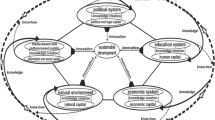
Abstract
The Fifth Ministerial Conference on Environment and Development in Asia and the Pacific (MCED-5) provided a regional implementation plan to pursue economic development in Asia-Pacific. Achieving environmentally sustainable economic growth or green growth is considered necessary by the ministerial declaration of the conference. The ministerial declaration defines green growth as an approach to sustaining economic growth and employment creation, a prerequisite for effective poverty reduction while coping with natural resource constraints and climate change. Based on the importance of green growth, the study seeks to investigate the progress towards sustainable economic development in Pakistan from 1990 to 2019. The study employs structural equation modeling (SEM) to determine the direct and indirect effects of the variables of the green growth model adopted in the MCED-5. The results of the study indicate that an increase in the net national income of the country leads to increased natural resource depletion. The declining stock of natural capital points towards the difficulty in fulfilling biocapacity sustainability in Pakistan while achieving social progress and declining carbon intensity in the quest for sustainable development. Based on the analysis, it can be claimed that the negative impact of increasing inclusive wealth on natural capital makes Pakistan in environmental terms a weakly sustainable nation. Thus, the conclusion is that Pakistan is following a path of weak sustainability. As a result, there is a need to shift the country’s sustainable economic development from weak sustainability to strong sustainability if the increasing natural resource depletion is to be restrained.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abdallah S, Michaelson J, Shah S, Stoll L, Marks N (2012) The Happy Planet Index: 2012 report. A global index of sustainable well-being. New Economics Foundation, London
Aghion P, Bolton P (1997) A theory of trickle-down growth and development. Rev Econ Stud 64:151–172. https://doi.org/10.2307/2971707
Autor DH, Dorn D, Hanson GH, Song J (2014) Trade adjustment: worker-level evidence. Q J Econ 129:1799–1860. https://doi.org/10.1093/qje/qju026
Barua A, Khataniar B (2016) Strong or weak sustainability: a case study of emerging Asia. Asia-Pac Dev J 22:1–31 https://doi.org/10.18356/9b582978-en
Bollen KA (1989) Structural equations with latent variables. John Wiley & Sons Inc, Hoboken, NJ, USA
Borel-Saladin JM, Turok IN (2013) The impact of the green economy on jobs in South Africa. SAJS 109:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1590/sajs.2013/a0033
Brand F (2009) Critical natural capital revisited: ecological resilience and sustainable development. Ecol Econ 68:605–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2008.09.013
Butt D, Myllyvirta L, Dahiya S (2021) CO2 emissions from Pakistan’s energy sector. Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air, Helsinki
Centre for Bhutan Studies and GNH Research (2016) A compass towards a just and harmonious society: 2015 GNH survey report. Centre for Bhutan Studies & GNH Research, Thimphu, Bhutan
Chelli FM, Ciommi M, Gigliarano C (2013) The index of sustainable economic welfare: a comparison of two Italian regions. Procedia - Soc Behav Sci 81:443–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2013.06.457
Curran J (2017) Getting the measure of sustainable economic growth: The ecologist. https://theecologist.org/2017/jan/30/getting-measure-sustainable-economic-growth. Accessed 15 Mar 2022
Daly HE, Farley J (2004) Ecological economics: principles and applications. Island Press, Washington, DC
Danish Baloch MA, Mahmood N, Zhang JW (2019) Effect of natural resources, renewable energy and economic development on CO2 emissions in BRICS countries. Sci Total Environ 678:632–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.028
Dedeurwaerdere T (2014) Sustainability science for strong sustainability. Edward Elgar Publishing, Northampton
DeFries R (2014) The big ratchet: how humanity thrives in the face of natural crisis. Basic Books, New York
Destek MA, Sarkodie SA (2019) Investigation of environmental Kuznets curve for ecological footprint: the role of energy and financial development. Sci Total Environ 650:2483–2489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.017
Dix-Carneiro R (2014) Trade liberalization and labor market dynamics. Econometrica 82:825–885. https://doi.org/10.3982/ECTA10457
Dogan E, Seker F (2016) The influence of real output, renewable and non-renewable energy, trade and financial development on carbon emissions in the top renewable energy countries. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 60:1074–1085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.02.006
Eckstein D, Künzel V, Schäfer L (2021) Global climate risk index 2021. Germanwatch e.V., Berlin
Efron B (1979) Bootstrap methods: another look at the jackknife. Ann Stat 7:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1214/aos/1176344552
Ekins P, Simon S, Deutsch L, Folke C, De Groot R (2003) A framework for the practical application of the concepts of critical natural capital and strong sustainability. Ecol Econ 44:165–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-8009(02)00272-0
ESCAP (2005) Key developments and activities at the regional level: managing globalization. United Nations Publication, Jakarta
Farand C (2021) Pakistan explores debt-for-nature scheme to accelerate its 10 billion tree tsunami. In: Climate Home News. https://www.climatechangenews.com/2021/04/16/pakistan-explores-debt-nature-scheme-accelerate-10-billion-tree-tsunami/. Accessed 15 Mar 2022
Galli A, Kitzes J, Niccolucci V, Wackernagel M, Wada Y, Marchettini N (2012) Assessing the global environmental consequences of economic growth through the ecological footprint: a focus on China and India. Ecol Indic 17:99–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2011.04.022
Gilani H, Naz HI, Arshad M, Nazim K, Akram U, Abrar A, Asif M (2021) Evaluating mangrove conservation and sustainability through spatiotemporal (1990–2020) mangrove cover change analysis in Pakistan. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 249:107128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2020.107128
Godil DI, Yu Z, Sharif A, Usman R, Khan SAR (2021) Investigate the role of technology innovation and renewable energy in reducing transport sector CO2 emission in China: a path toward sustainable development. Sustain Dev 29:694–707. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2167
Government of Pakistan (2019) Economic survey of Pakistan 2018-19. Finance Division, Islamabad
Government of Pakistan (2021) Economic survey of Pakistan 2020-21. Finance Division, Islamabad
Harris JM, Roach B (2017) National income and environmental accounting.Environmental and Natural Resource Economics. Routledge, New York 2017
Hershberger SL (2003) The growth of structural equation modeling: 1994–2001. Struct Equ Model Multidiscip J 10:35–46. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15328007SEM1001_2
Hynes W, Wang S (2012) Green growth and developing countries–consultation draft. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/index.php?page=view&type=400&nr=684&menu=1515
Jacob K, Quitzow R, Bär H (2015) green jobs: impacts of a green economy on employment. Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH, Germany
Johnson DG (2000) Population, food, and knowledge. Am Econ Rev 90:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1257/aer.90.1.1
Karnani AG (2009) Reducing poverty through employment. Social Science Research Network, Rochester, New York
Kellenberg J (1996) Accounting for natural resources in Ecuador: contrasting methodologies, conflicting results. Environment Department, World Bank, Washington, DC
Khan SAR, Sharif A, Golpîra H, Kumar A (2019) A green ideology in Asian emerging economies: from environmental policy and sustainable development. Sustain Dev 27:1063–1075. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.1958
Kline RB (1998) Principles and practice of structural equation modeling. The Guildford Press, New York, New York
Kwan JLY, Chan W (2014) Comparing squared multiple correlation coefficients using structural equation modeling. Struct Equ Model Multidiscip J 21:225–238. https://doi.org/10.1080/10705511.2014.882673
Lamb WF, Rao ND (2015) Human development in a climate-constrained world: what the past says about the future. Glob Environ Change 33:14–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2015.03.010
Lewis WA (1954) Economic development with unlimited supplies of labour. Manch Sch 22:139–191. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9957.1954.tb00021.x
OECD (2017) How’s life? 2017: measuring well-being. OECD Publishing, Paris
Perring MP, Erickson TE, Brancalion PHS (2018) Rocketing restoration: enabling the upscaling of ecological restoration in the Anthropocene. Restor Ecol 26:1017–1023. https://doi.org/10.1111/rec.12871
Raudsepp-Hearne C, Peterson GD, Tengö M, Bennett EM, Holland T, Benessaiah K, MacDonald GK, Pfeifer L (2010) Untangling the environmentalist’s paradox: why is human well-being increasing as ecosystem services degrade? BioScience 60:576–589. https://doi.org/10.1525/bio.2010.60.8.4
Repetto RC, Magrath W (1989) Wasting assets: natural resources in the national income accounts. World Resources Institute, Washington, DC
Rosenthal L, Carroll-Scott A, Earnshaw VA, Santilli A, Ickovics JR (2012) The importance of full-time work for urban adults’ mental and physical health. Soc Sci Med 75:1692–1696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2012.07.003
Sharif A, Afshan S, Chrea S, Amel A, Khan SAR (2020) The role of tourism, transportation and globalization in testing environmental Kuznets curve in Malaysia: new insights from quantile ARDL approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:25494–25509. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08782-5
Sharif A, Baris-Tuzemen O, Uzuner G, Ozturk I, Sinha A (2020) Revisiting the role of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on Turkey’s ecological footprint: evidence from quantile ARDL approach. Sustain Cities Soc 57:102138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2020.102138
Sharif A, Jammazi R, Raza SA, Shahzad SJH (2017) Electricity and growth nexus dynamics in Singapore: fresh insights based on wavelet approach. Energy Policy 110:686–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2017.07.029
Sharif A, Raza SA, Ozturk I, Afshan S (2019) The dynamic relationship of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption with carbon emission: a global study with the application of heterogeneous panel estimations. Renew Energy 133:685–691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.10.052
Sharif A, Saha S, Loganathan N (2017) Does tourism sustain economic growth? Wavelet-based evidence from the United States. Tour Anal 22:467–482. https://doi.org/10.3727/108354217X15023805452022
Solow R (1993) An almost practical step toward sustainability. Resour Policy 19:162–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/0301-4207(93)90001-4
Stjepanović S, Tomić D, Škare M (2017) A new approach to measuring green GDP: a cross-country analysis. JESI 4:574–590. https://doi.org/10.9770/jesi.2017.4.4(13)
Suki NM, Sharif A, Afshan S, Suki NM (2020) Revisiting the environmental Kuznets curve in Malaysia: the role of globalization in sustainable environment. J Clean Prod 264:121669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121669
Taraz V, Halliday S, Brookes-Gray H (2021) The impact of weather shocks on employment outcomes: evidence from South Africa. SSRN J. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3919152
Todaro MP, Smith SC (2020) Economic development. Pearson Education Limited, Harlow
Tremblay PF, Gardner RC (1996) On the growth of structural equation modeling in psychological journals. Struct Equ Model Multidiscip J 3:93–104. https://doi.org/10.1080/10705519609540035
UNDP (2011) Sustainability and equity: a better future for all. Palgrave Macmillan, Houndmills
UNEP (2021) Inclusive wealth of Pakistan: the case for investing in natural capital and restoration. United Nations Publication, Pakistan
United Nations, Commission of the European Communities, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, International Monetary Fund, World Bank (1993) System of National Accounts (SNA). Brussels/Luxembourg, New York, Paris, Washington, D.C.
UNU-IHDP, UNE (2014) Inclusive wealth report 2014: measuring progress toward sustainability. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Veklich OA, Shlapak NYu (2012) Environmentally adjusted GDP as an indicator of economic development. Stud Russ Econ Dev 23:244–248. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1075700712030100
World Bank (2021) The changing wealth of nations 2021: managing assets for the future. World Bank, Washington, DC
Xu L, Chen N, Chen Z (2017) Will China make a difference in its carbon intensity reduction targets by 2020 and 2030? Appl Energy 203:874–882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.06.087
Yuan J, Hou Y, Xu M (2012) China’s 2020 carbon intensity target: consistency, implementations, and policy implications. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 16:4970–4981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2012.03.065
Yusuf JA, Serafy SE, Lutz E (eds) (1989) Environmental accounting for sustainable development. World Bank, Washington, DC
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have a substantial contribution to this manuscript. AJ conceptualized the idea of the study and wrote the main manuscript. SAK supervised AJ throughout the study and formatted the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study follows all ethical practices of the institution.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
This is an original manuscript that has not been submitted to or is being considered for publication anywhere else.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Arshian Sharif
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jabeen, A., Khan, S.A. Economic growth, social inclusion, and environmental protection: assessing the existence of green growth in Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 66675–66688 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20467-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20467-9