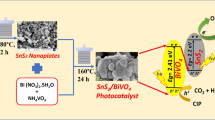
Abstract
Detection of residual organic and inorganic species in water bodies, including drinking water, has led to developing strategies for their removal. Here, we report a very efficient method of removing Cr(VI), organic dye, and antibiotic from water using a type-II heterojunction based on Sn3O4/SnS2 solar photocatalyst. The toxic Cr(VI) species are reduced by photocatalytic methodology, while methylene blue (MB) dye and ciprofloxacin (CIP) antibiotics are removed by photocatalytic degradation. The structural, compositional, morphological, and optical properties of the hydrothermally synthesized photocatalyst have been studied. Under sunlight exposure, more than 99.9% of Cr(VI) is reduced within 60 min at a reaction rate of 0.066 min−1. While 99.6% of MB and 90% of CIP degradation are achieved in 90 min and 120 min, corresponding to photocatalytic degradation rates of 0.043 min−1 and 0.019 min−1, respectively. The total organic carbon after degradation corresponded to 85.1% for MB and 72.4% for CIP mineralization. The observed photocatalytic degradation is attributed to in situ generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), e.g., superoxide radicals and hydroxyl radicals. The role of ROS towards photocatalytic degradation of MB and CIP, respectively, was confirmed from ROS scavenging studies. The MB and CIP degradation mechanism has been discussed by analyzing their degradation products.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Baghriche O, Rtimi S, Pulgarin C, Kiwi J (2017) Polystyrene CuO/Cu2O uniform films inducing MB-degradation under sunlight. Catal Today 284:77–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2016.10.018
Barrera-Díaz CE, Lugo-Lugo V, Bilyeu B (2012) A review of chemical, electrochemical and biological methods for aqueous Cr(VI) reduction. J Hazard Mater 223–224:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.04.054
Bethi B, Sonawane SH, Bhanvase BA, Gumfekar SP (2016) Nanomaterials-based advanced oxidation processes for wastewater treatment: a review. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif 109:178–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2016.08.016
Calvete MJF, Piccirillo G, Vinagreiro CS, Pereira MM (2019) Hybrid materials for heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of antibiotics. Coord Chem Rev 395:63–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2019.05.004
Coetzee JJ, Bansal N, Chirwa EMN (2020) Chromium in environment, its toxic effect from chromite-mining and ferrochrome industries, and its possible bioremediation. Expo Heal 12:51–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-018-0284-z
Daghrir R, Drogui P (2013) Tetracycline antibiotics in the environment: a review. Environ Chem Lett 11:209–227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-013-0404-8
Das D, Dutta RK (2015) A novel method of synthesis of small band gap SnS nanorods and its efficient photocatalytic dye degradation. J Colloid Interface Sci 457:339–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.07.002
Du Z, Feng L, Guo Z, Yan T, Hu Q, Lin J, Huang Y, Tang C, Feng Y (2021) Ultrathin h-BN/Bi2MoO6 heterojunction with synergetic effect for visible-light photocatalytic tetracycline degradation. J Colloid Interface Sci 589:545–555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.01.027
Fick J, Söderström H, Lindberg RH, Phan C, Tysklind M, Larsson DGJ (2009) Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the environment contamination of surface, ground, and drinking water from pharmaceutical production. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:2522–2527
Hafiane A, Lemordant D, Dhahbi M (2000) Removal of hexavalent chromium by nanofiltration. Desalination 130:305–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0011-9164(00)00094-1
He C, Gu L, Xu Z, He H, Fu G, Han F, Huang B, Pan X (2020) Cleaning chromium pollution in aquatic environments by bioremediation, photocatalytic remediation, electrochemical remediation and coupled remediation systems. Environ Chem Lett 18:561–576. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-019-00960-3
Huang D, Li J, Zeng G, Xue W, Chen S, Li Z, Deng R, Yang Y, Cheng M (2019) Facile construction of hierarchical flower-like Z-scheme AgBr/Bi2WO6 photocatalysts for effective removal of tetracycline: degradation pathways and mechanism. Chem Eng J 375:121991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.121991
Ji Y, Ferronato C, Salvador A, Yang X, Chovelon JM (2014) Degradation of ciprofloxacin and sulfamethoxazole by ferrous-activated persulfate: Implications for remediation of groundwater contaminated by antibiotics. Sci Total Environ 472:800–808. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.11.008
Karimi-Maleh H, Ayati A, Ghanbari S, Orooji Y, Tanhaei B, Karimi F, Alizadeh M, Rouhi J, Fu L, Sillanpaa M (2021) Recent advances in removal techniques of Cr(VI) toxic ion from aqueous solution: a comprehensive review. J Mol Liq 329:115062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.115062
Katheresan V, Kansedo J, Lau SY (2018) Efficiency of various recent wastewater dye removal methods: a review. J Environ Chem Eng 6:4676–4697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.06.060
Khan NA, Ahmed S, Farooqi IH, Ali I, Vambol V, Changani F, Yousefi M, Vambol S, Khan SU, Khan AH (2020) Occurrence, sources and conventional treatment techniques for various antibiotics present in hospital wastewaters: a critical review. TrAC - Trends Anal Chem 129:115921. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2020.115921
Khatri A, Peerzada MH, Mohsin M, White M (2015) A review on developments in dyeing cotton fabrics with reactive dyes for reducing effluent pollution. J Clean Prod 87:50–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.09.017
Kumar G, Dutta RK (2022a) Fabrication of plate-on-plate SnS2/Bi2WO6 nanocomposite as photocatalyst for sunlight mediated degradation of antibiotics in aqueous medium. J Phys Chem Solids 164:110639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2022.110639
Kumar G, Dutta RK (2022b) Sunlight mediated photo-Fenton degradation of tetracycline antibiotic and methylene blue dye in aqueous medium using FeWO4/Bi2MoO6 nanocomposite. Process Saf Environ Prot 159:862–873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2022.01.063
Kumar G, Cilamkoti V, Dutta RK (2022) Sunlight mediated enhanced photocatalytic degradation of antibiotics in aqueous medium using silicon doped carbon quantum dots decorated Bi2MoO6 nanoflakes. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 639:128368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.128368
Li H, Hu T, Zhang R, Liu J, Hou W (2016) Preparation of solid-state Z-scheme Bi2MoO6/MO (M=Cu, Co3/4, or Ni) heterojunctions with internal electric field-improved performance in photocatalysis. Appl Catal B Environ 188:313–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.02.015
Li Z, Meng X, Zhang Z (2018) Few-layer MoS2 nanosheets-deposited on Bi2MoO6 microspheres: a Z-scheme visible-light photocatalyst with enhanced activity. Catal Today 315:67–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2018.03.014
Lin Z, Zheng Y, Deng F, Luo X, Zou J, Shao P, Zhang S, Tang H (2021) Target-directed design of dual-functional Z-scheme AgIn5S8/SnS2 heterojunction for Pb(II) capture and photocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI): Performance and mechanism insight. Sep Purif Technol 277:119430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119430
Liu C, Lü H, Yu C, Ding B, Ye R, Ji Y, Dai B, Liu W (2020) Novel FeWO4/WO3 nanoplate with p-n heterostructure and its enhanced mechanism for organic pollutants removal under visible-light illumination. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104044
Manzetti S, Ghisi R (2014) The environmental release and fate of antibiotics. Mar Pollut Bull 79:7–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.01.005
Mukherjee I, Cilamkoti V, Dutta RK (2021) Sunlight-driven photocatalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin by carbon dots embedded in ZnO nanostructures. ACS Appl Nano Mater. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.1c00883
Narayani M, Shetty KV (2013) Chromium-resistant bacteria and their environmental condition for hexavalent chromium removal: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 43:955–1009. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2011.627022
Nenavathu BP, Krishna Rao AVR, Goyal A, Kapoor A, Dutta RK (2013) Synthesis, characterization and enhanced photocatalytic degradation efficiency of Se doped ZnO nanoparticles using trypan blue as a model dye. Appl Catal A Gen 459:106–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2013.04.001
Peng Y, Chen QG, Wang D, Zhou HY, Xu AW (2015) Synthesis of one-dimensional WO3-Bi2WO6 heterojunctions with enhanced photocatalytic activity. CrystEngComm 17:569–576. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ce01884b
Qiang T, Chen L, Xia Y, Qin X (2021) Dual modified MoS2/SnS2 photocatalyst with Z-scheme heterojunction and vacancies defects to achieve a superior performance in Cr(VI) reduction and dyes degradation. J Clean Prod 291:125213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125213
Ramachandra TV, Jain R, Krishnadas G (2011) Hotspots of solar potential in India. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 15:3178–3186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2011.04.007
Saadati F, Keramati N, Ghazi MM (2016) Influence of parameters on the photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline in wastewater: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 46:757–782. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2016.1159093
Sedman RM, Beaumont J, McDonald TA, Reynolds S, Krowech G, Howd R (2006) Review of the evidence regarding the carcinogenicity of hexavalent chromium in drinking water. J Environ Sci Heal - Part C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev 24:155–182. https://doi.org/10.1080/10590500600614337
Shaida MA, Sen AK, Dutta RK (2018) Alternate use of sulphur rich coals as solar photo-Fenton agent for degradation of toxic azo dyes. J Clean Prod 195:1003–1014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.286
Shaida MA, Dutta RK, Sen AK, Ram SS, Sudarshan M, Naushad M, Boczkaj G, Nawab MS (2022) Chemical analysis of low carbon content coals and their applications as dye adsorbent. Chemosphere 287:132286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132286
Sharma S, Bhattacharya A (2017) Drinking water contamination and treatment techniques. Appl Water Sci 7:1043–1067. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0455-7
Sharma A, Dutta RK (2018) Se-doped CuO NPs/H2O2/UV as a highly efficient and sustainable photo-Fenton catalytic system for enhanced degradation of 4-bromophenol. J Clean Prod 185:464–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.03.049
Singh R, Singh AP, Kumar S, Giri BS, Kim KH (2019) Antibiotic resistance in major rivers in the world: a systematic review on occurrence, emergence, and management strategies. J Clean Prod 234:1484–1505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.06.243
Suci PA, Mittelman MW, Yu FP, Geesey GG (1994) Investigation of ciprofloxacin penetration into Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 38:2125–2133. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.38.9.2125
Tauc J, Grigorovici R, Vancu A (1966) Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous germanium. Phys Status Solidi 15:627–637. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.19660150224
Tumolo M, Ancona V, De Paola D, Lossaco D, Campanale C, Masarelli C, Uricchio VF (2020) Chromium pollution in European water, sources, health risk, and remediation strategies: an overview. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:1–25. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17155438
Verma S, Kim KH, Kumar N, Bhattacharya SS, Naushad M, Dutta RK (2022) Amine-amide functionalized graphene oxide sheets as bifunctional adsorbent for the removal of polar organic pollutants. J Hazard Mater 429:128308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128308
Wang J, Zhuan R (2020) Degradation of antibiotics by advanced oxidation processes: an overview. Sci Total Environ 701:135023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135023
Wang Y, Su Y, Fang W, Zhang Y, Li X, Zhang G, Sun W (2020) SnO2/SnS2 nanocomposite anchored on nitrogen-doped RGO for improved photocatalytic reduction of aqueous Cr(VI). Powder Technol 363:337–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2020.01.009
Wang R, Zhu P, Liu M, Xu J, Duan M, Luo D (2021) Synthesis and characterization of magnetic ZnFe2O4/Bi0-Bi2MoO6 with Z-scheme heterojunction for antibiotics degradation under visible light. Sep Purif Technol 277:119339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119339
Xu L, Chen W-q, Ke S-q, Zhang SM, Zhu M, Zhang Y, Shi WY, Horike S, Tang L (2020) Construction of heterojunction Bi/Bi5O7I/Sn3O4 for efficient noble-metal-free Z-scheme photocatalytic H2 evolution. Chem Eng J 382:122810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122810
Yi J, Mo H, Zhang B, Song J, Liu D, Zhuo G (2019) CeO2/Bi2MoO6 heterostructured microspheres with synergistic effect for accelerating photogenerated charge separation. Sep Purif Technol 211:474–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.10.022
Zhang R, Tang J, Li J, Cheng Z, Chaemfa C, Liu D, Zheng Q, Song M, Luo C, Zhang G (2013) Occurrence and risks of antibiotics in the coastal aquatic environment of the Yellow Sea, North China. Sci Total Environ 450–451:197–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.02.024
Zhang F, Zhang Y, Zhou C, Yang Z, Xue H, Dionysiou DD (2017) A new high efficiency visible-light photocatalyst made of SnS2 and conjugated derivative of polyvinyl alcohol and its application to Cr(VI) reduction. Chem Eng J 324:140–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.05.009
Zhang H, Bian H, Zhang H, Xu B, Wang C, Zhang L, Li D, Wang F (2020) Magnetic separable Bi2Fe4O9/Bi2MoO6 heterojunctions in Z-Scheme with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity for organic pollutant degradation. Catal Lett 150:2464–2473. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-020-03157-4
Zhao W, Feng Y, Huang H, Zhou P, Li J, Zhang L, Dai B, Xu J, Zhu F, Sheng N, Leung DYC (2019) A novel Z-scheme Ag3VO4/BiVO4 heterojunction photocatalyst: Study on the excellent photocatalytic performance and photocatalytic mechanism. Appl Catal B Environ 245:448–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.01.001
Zhou Q, Huang W, Xu C, Liu X, Yang K, Li D, Hou Y, Dionysiou DD (2021) Novel hierarchical carbon quantum dots-decorated BiOCl nanosheet/carbonized eggshell membrane composites for improved removal of organic contaminants from water via synergistic adsorption and photocatalysis. Chem Eng J 420:129582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129582
Acknowledgements
Gandharve Kumar acknowledges the Quality Improvement Program (QIP) supported by the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) for providing scholarship to carry out his research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Gandharve Kumar contributed to the conception and design and experiments in consultation with RK Dutta, who supervised the work and prepared the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor:Sami Rtimi
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, G., Dutta, R.K. Sunlight-induced enhanced photocatalytic reduction of chromium (VI) and photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye and ciprofloxacin antibiotic by Sn3O4/SnS2 nanocomposite. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 57758–57772 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19853-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19853-0