CF, Ozturk I (2015) Does financial development reduce environmental degradation? Evidence from a panel study of 129 countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(19):14891–14900
Alvi S, Chaudhry IS, Farooq F, Safdar N (2019) Trade liberalization, foreign direct investment inflows, environmental quality and economic growth nexus: a comparative analysis of Pakistan and China. Rev Appl Manag Soc Sci 2(1):17–26
Amri F (2018) Carbon dioxide emissions, total factor productivity, ICT, trade, financial development, and energy consumption: testing environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis for Tunisia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(33):33691–33701
Ang JB (2007) CO2 emissions, energy consumption, and output in France. Energy Policy 35(10):4772–4778
Anser MK, Shabbir MS, Tabash MI, Shah SHA, Ahmad M, Peng MYP, Lopez LB (2021) Do renewable energy sources improve clean environmental-economic growth? Empirical investigation from South Asian economies. Energy Explor Exploit 39(5):1491–1514
Asongu SA, Le Roux S, Biekpe N (2017) Environmental degradation, ICT and inclusive development in Sub-Saharan Africa. Energy Policy 111:353–361
Avom D, Nkengfack H, Fotio HK, Totouom A (2020) ICT and environmental quality in Sub-Saharan Africa: effects and transmission channels. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 155:120028
Baloch MA, Zhang J, Iqbal K, Iqbal Z (2019) The effect of financial development on ecological footprint in BRI countries: evidence from panel data estimation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(6):6199–6208
Balsalobre-Lorente D, Shahbaz M, Roubaud D, Farhani S (2018) How economic growth, renewable electricity and natural resources contribute to CO2 emissions? Energy Policy 113:356–367
Balsalobre-Lorente D, Ibáñez-Luzón L, Usman M, Shahbaz M (2022) The environmental Kuznets curve, based on the economic complexity, and the pollution haven hypothesis in PIIGS countries. Renew Energy 185:1441–1455
Bello AK, Abimbola OM (2010) Does the level of economic growth influence environmental quality in Nigeria: a test of environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis. Pak J Soc Sci 7(4):325–329
Bibi A, Li XM (2022) The asymmetric dilemma of renewable energy, financial development, and economic growth: fresh evidence from Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(21):31797–31806
Butala P, Oosthuizen G (2011) A sustainable manufacturing network model for socio-economic development. Annals of DAAAM & Proceedings 275–277
Cederborg J, Snöbohm S (2016) Is there a relationship between economic growth and carbon dioxide emissions?
Chandio AA, Jiang Y, Rehman A (2018) Energy consumption and agricultural economic growth in Pakistan: is there a nexus?. International Journal of Energy Sector Management
Cho JS, Kim T-H, Shin Y (2015) Quantile co-integration in the autoregressive distributed-lag modeling framework. Journal of Econometrics 188:281–300
Danish (2019) Effects of information and communication technology and real income on CO2 emissions: the experience of countries along Belt and Road. Telematics and Informatics, 45. Economics 85:104571
Destek MA, Sarkodie SA (2019) Investigation of environmental Kuznets curve for ecological footprint: the role of energy and financial development. Sci Total Environ 650:2483–2489
Destek MA, Ulucak R, Dogan E (2018) Analyzing the environmental Kuznets curve for the EU countries: the role of ecological footprint. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(29):29387–29396
Dogan E, Ozturk I (2017) The influence of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption and real income on CO2 emissions in the USA: evidence from structural break tests. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(11):10846–10854
Dogan E, Seker F (2016) The influence of real output, renewable and non-renewable energy, trade and financial development on carbon emissions in the top renewable energy countries. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 60:1074–1085
Erdoǧan S, Gedikli A, Yılmaz AD, Haider A, Zafar MW (2019) Investigation of energy consumption: economic growth nexus: a note on MENA sample. Energy Rep 5:1281–1292
Export.gov (2018) Pakistan - renewable energy. Available at: https://www.export.gov/article?id= Pakistan-Renewable-Energy (accessed 1 December 2019)
Farhani S, Ozturk I (2015) Causal relationship between CO2 emissions, real GDP, energy consumption, financial development, trade openness, and urbanization in Tunisia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(20):15663–15676
Fodha M, Zaghdoud O (2010) Economic growth and pollutant emissions in Tunisia: an empirical analysis of the environmental Kuznets curve. Energy Policy 38(2):1150–1156
Godil DI, Sharif A, Agha H, Jermsittiparsert K (2020) The dynamic non-linear influence of ICT, financial development, and institutional quality on CO2 emission in Pakistan: new insights from QARDL approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(19):24190–24200
Gomez-Zavaglia A, Mejuto JC, Simal-Gandara J (2020) Mitigation of emerging implications of climate change on food production systems. Food Res Int 134:109256
Gozgor G (2017) Does trade matter for carbon emissions in OECD countries? Evidence from a new trade openness measure. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(36):27813–27821
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1995) Economic growth and the environment. Q J Econ 110(2):353–377
Guoyan S, Khaskheli A, Raza SA, Shah N (2022) Analyzing the association between the foreign direct investment and carbon emissions in MENA countries: a pathway to sustainable development. Environ Dev Sustain 24(3):4226–4243
Hamid I, Jena PK, Mukhopdhyay D (2022) Should China prefer more foreign direct investment inflows to environmental change? J Public Aff 22(2):e2466
Hanif I, Raza SMF, Gago-de-Santos P, Abbas Q (2019) Fossil fuels, foreign direct investment, and economic growth have triggered CO2 emissions in emerging Asian economies: some empirical evidence. Energy 171:493–501
Hassan SA, Nosheen M (2018) The impact of air transportation on carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide emissions in Pakistan: evidence from ARDL modelling approach. Int J Innov Econ Dev 3(6):7–32
Hassan SA, Zaman K, Gul S (2015) The relationship between growth-inequality-poverty triangle and environmental degradation: unveiling the reality. Arab Econ Bus J 10(1):57–71
Higón DA, Gholami R, Shirazi F (2017) ICT and environmental sustainability: a global perspective. Telematics Inform 34(4):85–95
Hossain S (2012) An econometric analysis for CO 2 emissions, energy consumption, economic growth, foreign trade and urbanization of Japan
Huang Y, Khan J (2022) Has the information and communication technology sector become the engine of China’s economic growth? Rev Dev Econ 26(1):510–533
Huang Y, Haseeb M, Usman M, Ozturk I (2022) Dynamic association between ICT, renewable energy, economic complexity and ecological footprint: is there any difference between E-7 (developing) and G-7 (developed) countries? Technol Soc 68:101853
IEP. Pakistan Energy Demand Forecast (2021–2030) Report. 2021
Jaunky VC (2011) The CO2 emissions-income nexus: evidence from rich countries. Energy Policy 39(3):1228–1240
Jebli MB, Youssef SB, Ozturk I (2016) Testing environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: the role of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption and trade in OECD countries. Ecol Ind 60:824–831
Jena PK, Mujtaba A, Joshi DPP, Satrovic E, Adeleye BN (2022) Exploring the nature of EKC hypothesis in Asia’s top emitters: role of human capital, renewable and non-renewable energy consumption. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–20
Jiang C, Ma X (2019) The impact of financial development on carbon emissions: a global perspective. Sustainability 11(19):5241
Kamal M, Usman M, Jahanger A, Balsalobre-Lorente D (2021) Revisiting the role of fiscal policy, financial development, and foreign direct investment in reducing environmental pollution during globalization mode: evidence from linear and non-linear panel data approaches. Energies 14(21):6968
Kang YQ, Zhao T, Yang YY (2016) Environmental Kuznets curve for CO2 emissions in China: a spatial panel data approach. Ecol Ind 63:231–239
Karasoy A (2019) Drivers of carbon emissions in Turkey: considering asymmetric impacts. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(9):9219–9231
Kartal MT (2022) The role of consumption of energy, fossil sources, nuclear energy, and renewable energy on environmental degradation in top-five carbon producing countries. Renewable Energy 184:871–880
Khan N, Baloch MA, Saud S, Fatima T (2018) The effect of ICT on CO2 emissions in emerging economies: does the level of income matters? Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(23):22850–22860
Khan MTI, Yaseen MR, Ali Q (2019) Nexus between financial development, tourism, renewable energy, and greenhouse gas emission in high-income countries: a continent-wise analysis. Energy Economics 83:293–310
Khan MK, Khan MI, Rehan M (2020) The relationship between energy consumption, economic growth and carbon dioxide emissions in Pakistan. Financial Innovation 6(1):1–13
Khan NH, Ju Y, Latif Z, Khan K (2021) Nexus between carbon emission, financial development, and access to electricity: incorporating the role of natural resources and population growth. J Public Aff 21(1):e2131
Khaskheli A, Jiang Y, Raza SA, Khan KA, Qureshi MA (2021) Financial development, international trade, and environmental degradation: a nonlinear threshold model based on panel smooth transition regression. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(21):26449–26460
Kim TH, White H (2003) Estimation, inference, and specification testing for possibly misspecified quantile regression. In Maximum likelihood estimation of misspecified models: twenty years later. Bingley: Emerald Group Publishing Limited
Kuriqi A, Pinheiro AN, Sordo-Ward A, Garrote L (2019) Influence of hydrologically based environmental flow methods on flow alteration and energy production in a run-of-river hydropower plant. J Clean Prod 232:1028–1042
Lahiani A (2020) Is financial development good for the environment? An asymmetric analysis with CO2 emissions in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(8):7901–7909
Li R, Wang X, Wang Q (2022) Does renewable energy reduce ecological footprint at the expense of economic growth? An empirical analysis of 120 countries. J Clean Prod 346:131207
Lu WC (2018) The impacts of information and communication technology, energy consumption, financial development, and economic growth on carbon dioxide emissions in 12 Asian countries. Mitig Adapt Strat Glob Change 23(8):1351–1365
Lu WC (2020) The interplay among ecological footprint, real income, energy consumption, and trade openness in 13 Asian countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(36):45148–45160
Mahmoodi M, Dahmardeh N (2022) Environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis with considering ecological footprint and governance quality: evidence from emerging countries. Front Environ Sci 114:849676
Majeed MT, Tauqir A, Mazhar M, Samreen I (2021) Asymmetric effects of energy consumption and economic growth on ecological footprint: new evidence from Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(25):32945–32961
Mansoor A, Sultana B (2018) Impact of population, GDP and energy consumption on carbon emissions: evidence from Pakistan using an analytic tool IPAT. Asian Journal of Economics and Empirical Research 5(2):183–190
Menyah K, Wolde-Rufael Y (2010a) CO2 emissions, nuclear energy, renewable energy and economic growth in the US. Energy Policy 38(6):2911–2915
Menyah K, Wolde-Rufael Y (2010b) Energy consumption, pollutant emissions and economic growth in South Africa. Energy Econ 32(6):1374–1382
Mirza FM, Kanwal A (2017) Energy consumption, carbon emissions and economic growth in Pakistan: dynamic causality analysis. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 72:1233–1240
Mujtaba A, Jena PK, Mukhopadhyay D (2020) Determinants of CO2 emissions in upper middle-income group countries: an empirical investigation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(30):37745–37759
Mujtaba A, Jena PK, Bekun FV, Sahu PK (2022) Symmetric and asymmetric impact of economic growth, capital formation, renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on environment in OECD countries. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 160:112300
Munir Q, Lean HH, Smyth R (2020) CO2 emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in the ASEAN-5 countries: a cross-sectional dependence approach. Energy Economics 85:104571
Narayan PK, Narayan S (2010) Carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth: panel data evidence from developing countries. Energy Policy 38(1):661–666
Nathaniel SP, Adeleye N, Adedoyin FF (2021) Natural resource abundance, renewable energy, and ecological footprint linkage in MENA countries. Estudios de economía aplicada 39(2)
Nosheen M, Iqbal J, Hassan SA (2019) Economic growth, financial development, and trade in nexuses of CO2 emissions for Southeast Asia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(36):36274–36286
Omri A, Nguyen DK, Rault C (2014) Causal interactions between CO2 emissions, FDI, and economic growth: evidence from dynamic simultaneous-equation models. Econ Model 42:382–389
Onanuga OT (2017) The impact of economic and financial development on carbon emissions: evidence from Sub-Saharan Africa (Doctoral dissertation)
Osman M, Gachino G, Hoque A (2016) Electricity consumption and economic growth in the GCC countries: panel data analysis. Energy Policy 98:318–327
Ozcan B, Apergis N (2018) The impact of internet use on air pollution: Evidence from emerging countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(5):4174–4189
Pao HT, Tsai CM (2010) CO2 emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in BRIC countries. Energy Policy 38(12):7850–7860
Park Y, Meng F, Baloch MA (2018) The effect of ICT, financial development, growth, and trade openness on CO2 emissions: an empirical analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(30):30708–30719
Pejović B, Karadžić V, Dragašević Z, Backović T (2021) Economic growth, energy consumption and CO2 emissions in the countries of the European Union and the Western Balkans. Energy Rep 7:2775–2783
Piaggio M, Padilla E, Román C (2017) The long-term relationship between CO2 emissions and economic activity in a small open economy: Uruguay 1882–2010. Energy Economics 65:271–282
Raggad B (2020) Economic development, energy consumption, financial development, and carbon dioxide emissions in Saudi Arabia: new evidence from a non-linear and asymmetric analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(17):21872–21891
Ramzan M, Raza SA, Usman M, Sharma GD, Iqbal HA (2022) Environmental cost of non-renewable energy and economic progress: Do ICT and financial development mitigate some burden? J Clean Prod 333:130066
Raza SA, Shah N, Qureshi MA, Qaiser S, Ali R, Ahmed F (2020a) Non-linear threshold effect of financial development on renewable energy consumption: evidence from panel smooth transition regression approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(25):32034–32047
Raza SA, Shah N, Khan KA (2020b) Residential energy environmental Kuznets curve in emerging economies: the role of economic growth, renewable energy consumption, and financial development. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(5):5620–5629
Razzaq A, Sharif A, Ahmad P, Jermsittiparsert K (2020) Asymmetric role of tourism development and technology innovation on carbon dioxide emission reduction in the Chinese economy: fresh insights from QARDL approach. Sustain Dev 29(1):176–193
Rehman A, Rauf A, Ahmad M, Chandio AA, Deyuan Z (2019) The effect of carbon dioxide emission and the consumption of electrical energy, fossil fuel energy, and renewable energy, on economic performance: evidence from Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(21):21760–21773
Sabir S, Gorus MS (2019) The impact of globalization on ecological footprint: empirical evidence from the South Asian countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(32):33387–33398
Sadorsky P (2010) The impact of financial development on energy consumption in emerging economies. Energy Policy 38(5):2528–2535
Sahoo M, Sethi N (2021) The intermittent effects of renewable energy on ecological footprint: evidence from developing countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(40):56401–56417
Salahuddin M, Alam K, Ozturk I (2016) The effects of Internet usage and economic growth on CO2 emissions in OECD countries: a panel investigation. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 62:1226–1235
Sanderson H, Irato DM, Cerezo NP, Duel H, Faria P, Torres EF (2019) How do climate risks affect corporations and how could they address these risks? SN Applied Sciences 1(12):1–6
Sarkodie SA, Strezov V (2018) Empirical study of the environmental Kuznets curve and environmental sustainability curve hypothesis for Australia, China, Ghana and USA. J Clean Prod 201:98–110
Saud S, Chen S, Haseeb A (2019) Impact of financial development and economic growth on environmental quality: an empirical analysis from Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(3):2253–2269
Shabani ZD, Shahnazi R (2019) Energy consumption, carbon dioxide emissions, information and communications technology, and gross domestic product in Iranian economic sectors: a panel causality analysis. Energy 169:1064–1078
Shahbaz M, Lean HH, Shabbir MS (2012) Environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in Pakistan: co-integration and Granger causality. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 16(5):2947–2953
Shaikh ZA, Khoja SA (2011) Role of ICT in shaping the future of pakistani higher education system. Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology-TOJET 10(1):149–161
Sharif A, Raza SA, Ozturk I, Afshan S (2019) The dynamic relationship of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption with carbon emission: a global study with the application of heterogeneous panel estimations. Renewable Energy 133:685–691
Shehzad K, Xiaoxing L, Sarfraz M (2021) Envisaging the asymmetrical association among FDI, ICT, and climate change: a case from developing country. Carbon Management 12(2):123–137
Shen Y, Su ZW, Malik MY, Umar M, Khan Z, Khan M (2021) Does green investment, financial development and natural resources rent limit carbon emissions? A provincial panel analysis of China. Sci Total Environ 755:142538
Siddique HMA, Majeed DMT, Ahmad DHK (2020) The impact of urbanization and energy consumption on CO2 emissions in South Asia. South Asian Studies 31(2)
Sirag A, Matemilola BT, Law SH, Bany-Ariffin AN (2018) Does environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis exist? Evidence from dynamic panel threshold. J Environ Econ Policy 7(2):145–165
Solarin SA (2019) Convergence in CO 2 emissions, carbon footprint and ecological footprint: evidence from OECD countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(6):6167–6181
Stern DI (2011) The role of energy in economic growth. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1219(1):26–51
Streimikiene D (2020) Ranking of Baltic States on progress towards the main energy security goals of European energy union strategy. J Int Stud 13(4):24–37
Tamazian A, Rao BB (2010) Do economic, financial and institutional developments matter for environmental degradation? Evidence from Transitional Economies. Energy Econ 32(1):137–145
Tang C, Wu X, Zheng Q, Lyu N (2018) Ecological security evaluations of the tourism industry in Ecological Conservation Development Areas: a case study of Beijing’s ECDA. J Clean Prod 197:999–1010
Toumi S, Toumi H (2019) Asymmetric causality among renewable energy consumption, CO2 emissions, and economic growth in KSA: evidence from a non-linear ARDL model. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(16):16145–16156
Tsaurai K (2019) The impact of financial development on carbon emissions in Africa. Int J Energy Econ Policy 9(3):144
Ullah A, Zhang Q, Raza SA, Ali S (2021) Renewable energy: is it a global challenge or opportunity? Focusing on different income level countries through Panel Smooth Transition Regression Model. Renew Energy 177:689–699
Usman M, Balsalobre-Lorente D (2022) Environmental concern in the era of industrialization: can financial development, renewable energy and natural resources alleviate some load? Energy Policy 162:112780
Usman M, Makhdum MSA (2021) What abates ecological footprint in BRICS-T region? Exploring the influence of renewable energy, non-renewable energy, agriculture, forest area and financial development. Renewable Energy 179:12–28
Usman M, Radulescu M (2022) Examining the role of nuclear and renewable energy in reducing carbon footprint: does the role of technological innovation really create some difference? Sci Total Environ 841:156662
Usman A, Ozturk I, Ullah S, Hassan A (2021) Does ICT have symmetric or asymmetric effects on CO2 emissions? Evidence from selected Asian economies. Technol Soc 67:101692
Usman M, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Jahanger A, Ahmad P (2022a) Pollution concern during globalization mode in financially resource-rich countries: do financial development, natural resources, and renewable energy consumption matter? Renewable Energy 183:90–102
Usman M, Jahanger A, Makhdum MSA, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Bashir A (2022b) How do financial development, energy consumption, natural resources, and globalization affect Arctic countries’ economic growth and environmental quality? An Advanced Panel Data Simulation. Energy 241:122515
Usman M, Jahanger A, Radulescu M, Balsalobre-Lorente D (2022c) Do nuclear energy, renewable energy, and environmental-related technologies asymmetrically reduce ecological footprint? Evidence from Pakistan. Energies 15(9):3448
Usman M, Kousar R, Makhdum MSA, Yaseen MR, Nadeem AM (2022d) Do financial development, economic growth, energy consumption, and trade openness contribute to increase carbon emission in Pakistan? An insight based on ARDL bound testing approach. Environ Dev Sustain 1–30
Wan X, Jahanger A, Usman M, Radulescu M, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Yu Y (2022) Exploring the effects of economic complexity and the transition to a clean energy pattern on ecological footprint from the Indian perspective. Front Environ Sci 736
Wang Z, Zhang B, Wang B (2018) Renewable energy consumption, economic growth and human development index in Pakistan: evidence form simultaneous equation model. J Clean Prod 184:1081–1090
Wolde-Rufael Y (2009) Energy consumption and economic growth: The experience of African countries revisited. Energy Econ 31(2):217–224
WWEA (2019) World Wind Energy Association
Yang B, Jahanger A, Ali M (2021a) Remittance inflows affect the ecological footprint in BICS countries: do technological innovation and financial development matter? Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(18):23482–23500
Yang B, Jahanger A, Usman M, Khan MA (2021b) The dynamic linkage between globalization, financial development, energy utilization, and environmental sustainability in GCC countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(13):16568–16588
Zaidi SAH, Zafar MW, Shahbaz M, Hou F (2019) Dynamic linkages between globalization, financial development and carbon emissions: evidence from Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation countries. J Clean Prod 228:533–543
Zhang F (2018) In the dark: how much do power sector distortions cost south Asia? World Bank Publications, Washington, D.C
Zhang N, Yu K, Chen Z (2017) How does urbanization affect carbon dioxide emissions? A cross-country panel data analysis. Energy Policy 107:678–687
Zhang B, Du Z, Wang B, Wang Z (2018) Motivation and challenges for e-commerce in e-waste recycling under “Big data” context: a perspective from household willingness in China. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 144:436–444
Zhongming Z, Linong L, Xiaona Y, Wangqiang Z, Wei L (2021) Global energy review 2021
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Syed Ali Raza: conceptualization, writing — original draft, writing — review and editing, and supervision. Sara Qamar: writing — original draft, writing — review and editing, data curation, methodology, and formal analysis. Maiyra Ahmed: writing — original draft, writing — review and editing, data curation, methodology, and formal analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ilhan Ozturk
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Raza, S.A., Qamar, S. & Ahmed, M. Asymmetric role of non-renewable energy consumption, ICT, and financial development on ecological footprints: evidence from QARDL approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 20746–20764 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23549-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23549-w