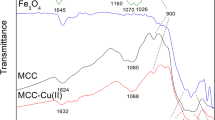
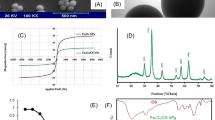
Abstract
Due to its wide use in anticonvulsant pharmacotherapy, phenobarbital (PHEN) is an aquatic contaminant with a high prevalence in the environment. In this adsorption study, chitosan and chitosan-based magnetic adsorbents containing different amounts of incorporated magnetite (CS, CS·Fe3O4 1:1, CS·Fe3O4 1:5, and CS·Fe3O4 1:10) were used for phenobarbital removal. The magnetic adsorbents were synthesized by co-precipitation method and characterized through FTIR, XRD, MEV, and VSM analysis. In PHEN adsorption, the equilibrium and adsorption kinetic were better adjusted by the Sips and pseudo-second-order model, respectively. Among the four nanoadsorbents used, the maximum phenobarbital adsorption capacity was 94.60 mg g−1 using 25 mg of CS·Fe3O4 1:5, with a concentration of PHEN (50 mg L−1), pH 7.0 at room temperature. The parameters of pH, adsorbent dosage, ionic strength, and thermodynamic study were tested for the adsorbent with the highest performance (CS·Fe3O4 1:5). The nanoadsorbent demonstrates efficiency in the removal of the contaminant for diverse adsorption cycles. Finally, the protocol employing magnetic adsorbents dispenses the subsequent steps of filtration and centrifugation.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Affonso LN, Marques JL Jr, Lima VV, Gonçalves JO, Barbosa SC, Primel EG, Burgo TAL, Dott GL, Pinto LAA, Cadaval TR Jr (2020) Removal of fluoride from fertilizer industry effluent using carbon nanotubes stabilized in chitosan sponge. J Hazard Mater 388:122042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122042
Alsamman MT, Sánchez J (2021) Recent advances on hydrogels based on chitosan and alginate for the adsorption of dyes and metal ions from water. Arab J Chem 14:103455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103455
Asgari E, Sheikhmohammadi A, Yeganeh J (2020) Application of the Fe3O4-chitosan nano-adsorbent for the adsorption of metronidazole from wastewater: optimization, kinetic, thermodynamic and equilibrium studies. Int J Biol 164:694–706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.188
Ashtarinezhad A, Panahyab A, Shaterzadeh-Oskouei S, Khoshniat H, Mohamadzadehasl B, Shirazi FH (2016) Teratogenic study of phenobarbital and levamisole on mouse fetus liver tissue using biospectroscopy. Pharm Biomed 128:174–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2016.05.05
Avdeef A (2014) Anomalous solubility behavior of several acidic drugs. ADMET and DMPK 2:33–42. https://doi.org/10.5599/admet.2.1.30
Bahrudin NN, Nawi MA, Jawad AH, Sabar S (2020) Adsorption characteristics and mechanistic study of immobilized chitosan-montmorillonite composite for methyl orange removal. J Polym Environ 28(7):1901–1913. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-020-01734-7
Baytar O, Şahin Ö, Saka C (2018) Sequential application of microwave and conventional heating methods for preparation of activated carbon from biomass and its methylene blue adsorption. Appl Therm Eng 138:542–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.04.039
Batur E, Baytar O, Kutluay S, Horoz S, Şahin O (2021) A comprehensive new study on the removal of Pb (II) from aqueous solution by şırnak coal-derived char Environ. Technol 42(3):505–520. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2020.1811397
Batur E, Kutluay S (2022) Dynamic adsorption behavior of benzene, toluene, and xylene VOCs in single- and multi-component systems by activated carbon derived from defatted black cumin (Nigella sativa L) biowaste. J Environ Chem Eng 10(3):107565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.107565
Boleda MR, Galceran MT, Ventura F (2013) Validation and uncertainty estimation of a multiresidue method for pharmaceuticals in surface and treated waters by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1286:146–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.07.066
Bruckmann FS, Viana AR, Lopes LQS, Santos RCV, Muller EI, Mortari SR, Rhoden CRB (2022a) Synthesis, characterization, and biological activity evaluation of magnetite-functionalized eugenol. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 1-14.https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02207-7
Bruckmann FS, Viana AR, Tonel MZ, Fagan SB, Garcia WJS, Oliveira AH, Dorneles LS, Mortari SR, Silva WL, Silva IZ, Rhoden CRB (2022b) Influence of magnetite incorporation into chitosan on the adsorption of the methotrexate and in vitro cytotoxicity. Accept for publication, Environ Sci Pollut Res
Bruckmann FS, Zuchetto T, Ledur CM, dos Santos CL, da Silva WL, Fagan SB, da Silva IZ, Rhoden CRB (2022c) Methylphenidate adsorption onto graphene derivatives: theory and experiment. New J Chem 46:4283–4291. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NJ03916D
Cao H, Lin X, Zhan H, Zhang H, Lin J (2013) Photocatalytic degradation kinetics and mechanism of phenobarbital in TiO2 aqueous solution. Chemosphere 90:1514–1519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.07.066
Da Silva Alves DC, Healy B, Pinto LA, Cadaval TR, Breslin CB (2021) Recent developments in chitosan-based adsorbents for the removal of pollutants from aqueous environments. Molecules 26(3):594. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26030594
da Rosa Salles T, de Bitencourt Rodrigues H, da Silva Bruckmann F, Alves LCS, Mortari, SR, Rhoden, CRB (2020) Graphene oxide optimization synthesis for application on laboratory of Universidade Franciscana. Discip Sci Sér Ciên Nat Tecnol 21:3:15–26. https://doi.org/10.37779/nt.v21i3.3632
Da Rosa Salles T, da Silva Bruckamann F, Viana AR, Krause LMF, Mortari SR, Rhoden CRB (2022) Magnetic nanocrystalline cellulose: azithromycin adsorption and in vitro biological activity against melanoma cells. J Polym Environ. 1-19.https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02388-3
da Silva Bruckmann F, Pimentel AC, Viana AR, da Rosa Salles T, Krause LMF, Mortari SR, da Silva IZ, Rhoden CRB (2020). Synthesis characterization and cytotoxicity evaluation of magnetic nanosilica in L929 cell line. Discip Sci Sér Ciên Nat Tecnol 21:3:01-14 https://doi.org/10.37779/nt.v21i3.3631
Da Silva Bruckmann, F, Ledur, CM, da Silva, IZ, Dotto, GL, Rhoden CRB (2022) A DFT theoretical and experimental study about tetracycline adsorption onto magnetic graphene oxide. J Mol Liq 118837.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2022.118837
De Oliveira ÉC, da Silva BF, Schopf PF, Viana AR, Mortari SR, Sagrillo MR, Vasconscelos NJ, Fernandes LS, Bohn Rhoden CR (2022) In vitro and in vivo safety profile assessment of graphene oxide decorated with different concentrations of magnetite. J Nanopart Res 24(7):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-022-05529-w
Dotto G, Moura J, Cadaval T, Pinto L (2013) Application of chitosan films for the removal of food dyes from aqueous solutions by adsorption. Chem Eng J 214:8–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.10.027
Dutta B, Checker S, Barick KC, Salunke HG, Gota V, Hassan PA (2021) Malic acid grafted Fe3O4 nanoparticles for controlled drug delivery and efficient heating source for hyperthermia therapy. J Alloys Compd 883:160950. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.160950
Genli N, Kutluay S, Baytar O, Şahin O (2022) Preparation and characterization of activated carbon from hydrochar by hydrothermal carbonization of chickpea stem: an application in methylene blue removal by RSM optimization. Int J Phytoremediation 24(1):88–100. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2021.1926911
Grujić S, Vasiljević T, Laušević M (2009) Determination of multiple pharmaceutical classes in surface and ground waters by liquid chromatography–ion trap–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1216:4989–5000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2009.04.059
Gupta KK, Kumar V, Tikoo KB, Kaushik A, Singhal S (2020) Encrustation of cadmium sulfide nanoparticles into the matrix of biomass derived silanized cellulose nanofibers for adsorptive detoxification of pesticide and textile waste. Chem Eng 385:123700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123700
Hass U, Duennbier U, Massmann G (2012) Occurrence and distribution of psychoactive compounds and their metabolites in the urban water cycle of Berlin (Germany). Water Res 46:6013–6022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.08.025
Hizal J, Kanmaz N, Yilmazoğlu M (2021) Adsorption efficiency of sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) (sPEEK) as a novel low-cost polymeric adsorbent for cationic organic dyes removal from aqueous solution. J Mol Liq 322:114761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114761
Johannessen SI (2004) Therapeutic drug monitoring of antiepileptic drugs. In: Handb. Anal. Sep. Elsevier Science BV 221–253
Khmara I, Molcan M, Antosova A, Zavisova BZ, V, Kubovcikova M, Jurikova A, Girman V, Baranovicova E, Koneracka M, Gazova Z, (2020) Bioactive properties of chitosan stabilized magnetic nanoparticles–focus on hyperthermic and anti-amyloid activities. J Magn Magn Mater 513:167056. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2020.167056
Kutluay S, Baytar O, Şahin O, Arran A (2020) Optimization of process conditions for adsorption of methylene blue on formaldehyde-modified peanut shells using box-behnken experimental design and response surface methodology. EJT, 10:1, 131–142. https://doi.org/10.36222/ejt.649205
Kwon JH, Wilson LD, Ramaswami S (2014) Sorptive uptake studies of an aryl-arsenical with iron oxide composites on an activated carbon support. Materials 7(3):1880–1898. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7031880
Luján-Facundo MJ, Iborra-Clar MI, Mendoza-Roca JA, Alcaina-Miranda MI (2019) Pharmaceutical compounds removal by adsorption with commercial and reused carbon coming from a drinking water treatment plant. J Clean Prod 238:11786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117866
Machado TS, Crestani L, Marchezi G, Melara F, de Mello JR, Dotto GL, Piccin JS (2022) Synthesis of glutaraldehyde-modified silica/chitosan composites for the removal of water-soluble diclofenac sodium. Carbohydr Polym 277:118868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118868
Nicomel NR, Otero-Gonzalez L, Folens K, Mees B, Hennebel T, Du Laing G (2021) Selective and enhanced nickel adsorption from sulfate-and calcium-rich solutions using chitosan. Sep Purif Technol 276:119283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119283
Payel S, Hashem MdA, Hasan MdA (2021) Recycling biochar derived from tannery liming sludge for chromium adsorption in static and dynamic conditions. Environ Technol Innov 24:102010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.102010
Pohndorf R, Cadaval T, Pinto L (2016) Kinetics and thermodynamics adsorption of carotenoids and chlorophylls in rice bran oil bleaching. J Food Eng 185:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2016.03.028
Raol YH, Zhang G, Budreck EC, Brooks-Kayal AR (2005) Long-term effects of diazepam and phenobarbital treatment during development on GABA receptors, transporters and glutamic acid decarboxylase. Neuroscience 132:399–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.01.005
Ribicki AC, Sperandio, ML, Haandel VJV, Estrada RA, Fujiwara ST (2020) Synthesis and characterization of hybrid polymer based on functionalized silica as efficient adsorbent for heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. J Braz Chem Soc 31:2049–2057. https://doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20200105
Rhoden CRB, da Silva BF, da Rosa ST, Junior CGK, Mortari SR (2021) Study from the influence of magnetite onto removal of hydrochlorothiazide from aqueous solutions applying magnetic graphene oxide. J Water Process Eng 43:102262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102262
Samadi A, Xie M, Li J, Shon H, Zheng C, Zhao S (2021) Polyaniline-based adsorbents for aqueous pollutants removal: A review. Chem Eng J 418:129425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129425
Saka C, Kutluay ŞÖ, S, (2016) Cold plasma and microwave radiation applications for surface modification on the pistachio husk-based adsorbent and its effects on the adsorption of rhodamine B. Energy Sources a: Recovery Util 38(3):339–346. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2013.766659
Sarker S, Akbor MA, Nahar A, Hasan M, Islam ARMT, Siddique MAB (2021) Level of pesticides contamination in the major river systems: a review on South Asian countries perspective. Heliyon 7(6):07270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07270
Şahin O, Saka C, Ceyhan AA, Baytar Ö et al (2015) Preparation of high surface area activated carbon from Elaeagnus angustifolia seeds by chemical activation with ZnCl2 in one-step treatment and its iodine adsorption. Sep Sci Technol 50(6):886–891. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2014.966204
Subedi N, Lähde A, Abu-Danso E, Iqbal J, Bhatnagar A (2019) A comparative study of magnetic chitosan (Chi@ Fe3O4) and graphene oxide modified magnetic chitosan (Chi@ Fe3O4GO) nanocomposites for efficient removal of Cr (VI) from water. Int J Biol 137:948–959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.06.151
Subramaniam S, Foo KY, Yusof EM, Jawad AH, Wilson LD, Sabar S (2021) Hydrothermal synthesis of phosphorylated chitosan and its adsorption performance towards Acid Red 88 dye. Int J Biol 193:1716–1726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.11.009
Tran HN, Lima EC, Juang RS, Bollinger JC, Chao HP (2021) Thermodynamic parameters of liquid–phase adsorption process calculated from different equilibrium constants related to adsorption isotherms: a comparison study. J Environ Chem Eng 9(6):106674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106674
Velayati S, Saadati F, Shayani-Jam H, Shekari A, Valipour R, Yaftian MR (2022) Fabrication and evaluation of a molecularly imprinted polymer electrochemical nanosensor for the sensitive monitoring of phenobarbital in biological samples. J Microchem 174:107063. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.107063
Viana AR, Salles B, da Silva Bruckmann F, Krause LMF, Mortari SR, Rhoden CRB (2019) Cytotoxicity study of graphene oxide against vero lineage cells. Discip Sci Sér Ciên Nat Tecnol 20(3):355–364
Wang F, Qi X, Geng J, Liu X, Li D, Zhang H, Wang G (2022a) Template-free construction of hollow mesoporous Fe3O4 nanospheres as controlled drug delivery with enhanced drug loading capacity. J Mol Liq 347:118000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.118000
Wang Z, Kang SB, Won SW (2022b) Polyethylenimine-aminated polyvinyl chloride fiber for adsorption of reactive dyes from single and binary component systems: adsorption kinetics and isotherm studies. Colloids Surf 128983.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022b.128983
Yeamsuksawa TT, Zhao H, Liang J (2021) Characterization and antimicrobial performance of magnetic Fe3O4@Chitosan@Ag nanoparticles synthesized via suspension technique. Mater Today Commun 28:102481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2021.102481
Yu HC, Huang XY, Lei FH, Tan XC, Wei YC, Li H (2014) Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on nickel nanoparticle-modified electrodes for phenobarbital determination. Electrochim Acta 14:45–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.07.050
Zadaliasghar S, Rahimpour E, Khoubnasabjafari M, Pournaghi-Azar MH, Nokhodchi A, Jouyban A (2020) A nano-platform for phenobarbital determination based on its inhibitory effect on the aggregation of silver nanoparticles/melamine system. J Mol Liq 316:113891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113891
Zhai W, He J, Han P, Zeng M, Gao X, He Q (2022) Adsorption mechanism for tetracycline onto magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles: adsorption isotherm and dynamic behavior, location of adsorption sites and interaction bonds. Vacuum 195:110634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2021.110634
Zhao R, Ma T, Zhao S, Rong H, Tian Y, Zhu G (2020) Uniform and Stable Immobilization of Metal-Organic Frameworks into Chitosan Matrix for Enhanced Tetracycline Removal from water. Chem Eng J 382:122893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122893
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank CAPES, FAPERGS, Laboratório de Materiais Magnéticos Nanoestruturados (LaMMaN), Laboratório de Simulação e Modelagem de Nanomateriais (LASIMON), Laboratório de Magnetismo e Materiais Magnéticos–LMMM, UFSM, and Universidade Franciscana–UFN for the support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Franciane Batista Nunes: methodology, investigation, writing—original draft (batistanunesfranciane@gmail.com). Franciele da Silva Bruckmann: visualization, writing—review and editing (francielebruckmann2@gmail.com). Theodoro da Rosa Salles: software, visualization, writing (theodoro.rsalles@gmail.com). Cristiano Rodrigo Bohn Rhoden: conceptualization; writing—review and editing; supervision (cristianorbr@gmail.com).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nunes, F.B., da Silva Bruckmann, F., da Rosa Salles, T. et al. Study of phenobarbital removal from the aqueous solutions employing magnetite-functionalized chitosan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 12658–12671 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23075-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23075-9