Abstract
Environmental geological disasters pose a significant threat to human life, property and environmental safety. It is necessary to conduct targeted governance in key prevention and control areas based on reasonable susceptibility assessment. Using the debris flow disaster in Xiuyan County as an example, this study compares and analyzes prone prediction models such as the frequency ratio (FR), decision tree (DT) and random forest (FR) models and evaluates the cost of prevention and control and the protection of life and property. The research results show that the FR, DT and RF models have good performance. The ROC test, disaster point density statistics and cross-validation results show that the RF model has the best performance. The study area was mainly less and mildly prone areas. The highly prone areas are mainly distributed in the northeast and southwest of the study area. It is the key area of disaster prevention and control. Elevation, rainfall intensity and population density have the largest influence on the susceptibility to debris flows. Based on the RF model, the disaster points in the highly prone areas account for 54% of the disaster points of the whole area, and the project treatment cost of the disaster points is 0.78 million yuan per single gully, which protects 56% of the lives and property in the study area, which is better than the DT and FR models. The RF model not only has good prediction performance in terms of susceptibility. It can realize the targeted management of disasters, achieve the targeted investment of governance costs and the effective protection of life and property and serve the sustainable development of the regional environment and economy with greater value.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data were included in this manuscript.
References
Aditian A, Kubota T, Shinohara Y (2018) Comparison of GIS-based landslide susceptibility models using frequency ratio, logistic regression, and artificial neural network in a tertiary region of Ambon, Indonesia. Geomorphology 318:101–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.06.006
Akinci H, Ayse YO (2021) Landslide susceptibility mapping and hazard assessment in Artvin (Turkey) using frequency ratio and modified information value model. Acta Geophys 69:725–745. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-021-00577-7
Akinci H, Kilicoglu C, Dogan S (2020) Random Forest-Based Landslide Susceptibility Mapping in Coastal Regions of Artvin, Turkey. Isprs Int J Geo-Inf 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9090553
Ali MZ, Chu HJ, Chen YC, Ullah S (2021) Machine learning in earthquake- and typhoon-triggered landslide susceptibility mapping and critical factor identification. Environ Earth Sci 80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09510-z
Behnia P, Andree BS (2018) Landslide susceptibility modelling using the quantitative random forest method along the northern portion of the Yukon Alaska Highway Corridor, Canada. Nat Hazards 90:1407–1426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-017-3104-z
Bordbar M, Aghamohammadi H, Pourghasemi HR, Azizi Z (2022) Multi-hazard spatial modeling via ensembles of machine learning and meta-heuristic techniques. Sci Rep 12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-05364-y
Bragagnolo L, Da Silva RV, Grzybowski JMV (2020) Artificial neural network ensembles applied to the mapping of landslide susceptibility. Catena 184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.104240
Bui DT, Tuan TA, Klempe H, Pradhan B, Revhaug I (2016) Spatial prediction models for shallow landslide hazards: a comparative assessment of the efficacy of support vector machines, artificial neural networks, kernel logistic regression, and logistic model tree. Landslides 13:361–378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-015-0557-6
Castellanos AEA, Van WCJ (2007) Generation of a landslide risk index map for Cuba using spatial multi-criteria evaluation. Landslides 4:311–325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-007-0087-y
Catani F, Lagomarsino D, Segoni S, Tofani V (2013) Landslide susceptibility estimation by random forests technique: sensitivity and scaling issues. Nat Hazard Earth Sys 13:2815–2831. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-13-2815-2013
Chen HY, Ruan HC, Chen JA, Li X, Yu YH (2022) Review of investigations on hazard Chains triggered by River-Blocking debris flows and Dam-Break floods. Front Earth Sci 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2022.830044
Chen JJ, Qin SW, Li GJ, Peng SY, Ma Q, Cao C, Liu X, Zhai JJ (2021) debris flow susceptibility assessment based on RS-IVM method in Jilin province. J Basic Sci Eng 29:1359–1371. https://doi.org/10.16058/j.issn.1005-0930.2021.06.004
Chen NS, Zhang Y, Tian SF, Deng MF, Wang T, Liu LH, Liu M, Hu GS (2020) Effectiveness analysis of the prediction of regional debris flow susceptibility in post-earthquake and drought site. J Mt Sci 17:329–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-019-5684-4
Chen W, Tsangaratos P, Ilia I, Duan Z, Chen XJ (2019) Groundwater spring potential mapping using population-based evolutionary algorithms and data mining methods. Sci Total Environ 684:31–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.312
Cheng JY, Dai XA, Wang ZK, Li JZ, Qu G, Li WL, She JX, Wang YL (2022) Landslide susceptibility assessment model construction using typical machine learning for the three Gorges Reservoir Area in China. Remote Sens 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14092257
Ciurleo M, Mandaglio MC, Moraci N (2021) A quantitative approach for debris flow inception and propagation analysis in the lead up to risk management. Landslides 18:2073–2093. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-021-01630-8
Dash RK, Falae PO, Kanungo DP (2022) Debris flow susceptibility zonation using statistical models in parts of Northwest Indian Himalayas-implementation, validation, and comparative evaluation. Nat Hazards 111:2011–2058. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-021-05128-3
Department of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of Liaoning Province (2017) The 2017 edition of Liaoning Province Construction Project Pricing Based on Construction Budget Quota A full set of 26 volumes. Northern United Publishing & Media (Group) Company Limited, Shenyang
Dwivedi SK, Chandra N, Bahuguna S, Pandey A, Khanduri S, Lingwal S, Sharma N, Singh G (2022) Hydrometeorological disaster risk assessment in upper Gori-Ramganga catchment. Geocarto Int, Uttarakhand, India. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2022.2063403
Farooq S, Akram MS (2021) Landslide susceptibility mapping using information value method in Jhelum Valley of the Himalayas. Arab J Geosci 14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07147-7
Feizizadeh B, Garajeh MK, Lakes T, Blaschke T (2021) A deep learning convolutional neural network algorithm for detecting saline flow sources and mapping the environmental impacts of the Urmia Lake drought in Iran. Catena 207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2021.105585
Gao ZM, Ding MT (2022) Application of convolutional neural network fused with machine learning modeling framework for geospatial comparative analysis of landslide susceptibility. Nat Hazards. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-022-05326-7
Geological Environment, Monitoring Institute of China Geological Survey (2020) Technical requirements for geological disaster risk investigation and evaluation (Trial version). https://gdgpo.czt.gd.gov.cn/gpx-bid-file/441301/gpx-tender/2022/5/30/8a7e15d481107bd3018112c58b0d2c9c.pdf. Accessed 10 Jan 2022
Ghosh A, Maiti R (2021) Soil erosion susceptibility assessment using logistic regression, decision tree and random forest: study on the Mayurakshi river basin of Eastern India. Environ Earth Sci 80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09631-5
Gong XL, Chen XQ, Chen KT, Zhao WY, Chen JG (2021) Engineering planning method and control modes for debris flow disasters in scenic areas. Front Earth Sci 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2021.712403
He BH, Bai MZ, Shi H, Li X, Qi YL, Li YJ (2021) Risk assessment of pipeline engineering geological disaster based on GIS and WOE-GA-BP models. Appl Sci-Basel 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11219919
Hu XD, Mei HB, Zhang H, Li YY, Li MD (2021) Performance evaluation of ensemble learning techniques for landslide susceptibility mapping at the Jinping county, Southwest China. Nat Hazards 105:1663–1689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-04371-4
Hu XY, Qin SW, Dou Q, Liu F, Qiao SS, Dong D (2019) Susceptibility analysis of debris flow based on GIS and RandomForest — a case study of a mountainous area in northern taonan city, jilin province. Bull Soil Water Conserv 39: 204-210+217+202. 10.13961/j.cnki.stbctb.2019.05.028
Janizadeh S, Pal SC, Saha A, Chowdhuri I, Ahmadi K, Mirzaei S, Mosavi AH, Tiefenbacher JP (2021) Mapping the spatial and temporal variability of flood hazard affected by climate and land-use changes in the future. J Environ Manage 298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113551
Jin X, Jin Y, Mao X (2019) Ecological risk assessment of cities on the Tibetan Plateau based on land use/land cover changes - Case study of Delingha City. Ecol Indic 101:185–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.12.050
Kang SH, Lee SR (2018) Debris flow susceptibility assessment based on an empirical approach in the central region of South Korea. Geomorphology 308:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.01.025
Kanwal S, Atif S, Shafiq M (2017) GIS based landslide susceptibility mapping of northern areas of Pakistan, a case study of Shigar and Shyok Basins. Geomat Nat Haz Risk 8:348–366. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2016.1220023
Kasymov U, Wang XX, Zikos D, Chopan M, Ibele B (2022) Institutional barriers to sustainable forest management: evidence from an experimental study in Tajikistan. Ecol Econ 193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2021.107276
Khan AA, Jamil A, Hussain D, Taj M, Jabeen G, Malik MK (2020) Machine-learning algorithms for mapping debris-covered glaciers: the Hunza basin case study. IEEE Access 8:12725–12734. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2965768
Khosravi K, Binh Thai P, Chapi K, Shirzadi A, Shahabi H, Revhaug I, Prakash I, Dieu Tien B (2018) A comparative assessment of decision trees algorithms for flash flood susceptibility modeling at Haraz watershed, northern Iran. Sci Total Environ 627:744–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.266
Kong F, Sun S, Lei TJ (2021) Understanding China's urban rainstorm waterlogging and its potential governance. Water 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13070891
Lee S, Talib JA (2005) Probabilistic landslide susceptibility and factor effect analysis. Environ Geol 47:982–990. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-005-1228-z
Li CX, Ma Y, He YX (2020) Sensitivity analysis of debris flow to environmental factors: a case of Longxi River basin in Dujiangyan, Sichuan Province. Chin J Geol Hazard Control 31:32–39. https://doi.org/10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2020.05.05
Li CY, Meng H, Zhang RL, Wen MS (2021b) Geological hazard risk assessment based on vulnerability of disaster-bearing body at county unite scale. Geol Bull Chin 40:1547–1559
Li M, Tian CS, Wang YK, Liu Q, Lu YF, Wang S (2018) Impacts of future climate change (2030-2059) on debris flow hazard: A case study in the Upper Minjiang River basin, China. J Mt Sci 15:1836–1850. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-017-4787-z
Li Y, Chen W, Rezaie F, Rahmati O, Moghaddam DD, Tiefenbacher J, Panahi M, Lee MJ, Kulakowski D, Bui DT, Lee S (2021a) Debris flows modeling using geo-environmental factors: developing hybridized deep-learning algorithms. Geocarto Int. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2021.1912194
Liang Z, Wang CM, Zhang ZM, Khan KUJ (2020) A comparison of statistical and machine learning methods for debris flow susceptibility mapping. Stoch Env Res Risk A 34:1887–1907. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-020-01851-8
Lin YT, Chen YK, Yang KH, Chen CS, Han JY (2021) Integrating InSAR observables and multiple geological factors for landslide susceptibility assessment. Appl Sci-Basel 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11167289
Liu YY, Di BF, Zhan Y, Stamatopoulos CA (2018) Debris flows susceptibility assessment in Wenchuan earthquake areas based on random forest algorithm model. Mt Res 36:765–773. https://doi.org/10.16089/j.cnki.1008-2786.000372
Mahmoodzadeh A, Mohammadi M, Noori KMG, Khishe M, Ibrahim HH, Ali HFH, Abdulhamid SN (2021) Presenting the best prediction model of water inflow into drill and blast tunnels among several machine learning techniques. Automat Constr 127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2021.103719
Meng FQ, Li GJ, Wang QB, Qin SW, Zhao HQ, Jin X (2012) Research on early warning of debris flow based on efficacy coefficient method. Rock Soil Mech 33:835–840. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2012.03.013
Monge JJ, McDonald N, McDonald GW (2022) A review of graphical methods to map the natural hazard-to-wellbeing risk chain in a socio-ecological system. Sci Total Environ 803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149947
O'Brien RM (2007) A caution regarding rules of thumb for variance inflation factors. Qual Quant 41:673–690. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-006-9018-6
Oh HJ, Pradhan B (2011) Application of a neuro-fuzzy model to landslide-susceptibility mapping for shallow landslides in a tropical hilly area. Comput Geosci 37:1264–1276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2010.10.012
Pal SC, Chakrabortty R, Saha A, Bozchaloei SK, Pham QB, Linh NTT, Anh DT, Janizadeh S, Ahmadi K (2022) Evaluation of debris flow and landslide hazards using ensemble framework of Bayesian- and tree-based models. B Eng Geol Environ 81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02546-2
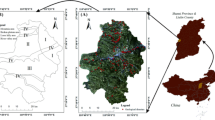
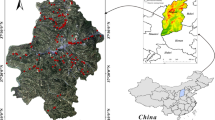
Pan Y, Cong W, Pan M (2010) Research on hazard zonation of debris flows based on GIS in Xiuyan County, Liaoning province. Acta Sci Nat Univ Pekin 46:601–606. https://doi.org/10.13209/j.0479-8023.2010.086
Paudel B, Fall M, Daneshfar B (2021) Gis-based assessment of debris flow runout in Kulekhani Watershed, Nepal. Geotech Geol Eng 39:2755–2775. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-020-01655-1
Pourghasemi HR, Gayen A, Panahi M, Rezaie F, Blaschke T (2019) Multi-hazard probability assessment and mapping in Iran. Sci Total Environ 692:556–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.203
Pradhan B, Lee S (2010) Delineation of landslide hazard areas on Penang Island, Malaysia, by using frequency ratio, logistic regression, and artificial neural network models. Environ Earth Sci 60:1037–1054. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0245-8
Qin YZ, Cao L, Boloorani AD, Wu WC (2021) High-resolution mining-induced geo-hazard mapping using random forest: a case study of Liaojiaping Orefield, Central China. Remote Sens 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13183638
Rashid B, Iqbal J, Su LJ (2020) Landslide susceptibility analysis of Karakoram highway using analytical hierarchy process and scoops 3D. J Mt Sci 17:1596–1612. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-018-5195-8
Reichenbach P, Rossi M, Malamud BD, Mihir M, Guzzetti F (2018) A review of statistically-based landslide susceptibility models. Earth-Sci Rev 180:60–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.03.001
Roy P, Pal SC, Chakrabortty R, Chowdhuri I, Malik S, Das B (2020) Threats of climate and land use change on future flood susceptibility. J Cleaner Prod 272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122757
Salmeron R, Garcia CB, Garcia J (2018) Variance inflation factor and condition number in multiple linear regression. J Stat Comput Sim 88:2365–2384. https://doi.org/10.1080/00949655.2018.1463376
Schwartz JY, Oakley NS, Alessio P (2021) Assessment of a post-fire debris flow impacting El capitan watershed, Santa Barbara county, California, USA. Environ Eng Geosci 27:423–437
Shang M, Ma R, Zhang YY, Liu YT (2018) Gis based weights of evidence method for rock fall susceptibility. J Eng Geol 26:1211–1218
Shirzadi A, Bui DT, Binh Thai P, Solaimani K, Chapi K, Kavian A, Shahabi H, Revhaug I (2017) Shallow landslide susceptibility assessment using a novel hybrid intelligence approach. Environ Earth Sci 76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6374-y
Spanos A (2019) Near-collinearity in linear regression revisited: The numerical vs. the statistical perspective. Commun Stat-Theor M 48:5492–5516. https://doi.org/10.1080/03610926.2018.1513147
Su G, Qin SW, Qiao SS, Hu XY, Chen J, Che WC (2021) Debris flow susceptibility evaluation based on St acking ensemble learning: a case study in Yajiang, Sichuar n Province. Global Geol 40:175–184
Sun XH, Chen JP, Li YR, Rene NN (2022) Landslide susceptibility mapping along a rapidly uplifting river valley of the upper Jinsha river, Southeastern Tibetan Plateau, China. Remote Sens 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071730
Tang W, Ding HT, Chen NS, Ma SC, Liu LH, Wu KL, Tian SF (2021) Artificial Neural Network-based prediction of glacial debris flows in the ParlungZangbo Basin, southeastern Tibetan Plateau, China. J Mt Sci 18:51–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-020-6414-7
Tehrany MS, Jones S, Shabani F (2019) Identifying the essential flood conditioning factors for flood prone area mapping using machine learning techniques. Catena 175:174–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.12.011
Termeh SVR, Kornejady A, Pourghasemi HR, Keesstra S (2018) Flood susceptibility mapping using novel ensembles of adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system and metaheuristic algorithms. Sci Total Environ 615:438–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.262
Tsangaratos P, Ilia I (2016) Comparison of a logistic regression and Naive Bayes classifier in landslide susceptibility assessments: The influence of models complexity and training dataset size. Catena 145:164–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.06.004
Veronesi F, Hurni L (2014) Random Forest with semantic tie points for classifying landforms and creating rigorous shaded relief representations. Geomorphology 224:152–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2014.07.020
Vojinovic Z, Alves A, Gomez JP, Weesakul S, Keerakamolchai W, Meesuk V, Sanchez A (2021) Effectiveness of small- and large-scale Nature-Based Solutions for flood mitigation: The case of Ayutthaya, Thailand. Sci Total Environ 789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147725
Wang N, Cheng WM, Marconcini M, Bachofer F, Liu CJ, Xiong JN, Lombardo L (2022) Space-time susceptibility modeling of hydro-morphological processes at the Chinese national scale. Eng Geol 301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106586
Wang XD, Wang C, Zhang CB (2020) Early warning of debris flow using optimized self-organizing feature mapping network. Water Supply 20:2455–2470. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2020.142
Wang XD, Zhang CB, Wang C, Liu GW, Wang HX (2021) GIS-based for prediction and prevention of environmental geological disaster susceptibility: From a perspective of sustainable development. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112881
Wang XZ (2018) Remote sensing interpretation and analysis of geological disasters in Xiuyan County based on Worldview 2. Jilin Geol 37:62-66+78
Wang Y, Hong H, Chen W, Li S, Panahi M, Khosravi K, Shirzadi A, Shahabi H, Panahi S, Costache R (2019) Flood susceptibility mapping in Dingnan County (China) using adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system with biogeography based optimization and imperialistic competitive algorithm. J Environ Manage 247:712–729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.06.102
Wenner M, Hibert C, Alec VH, Meier L, Walter F (2021) Near-real-time automated classification of seismic signals of slope failures with continuous random forests. Nat Hazard Earth Sys 21:339–361. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-21-339-2021
Wu S, Chen J, Xu C, Zhou W, Yao LH, Yue W, Cui ZJ (2020) Susceptibility assessments and validations of debris-flow events in meizoseismal areas: case study in China's Longxi river watershed. Nat Hazards Rev 21. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)NH.1527-6996.0000347
Wu XL, Hu F (2020) Analysis of ecological carrying capacity using a fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method. Ecol Indic 113:106243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106243
Xia HC, Zhu J, Chang M, Yang Y (2017) Susceptibility assessment of debris flow using a probabilistic and GIS approach: a case study on the Wenchuan County. J Yangtze River Sci Res Inst 34: 34-38+44. 10.11988/ckyyb.20160664
Xiong JN, Wei FQ, Liu ZQ (2017) Hazard assessment of debris flow in Sichuan Province. J Geo-inf Sci 19:1604–1612. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1047.2017.01604
Yan G, Liang SY, Gui XG, Xie Y, Zhao HL (2019) Optimizing landslide susceptibility mapping in the Kongtong District, NW China: comparing the subdivision criteria of factors. Geocarto Int 34:1408–1426. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2018.1499816
Yang X, Guo SL, Deng X, Wang W, Xu DD (2021) Study on livelihood vulnerability and adaptation strategies of farmers in areas threatened by different disaster types under climate change. Agriculture-Basel 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11111088
Yilmaz I (2009) A case study from Koyulhisar (Sivas-Turkey) for landslide susceptibility mapping by artificial neural networks. B Eng Geol Environ 68:297–306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-009-0185-2
Youssef AM, Pourghasemi HR, El-Haddad BA (2022) Advanced machine learning algorithms for flood susceptibility modeling - performance comparison: Red Sea, Egypt. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20213-1
Yu B, Wang T, Zhu Y (2016) Research on the topographical and rainfall factors of debris flows caused by shallow landslides. Adv Water Sci 27: 542-550. 10. 14042 /j. cnki. 32. 1309. 2016. 04. 008
Yunus AP, Fan X, Tang X, Jie D, Xu Q, Huang R (2020) Decadal vegetation succession from MODIS reveals the spatio-temporal evolution of post-seismic landsliding after the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake (vol 236, 111476, 2020). Remote Sens Environ 237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.111541
Zhang Y, Bo, Zeng L, Fu H, Liu, Zhang Z, Yuan (2022) Evaluation of geological hazard susceptibility in Shiqian county based on information model method. J Geol Hazard Environ Pre 33: 44-49.
Zhao WD, Gong JH, Zhao JT, Yang WT, Gao F (2019) Research on topographic wetness index and its implications of surface water environment considering micro-reliefs on plains. J Hefei Univ Technol, Nat Sci 42:113–118
Zheng ZZ, Xie CH, He Y, Zhu MC, Huang WF, Shao TM (2022) Monitoring potential geological hazards with different InSAR algorithms: the case of western Sichuan. Remote Sens 14:2049. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14092049
Zhu XJ, Ning ZY, Cheng H, Zhang PF, Sun R, Yang XY, Liu H (2022) A novel calculation method of subsidence waterlogging spatial information based on remote sensing techniques and surface subsidence prediction. J Cleaner Prod 335:130366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130366
Funding
The financial support was provided by the National Natural Science Fund of China (grant no. 51604140), Foundation of Liaoning Province Education Administration (Grant numbers: LJ2020FWL006) and Discipline Innovation Team of Liaoning Technical University (Grant numbers: LNTU20TD-07; LNTU20TD-14).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by X.L, F.M. and H. Z. The first draft of the manuscript was written by C.W. and X.W., and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Wang, X., Zhang, H. et al. Assessment of environmental geological disaster susceptibility under a multimodel comparison to aid in the sustainable development of the regional economy. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 6573–6591 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22649-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22649-x