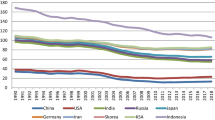
Abstract
The economies of the emerging seven (E7) are not insulated from the climate change challenges, which is a key concern for most countries. The E7 nations have undertaken part in initiatives to combat climate change, particularly in terms of reducing CO2 emissions from the trajectory of productivity expansion in their countries. It is for this reason that this study examines the impact of resource volatility, renewable energy, and fossil fuel on both economic performance and CO2 emission from 1990 to 2018. The present study used panel quantile regression and Driscoll-Kraay fixed effect-OLS estimators to examine these associations. From model I, the outcome shows that economic performance, natural gas rent, coal rent, and fossil fuel impact CO2 emission positively. Moreover, oil rent, renewable energy, investment in energy, and the interaction between investment in energy and renewable energy also negatively and significantly impact CO2 emission. On the other hand, model II which has economic performance as a dependent variable shows that all the understudy variables have significant positive relations with economic performance. Based on the empirical outcome, policy ramifications are provided.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- E7:
-
Emerging seven
- G7:
-
Group of seven
- FMOLS:
-
Fully modified least square
- ARDL:
-
Autoregressive distributed lag model
- FDI:
-
Foreign direct investment
- QQ:
-
Quantile on quantile regression
- MMQR:
-
Moment of moment quantile regression
- CS-ARDL:
-
Cross-sectional Autoregressive distributed lag model
- DOLS:
-
Dynamic ordinal least square
References
AbdulKareem HK, Kirikkaleli D, Adebayo TS, Shah MI, Abbas S (2022) CO2 behavior amidst the COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom: the role of renewable and nonrenewable energy development. Renew Energy
Adabor O, Buabeng E, Dunyo JF (2022) The causative relationship between natural resource rent and economic growth: evidence from Ghana’s crude oil resource extraction. Intl J Energy Sect Manag
Adams S, Klobodu EKM, Apio A (2018) Renewable and nonrenewable energy, regime type and economic growth. Renew Energy 125:755–767
Adebayo TS, Rjoub H (2022) A new perspective into the impact of renewable and nonrenewable energy consumption on environmental degradation in Argentina: a time–frequency analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(11):16028–16044
Adebayo TS, Agyekum EB, Kamel S, Zawbaa HM, Altuntaş M (2022a) Drivers of environmental degradation in Turkey: designing an SDG framework through advanced quantile approaches. Energy Rep 8:2008–2021
Adebayo TS, Kalmaz Beton D (2020) Ongoing debate between foreign aid and economic growth in Nigeria: a wavelet analysis. Soc Sci Quart 101(5):2032–2051
Adebayo TS, Rjoub H, Akinsola GD, Oladipupo SD (2022b) The asymmetric effects of renewable energy consumption and trade openness on carbon emissions in Sweden: new evidence from quantile-on-quantile regression approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(2):1875–1886
Adebayo TS, Wang C, Raza SA, Yi S, Shah MI (2021) The roles of hydro, nuclear and biomass energy towards carbon neutrality target in China: a policy-based analysis. Energy 262:125303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.125303
Adedoyin FF, Bein MA, Gyamfi BA, Bekun FV (2021) Does agricultural development induce environmental pollution in E7? A myth or reality. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(31):41869–41880
Agboola MO, Bekun FV, Joshua U (2021) Pathway to environmental sustainability: Nexus between economic growth, energy consumption, CO2 emission, oil rent and total natural resources rent in Saudi Arabia. Res Policy 74:102380
Agboola MO, Bekun FV, Osundina OA, Kirikkaleli D (2022a) Revisiting the economic growth and agriculture nexus in Nigeria: evidence from asymmetric cointegration and frequency domain causality approaches. J Public Aff 22(1):e2271
Agboola PO, Hossain M, Gyamfi BA, Bekun FV (2022b) Environmental consequences of foreign direct investment influx and conventional energy consumption: evidence from dynamic ARDL simulation for Turkey. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–14
Agozie DQ, Gyamfi BA, Bekun FV, Ozturk I, Taha A (2022) Environmental Kuznets Curve hypothesis from lens of economic complexity index for BRICS: evidence from second generation panel analysis. Sustain Energy Technol Assess 53:102597
Akadiri SS, Bekun FV, Taheri E, Akadiri AC (2019) Carbon emissions, energy consumption and economic growth: a causality evidence. Intl J Energy Technol Policy 15(2-3):320–336
Akinsola GD, Kirikkaleli D, Adebayo TS, Bekun FV, Umarbeyli S, Osemeahon OS (2021) Economic performance of Indonesia amidst CO2 emissions and agriculture: a time series analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(35):47942–47956
Appiah M, Gyamfi BA, Adebayo TS, Bekun FV (2022) Do financial development, foreign direct investment, and economic growth enhance industrial development? Fresh evidence from Sub-Sahara African countries. Port Econ J:1–25
Asif M, Bashir S, Khan S (2021) Impact of nonrenewable and renewable energy consumption on economic growth: evidence from income and regional groups of countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(29):38764–38773
Awosusi AA, Adebayo TS, Altuntaş M, Agyekum EB, Zawbaa HM, Kamel S (2022) The dynamic impact of biomass and natural resources on ecological footprint in BRICS economies: a quantile regression evidence. Energy Rep 8:1979–1994
Awosusi AA, Adebayo TS, Kirikkaleli D, Akinsola GD, Mwamba MN (2021) Can CO2 emissions and energy consumption determine the economic performance of South Korea? A time series analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(29):38969–38984
Balcilar M, Bekun FV, Uzuner G (2019) Revisiting the economic growth and electricity consumption nexus in Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(12):12158–12170
Balsalobre-Lorente D, Bekun FV, Etokakpan MU, Driha OM (2019) A road to enhancements in natural gas use in Iran: a multivariate modelling approach. Res Policy 64:101485
Bamidele R, Ozturk I, Gyamfi BA, Bekun FV (2022) Tourism-induced pollution emission amidst energy mix: evidence from Nigeria. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(13):19752–19761
Bekun FV (2022) Mitigating emissions in India: accounting for the role of real income, renewable energy consumption and investment in energy. Int J Energy Econ Policy 12(1):188–192
Bekun FV, Agboola MO (2019) Electricity consumption and economic growth nexus: evidence from Maki cointegration. Eng Econ 30(1):14–23
Bekun FV, Alola AA, Gyamfi BA, Ampomah AB (2021b) The environmental aspects of conventional and clean energy policy in sub-Saharan Africa: is N-shaped hypothesis valid? Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(47):66695–66708
Bekun FV, Alola AA, Gyamfi BA, Yaw SS (2021a) The relevance of EKC hypothesis in energy intensity real-output trade-off for sustainable environment in EU-27. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(37):51137–51148
Ben-Amar W, Francoeur C, Hafsi T, Labelle R (2013) What makes better boards? A closer look at diversity and ownership. Br J Manag 24(1):85–101
Breusch TS, Pagan AR (1980) The Lagrange multiplier test and its applications to model specification in econometrics. Rev Econ Stud 47(1):239–253. https://doi.org/10.2307/2297111
Bright BA, Ozturk I, Bein MA, Bekun FV (2021) An investigation into the anthropogenic effect of biomass energy utilization and economic sustainability on environmental degradation in E7 economies. Biofuels Bioprod Bioref 15(3):840–851
Canh NP, Schinckus C, Thanh SD (2020) The natural resources rents: is economic complexity a solution for resource curse? Res Policy 69:101800
Etokakpan MU, Solarin SA, Yorucu V, Bekun FV, Sarkodie SA (2020) Modeling natural gas consumption, capital formation, globalization, CO2 emissions and economic growth nexus in Malaysia: fresh evidence from combined cointegration and causality analysis. Energy Strat Rev 31:100526
Farabi A, Abdullah A, Setianto RH (2019) Energy consumption, carbon emissions and economic growth in Indonesia and Malaysia. Int J Energy Econ Policy 9:338–345
Fareed Z, Salem S, Adebayo TS, Pata UK, Shahzad F (2021) Role of export diversification and renewable Energy on the load capacity factor in Indonesia: a Fourier quantile causality approach. Front Environ Sci 434
Gyamfi BA (2022) Consumption-based carbon emission and foreign direct investment in oil-producing Sub-Sahara African countries: the role of natural resources and urbanization. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(9):13154–13166
Gyamfi BA, Adebayo TS, Bekun FV, Agyekum EB, Kumar NM, Alhelou HH, Al-Hinai A (2021a) Beyond environmental Kuznets curve and policy implications to promote sustainable development in Mediterranean. Energy Rep 7:6119–6129
Gyamfi BA, Adedoyin FF, Bein MA, Bekun FV, Agozie DQ (2021b) The anthropogenic consequences of energy consumption in E7 economies: juxtaposing roles of renewable, coal, nuclear, oil and gas energy: evidence from panel quantile method. J Clean Prod 295:126373
Gyamfi BA, Onifade ST, Nwani C, Bekun FV (2022) Accounting for the combined impacts of natural resources rent, income level, and energy consumption on environmental quality of G7 economies: a panel quantile regression approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(2):2806–2818
He K, Ramzan M, Awosusi AA, Ahmed Z, Ahmad M, Altuntaş M (2021) Does globalization moderate the effect of economic complexity on CO2 emissions? Evidence from the top 10 energy transition economies. Front Environ Sci 555
Inuwa N, Adamu S, Sani MB, Modibbo HU (2022) Natural resource and economic growth nexus in Nigeria: a disaggregated approach. Lett Spat Resour Sci 1–21
Iqbal A, Tang X, Rasool SF (2022) Investigating the nexus between CO2 emissions, renewable energy consumption, FDI, exports and economic growth: evidence from BRICS countries. Environ Dev Sustain 1–30
Kirikkaleli D, Adebayo TS, Khan Z, Ali S (2021) Does globalization matter for ecological footprint in Turkey? Evidence from dual adjustment approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(11):14009–14017
Koenker R (2004) Quantile regression for longitudinal data. J Multivar Anal 91(1):74–89
Koenker, R., & Bassett Jr, G. (1978). Regression quantiles. Econometrica: J Econ Soc 33–50
Ma H, Rehman A, Ozturk I, Murshed M, Dagar V (2021) The dynamic impacts of CO2 emissions from different sources on Pakistan’s economic progress: a roadmap to sustainable development. Environ Dev Sustain 23(12):17857–17880
Mahmood H, Furqan M (2021) Oil rents and greenhouse gas emissions: spatial analysis of Gulf cooperation council countries. Environ Dev Sustain 23(4):6215–6233
Miao Y, Razzaq A, Adebayo TS, Awosusi AA (2022) Do renewable energy consumption and financial globalisation contribute to ecological sustainability in newly industrialized countries? Renew Energy
Nakhli MS, Shahbaz M, Jebli MB, Wang S (2022) Nexus between economic policy uncertainty, renewable & nonrenewable energy and carbon emissions: contextual evidence in carbon neutrality dream of USA. Renew Energy 185:75–85
Ohajionu UC, Gyamfi BA, Haseki MI, Bekun FV (2022) Assessing the linkage between energy consumption, financial development, tourism and environment: evidence from method of moments quantile regression. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(20):30004–30018
Onifade ST, Gyamfi BA, Bekun FV, Altuntaş M (2022) Significance of air transport to tourism-induced growth hypothesis in e7 economies: exploring the implications for environmental quality. Tour Intl Interdisc J 70(3):339–353
Onifade ST, Gyamfi BA, Haouas I, Bekun FV (2021) Re-examining the roles of economic globalization and natural resources consequences on environmental degradation in E7 economies: are human capital and urbanization essential components? Res Policy 74:102435
Ozcan B, Tzeremes PG, Tzeremes NG (2020) Energy consumption, economic growth and environmental degradation in OECD countries. Econ Model 84:203–213
Pesaran HM (2007) A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross-section dependence. J Appl Econ 22:265–312. https://doi.org/10.1002/jae.951
Pesaran MH (2015) Testing weak cross-sectional dependence in large panels. Econ Rev 34(6-10):1089–1117. https://doi.org/10.1080/07474938.2014.956623
Pesaran MH, Yamagata T (2008) Testing slope homogeneity in large panels. J Econ 142(1):50–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeconom.2007.05.010
Pesaran MH, Ullah A, Yamagata T (2008) A bias-adjusted LM test of error cross-section independence. Econ J 11(1):105–127
Powell D (2016) Quantile regression with nonadditive fixed effects. Quant Treat Eff 1(28):1–33
Rahman MM, Velayutham E (2020) Renewable and nonrenewable energy consumption-economic growth nexus: new evidence from South Asia. Renew Energy 147:399–408
Ramzan M, Raza SA, Usman M, Sharma GD, Iqbal HA (2022) Environmental cost of nonrenewable energy and economic progress: do ICT and financial development mitigate some burden? J Clean Prod 333:130066
Rjoub H, Adebayo TS, Oladipupo SD, Adeshola I (2021) Wavelet analysis of impact of renewable energy consumption and technological innovation on CO2 emissions: evidence from Portugal. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–18
Sinha A, Zafar MW, Ahmed Z, Qin Q, Zaidi SAH (2021) Effects of biomass energy consumption on environmental quality: the role of education and technology in Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation countries. Renew Sust Energ Rev 142:110868
Solarin SA, Bello MO, Bekun FV (2021b) Sustainable electricity generation: the possibility of substituting fossil fuels for hydropower and solar Energy in Italy. Int J Sustain Dev World Ecol 28(5):429–439
Solarin SA, Nathaniel SP, Bekun FV, Okunola AM, Alhassan A (2021a) Towards achieving environmental sustainability: environmental quality versus economic growth in a developing economy on ecological footprint via dynamic simulations of ARDL. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(14):17942–17959
Steve YS, Murad AB, Gyamfi BA, Bekun FV, Uzuner G (2022) Renewable energy consumption a panacea for sustainable economic growth: panel causality analysis for African blocs. Int J Green Energy 19(8):847–856
Udemba EN, Güngör H, Bekun FV, Kirikkaleli D (2021) Economic performance of India amidst high CO2 emissions. Sustain Product Consump 27:52–60
Wang KH, Liu L, Adebayo TS, Lobonț OR, Claudia MN (2021) Fiscal decentralization, political stability and resources curse hypothesis: a case of fiscal decentralized economies. Resour Policy 72:102071
Westerlund J (2007) Testing for error correction in panel data. Oxf Bull Econ Stat 69(6):709–748
World Bank (2021) World Development Indicators. https://databank.worldbank.org/source/world-development-indicators#
Wu D, Yang Y, Shi Y, Xu M, Zou W (2022) Renewable energy resources, natural resources volatility and economic performance: evidence from BRICS. Res Policy 76:102621
Zahoor Z, Khan I, Hou F (2022) Clean energy investment and financial development as determinants of environment and sustainable economic growth: evidence from China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(11):16006–16016
Acknowledgements
Author gratitude is extended to the prospective editor(s) and reviewers that will/have spared time to guide toward a successful publication.
The Author of this article also assures that they follow the springer publishing procedures and agree to publish it as any form of access article confirming to subscribe access standards and licensing.
Many thanks in advance look forward to your favorable response
Yours truly,
Authors
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The first author Dr, Bright Akwasi Gyamfi was responsible for the conceptual construction of the study’s idea, managed the data gathering and preliminary analysis, and was responsible for proofreading and manuscript editing. The second author Dr. Tomiwa Sunday Adebayo handled the introduction, and the literature section managed the data gathering, and preliminary analysis, and was responsible for proofreading and manuscript editing. For blinded copy’s sake. A list of authorship contributions is appended in a separate file. All authors have contributed equally as well as approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The authors mentioned in the manuscript have agreed to authorship read and approved the manuscript and given consent for submission and subsequent publication of the manuscript.
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Roula Inglesi-Lotz
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• The study investigates the effect of natural resources volatilities and renewable energy on both environmental and economic performance.
• Natural gas rent and coal rent have positive impact on environmental degradation.
• Renewable energy consumption impact CO2 emissions negatively.
• All the variables impact economic performance positively.
• To reduce CO2 emission, the E7 economics should shift to renewable energy consumption.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gyamfi, B.A., Adebayo, T.S. Do natural resource volatilities and renewable energy contribute to the environment and economic performance? Empirical evidence from E7 economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 19380–19392 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23457-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23457-z