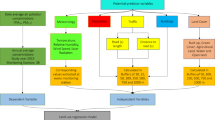
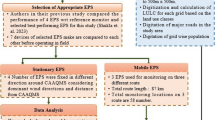
Abstract
Land use regression (LUR) models are mainly used for the simulation and prediction of conventional atmospheric pollutants. Whether the LUR models can be expanded to study more toxic and hazardous pollutants (such as heavy metals) remains to be verified. Combined with the factors of road, land use type, population, pollution enterprise, meteorology, and terrain, the LUR models were used to simulate the spatial distribution characteristics of heavy metals in road dust and determine the main influencing factors. Samples of road surface dust were collected from 144 evenly distributed points in Tianjin, China, with 108 modelling points and 36 verification points. The R2 values of the LUR models of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, and Pb contents were 0.301, 0.412, 0.399, 0.496, and 0.377, and their error rates were 2.72%, 4.96%, 4.64%, 8.91%, and 4.94%, respectively. The error rates of the kriging interpolation models were 3.33%, 6.50%, 5.14%, 18.30%, and 22.87%, which were all greater than those of the LUR models. The estimation effect of the LUR models was more refined than that of the kriging interpolation models. The contents of most heavy metals (except Ni) in road dust of the central area in Tianjin were generally higher than those of the surrounding areas. The heavy metal contents in road dust of Tianjin were mainly affected by road variables and meteorological variables. The LUR models were suitable for small-scale spatial prediction of heavy metals in urban road dust within urban areas.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abernethy RC, Allen RW, Mckendry IG, Brauer M (2013) A land use regression model for ultrafine particles in Vancouver, Canada. Environ Sci Technol 47(10):5217–5225. https://doi.org/10.14288/1.0072650
Abraham JS, Comrie AC (2004) Real-time Ozone mapping using a regression-interpolation hybrid approach, applied to Tucson. Arizona J Air Waste Manage Assoc 54(8):914–925. https://doi.org/10.1080/10473289.2004.10470960
Amini H, Yunesian M, Hosseini V, Schindler V, Henderson SB, Künzli N (2017) Asystematic review of land use regression models for volatile organic compounds. Atmos Environ 171:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2017.10.010
Aminiyan MM, Baalousha M, Mousavi R, Aminiyan FM, Hosseini H, Heydariyan A (2017) The ecological risk, source identification, and pollution assessment of heavy metals in road dust: a case study in Rafsanjan. SE Iran Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(14):13382–13395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8539-y
Apeagyei E, Bank MS, Spengler JD (2011) Distribution of heavy metals in road dust along an urban-rural gradient in Massachusetts. Atmos Environ 45:2310–2323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.11.015
Atari DO, Luginaah IN (2009) Assessing the distribution of volatile organic compounds using land use regression in Sarnia, “Chemical Valley”, Ontario. Canada Environ Health 8(1):16. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-069X-8-16
Bi CJ, Zhou Y, Chen ZL, Jia JP, Bao XY (2018) Heavy metals and lead isotopes in soils, road dust and leafy vegetables and health risks via vegetable consumption in the industrial areas of Shanghai. China Sci Total Environ 619–620:1349–1357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.177
Briggs DJ, Collins S, Elliott P, Fischer P, Kingham S, Lebret E, Pryl K, Reeuwijk HV, Smallbone K, Veen AVD (1997) Mapping urban air pollution using GIS: a regression-based approach. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 11(7):699–718. https://doi.org/10.1080/136588197242158
Briggs DJ, Hoogh DC, Gulliver J, Wills J, Elliott P, Kingham S, Smallbone K (2000) A regression-based method for mapping traffic-related air pollution: application and testing in four contrasting urban environments. Sci Total Environ 253(1–3):151–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00429-0
Budai P, Clement A (2018) Spatial distribution patterns of four traffic-emitted heavy metals in urban road dust and the resuspension of brake-emitted particles: Findings of a field study. Transport Res Part d: Transport Environ 62:179–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2018.02.014
Chen W, He XY, Zhang Y, Sun Y, Wang WF, Ning ZH (2003) Dust absorption effect of urban conifers in Northeast China. Chin J Appl Ecol 14(12):2113–2116 (In Chinese)
Chen L, Bai ZP, Su D, You Y, Li HM, Liu Q (2009) Application of land use regression to simulate ambient air PM10 and NO2 concentration in Tianjin City. China Environ Sci 29(7):685–691 (In Chinese)
Christoforidis A, Stamatis N (2009) Heavy metal contamination in street dust and roadside soil along the major national road in Kavala’s region. Greece Geoderma 151(3–4):257–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2009.04.016
Di Q, Kloog I, Koutrakis P, Lyapustin A, Wang YJ, Schwartz J (2016) Assessing PM2.5 exposures with high spatiotemporal resolution across the Continental United States. Environ Sci Technol 50:4712–4721. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b06121
Di Q, Rowland S, Koutrakis P, Schwartz J (2016) A hybrid model for spatially and temporally resolved ozone exposures in the continental United States. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 67(1):39–52. https://doi.org/10.1080/10962247.2016.1200159
Divrikli U, Soylak M, Elci L, Dogan K (2003) Trace heavy metal levels in street dust samples from Yozgat City Center. Turkey J Trace Microprobe Tech 21(2):351–361. https://doi.org/10.1081/TMA-120020270
Dong J, Ma R, Cai PL, Liu P, Yue HD, Zhang XP, Song XF (2021) Effect of sample number and location on accuracy of land use regression model in NO2 prediction. Atmos Environ 246(10):118057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2020.118057
Ge YH, Fu QY, Yi M, Chao Y, Lei XN, Xu XY, Cai J (2022) High spatial resolution land-use regression model for urban ultrafine particle exposure assessment in Shanghai. China Sci Total Environ 816:151633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151633
Gilbert NL, Goldberg MS, Beckerman B, Brook JR, Jerrett M (2005) Assessing spatial variability of ambient nitrogen dioxide in Montréal, Canada, with a land-use regression model. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 55(8):1059–1063. https://doi.org/10.1080/10473289.2005.10464708
Han RR, Zhou BH, Huang YY, Lu XH, Li S, Li N (2020) Bibliometric overview of research trends on heavy metal health risks and impacts in 1989–2018. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151633
Harrison RM, Laxen DPH, Wilson SJ (1981) Chemical associations of Lead, Cadmium, Copper, and Zinc in street dusts and roadside soils. Environ Sci Technol 15(11):1378–1383. https://doi.org/10.1021/ES00093A013
Hoek G, Beelen R, Hoogh KD, Vienneau D, Gulliver J (2008) A review of land-use regression models to assess spatial variation of outdoor air pollution. Atmos Environ 42(33):7561–7578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.05.057
Hoek G, Beelen R, Kos G, Dijkema M, Zee SCVD, Fischer PH, Brunekreef B (2011) Land use regression model for ultrafine particles in Amsterdam. Environ Sci Technol 45(2):622–628. https://doi.org/10.1021/es1023042
Hu BB, Liu BQ, Zhou J, Guo JT, Sun ZB, Meng WQ, Guo X, Duan JH (2016) Health risk assessment on heavy metals in urban street dust of Tianjin based on trapezoidal fuzzy numbers. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 22(3):678–692. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2015.1104625
Johnson M, Isakov V, Touma JS, Mukerjee S, Özkaynak H (2010) Evaluation of land-use regression models used to predict air quality concentrations in an urban area. Atmos Environ 44(30):3660–3668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.06.041
Li F, Zhang JD, Huang JH, Huang DW, Yang J, Song YW, Zeng GM (2016) Heavy metals in road dust from Xiandao District, Changsha City, China: characteristics, health risk assessment, and integrated source identification. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(13):13100–13113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6458-y
Luminati O, de Campos BLD, Fluckiger B, Brentani A, Roosli M, Fink G, de Hoogh K (2021) Land use regression modelling of NO2 in Sao Paulo. Brazil Environ Pollut 289(2):117832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117832
Mavko ME, Tang B, George LA (2008) A sub-neighborhood scale land use regression model for predicting NO2. Sci Total Environ 398(1–3):68–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.02.017
Men C, Liu RM, Xu F, Wang QR, Guo LJ, Shen ZY (2018) Pollution characteristics, risk assessment, and source apportionment of heavy metals in road dust in Beijing. China Sci Total Environ 612:138–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.123
Men C, Liu RM, Wang QR, Guo LJ, Shen ZY (2018) The impact of seasonal varied human activity on characteristics and sources of heavy metals in metropolitan road dusts. Sci Total Environ 637:844–854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.059
Men C, Liu RM, Xu LB, Wang QR, Guo LJ, Miao YX, Shen ZY (2019) Source-specific ecological risk analysis and critical source identification of heavy metals in road dust in Beijing. China J Hazard Mater 388:121763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121763
Meng X, Chen L, Cai J, Zou B, Wu CF, Fu QY, Zhang Y (2015) A land use regression model for estimating the NO2 concentration in shanghai. China Environ Res 137:308–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2015.01.003
Meng X, Fu QY, Ma ZW, Chen L, Zou B, Zhang Y, Xue WB, Wang JN, Wang DF, Kan HD, Liu Y (2016) Estimating ground-level PM10 in a Chinese city by combiningsatellite data, meteorological information and a land use regression model. Environ Pollut 208:177–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.09.042
Montagne DR, Hoek G, Klompmaker JO, Wang M, Meliefste K, Brunekreef B (2015) Land use regression models for ultrafine particles and black carbon based on short-term monitoring predict past spatial variation. Environ Sci Technol 49(14):8712–8720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134234
Mummullage S, Egodawatta P, Ayoko GA, Goonetilleke A (2016) Use of physicochemical signatures to assess the sources of metals in urban road dust. Sci Total Environ 541:1303–1309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.10.032
Roy S, Gupta SK, Prakash J, Habib G, Baudh K, Nasr M (2019) Ecological and human health risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in road dust in the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi. India Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(29):30413–30425. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06216-5
Saeedi M, Li LY, Salmanzadeh M (2012) Heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: pollution and ecological risk assessment in street dust of Tehran. J Hazard Mater 227–228:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.04.047
Sezgin N, Ozcan HK, Demir G, Nemlioglu S, Bayat C (2004) Determination of heavy metal concentrations in street dusts in Istanbul E-5 highway. Environ Int 29(7):979–985. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00075-8
Shabanda IS, Koki IB, Low KH, Zain SM, Khor SM, Anu Bakar NK (2019) Daily exposure to toxic metals through urban road dust from industrial, commercial, heavy traffic, and residential areas in Petaling Jaya, Malaysia: a health risk assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(36):37193–37211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06718-2
Shi Y, Bilal M, Ho HC, Omar A (2020) Urbanization and regional air pollution across South Asian developing countries - A nationwide land use regression for ambient PM2.5 assessment in Pakistan. Environ. Pollut 266:115145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115145
Soltani N, Keshavarzi B, Moore F, Tavakol T, Lahijianzadeh AR, Jaafarzadeh N, Kermani M (2015) Ecological and human health hazards of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in road dust of Isfahan metropolis. Iran Sci Total Environ 505:712–723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.09.097
Sun ZB, Zhou J, Hu BB, Wang ZW, Meng WQ, Wang ZL (2014) Characteristics of heavy metal pollution in urban street dust of Tianjin. Ecol Environ Sci 23(1):157–163 (In Chinese)
Sun ZB, Liu BQ, Zhou J, Hu BB, Meng WQ, Wang ZL (2015) Heavy metals pollution and ecological risk assessment on urban street dust of Tianjin. Environ Sci Technol 38(8):244–250 (In Chinese)
Sun D, Fang J, Sun JQ (2018) Health-related benefits of air quality improvement from coal control in China: evidence from the Jing-Jin-Ji region. Resour Conserv Recycl 129:416–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2016.09.021
Tianjin Municipal Bureau of Statistics & Survey Office of the National Bureau of Statistics in Tianjin (2020) Tianjin Statistical Yearbook 2020. http://stats.tj.gov.cn/nianjian/2020nj/zk/indexch.htm (In Chinese)
Trujillo-González JM, Torres-Mora MA, Keesstra S, Brevik EC, Jiménez-Ballesta R (2016) Heavy metal accumulation related to population density in road dust samples taken from urban sites under different land uses. Sci Total Environ 553:636–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.02.101
Wahab MIA, Abd Razak WMA, Sahani M, Khan MF (2020) Characteristics and health effect of heavy metals on non-exhaust road dusts in Kuala Lumpur. Sci Total Environ 703:135535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135535
Wang JW, Xu H (2021) A novel hybrid spatiotemporal land use regression model system at the megacity scale. Atmos Environ 244:117971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2020.117971
Wang M, Beelen R, Eeftens M, Meliefste K, Hoek G, Brunekreef B (2012) Systematic evaluation of land use regression models for NO2. Environ Sci Technol 46(8):4481–4489. https://doi.org/10.1021/es204183v
Wang M, Beelen R, Bellander T, Birk M, Cesaroni G, Cirach M, Cyrys J, Hoogh KD, Declercq C, Dimakopoulou K et al (2014) Performance of multi-city land use regression models for nitrogen dioxide and fine particles. Environ Health Perspect 122(8):843–849. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1307271
Wang JH, Li SW, Cui XY, Li HM, Qian X, Wang C, Sun YX (2016) Bioaccessibility, sources and health risk assessment of trace metals in urban park dust in Nanjing, Southeast China. Ecotox Environ Safe 128:161–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.02.020
Wang S, Cai LM, Wang QS, Luo J, Tang CH, Mu GZ, Jiang HH, Liu TY (2018) Spatial distribution and accumulation of heavy metals in urban surface dust of China. Geogr Res 37(8):1624–1640 (In Chinese)
Wang HL, Shen CY, Kang YF, Deng Q, Lin XY (2020) Spatial distribution of pollution characteristics and human health risk assessment of exposure to heavy elements in road dust from different functional areas of Zhengzhou. China Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(21):26650–26667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.118861
Wang JW, Cohan DS, Xu H (2020b) Spatiotemporal ozone pollution LUR models: Suitable statistical algorithms and time scales for a megacity scale. Atmos Environ 237:117671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2020.117671
Weichenthal S, Ryswyk KV, Goldstein A, Bagg S, Shekkarizfard M, Hatzopoulou M (2016) A land use regression model for ambient ultrafine particles in Montreal, Canada: A comparison of linear regression and a machine learning approach. Environ Res 146:65–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2015.12.016
White KB, Sanka O, Melymuk L, Pribylova P, Klanova J (2021) Application of land use regression modelling to describe atmospheric levels of semivolatile organic compounds on a national scale. Sci Total Environ 793:148520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148520
Wu ZL, Zhou J, Hu BB, Wang ZL, Wang ZW, Meng WQ (2013) Characteristics of heavy metal pollution in dust and soil of Tianjin City. North China Chin J Ecol 32(1):1030–1037 (In Chinese)
Wu JS, Liao X, Peng J, Huang XL (2015) Simulation and influencing factors of spatial distribution of PM2.5 concentrations in Chongqing. Environ Sci 36(3):759–767 (In Chinese)
Xiao Q, Zong YT, Malik Z, Lu SG (2019) Source identification and risk assessment of heavy metals in road dust of steel industrial city (Anshan), Liaoning. Northeast China Hum Ecol Risk Assess 26(5):1359–1378. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2019.1578946
Zgłobicki W, Telecka M, Skupiński S, Pasierbińska A, Kozieł M (2018) Assessment of heavy metal contamination levels of street dust in the city of Lublin. E Poland Environ Earth Sci 77(23):774. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7969-2
Zhang J, Chen ZL, Xu SY, YaoWei CXL, Deng HG (2006) Lead Pollution and Its Assessment in Urban Street Dust of Shanghai. Environ Sci 27(03):3519–3523 (In Chinese)
Zhong PR, Huang SC, Zhu YH, Li Y, Ma L (2018) Application of land use regression model in simulation of spatial distribution of ambient NO2 concentration. J Environ Health 35(4):307–310 (In Chinese)
Zou B, Luo YQ, Wan N, Zheng Z, Sternberg T, Liao YL (2015) Performance comparison of LUR and OK in PM2.5 concentration mapping: a multidimensional perspective. Sci Rep 5:8698. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep08698
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank the editor and the anonymous reviewers for their insightful comments and suggestions.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Grant No. 41301221).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BH and XY conceived the idea; BH and TA organized the data and designed the model; JZ and XY performed the data analysis and interpretation; BH, XY, and TA wrote the paper and provided feedback to all authors. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, X., An, T., Hu, B. et al. Analysis of spatial distribution characteristics and main influencing factors of heavy metals in road dust of Tianjin based on land use regression models. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 837–848 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22151-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22151-4