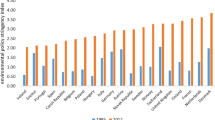
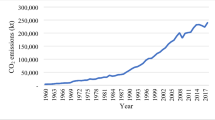
Abstract
Electric power industry, as one of the main industries leading to the increase of China's carbon emissions, accounts for about 40% of the total carbon emissions. It is of great practical significance to study the influencing factors of carbon emission decoupling index in power industry and put forward relevant policy suggestions. Based on the decoupling index of China’s electric power industry from 1995 to 2018, this paper explores the influence of each index on the decoupling index through the autoregressive- distributed lag model. It turns out that the policy will significantly change the rate of change of carbon emissions and the rate of economic growth, but the impact of the policy is extremely short-lived; power generation structure, environmental regulations, and total lighting value at night play a positive role in promoting the decoupling index, while thermal power fuel efficiency and power generation conversion ratio play a negative role in inhibiting the decoupling index. In addition, the influence of power generation structure, environmental regulations, and the total value of night light on decoupling index also has a lagging and cumulative effect. Therefore, we propose targeted policy recommendations for policy formulation, green development, and low carbon construction in China’s power industry from different perspectives based on the findings of the study.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The author declares that the data found in support of this study are publicly available, and the data source is provided in the paper.
References
Arunrat N, Wang C, Pumijumnong N (2016) Alternative cropping systems for greenhouse gases mitigation in rice field: a case study in Phichit province of Thailand. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.05.137
Bao J, Xu J, Xie B, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Jia H, Zheng W (2020) Research on the relationship between industrial energy consumption and economic growth and industrial carbon emissions in Nanyang City based on Tapio decoupling analysis[J]. China Market (04): 77–80. https://doi.org/10.13939/j.cnki.zgsc.2020.04.077
Budzinski M, Bezama A, Thrän D (2020) Estimating the potentials for reducing the impacts on climate change by increasing the cascade use and extending the lifetime of wood products in Germany. Resour Conserv Recycl X 6:100034. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcrx.2020.100034
Cansino JM, Roman R, Ordonez M (2016) Main drivers of changes in CO2 emissions in the Spanish economy: a structural decomposition analysis. Energy Polic 89:150–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2015.11.020
Cao J, Jiang W (2018) Comprehensive evaluation on circular economy level based on AHP-TOPSIS analytical method[J]. Stat Decis 34(14):128–131. https://doi.org/10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2018.14.030
Charemza WW, Deadman DF (1997) New directions in econometric practice, 2nd edn.
Chen GJ, Hou FJ, Chang KL, Feng YJ, Zhang Z, Meng XQ (2019) Factor decomposition analysis of CO_2 emissions caused by power industry in trianger region of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei. J Saf Environ https://doi.org/10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2019.03.030
Chi Z, Su B, Zhou K, Yang S (2018) Analysis of electricity consumption in China (1990–2016) using index decomposition and decoupling approach. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.246
De Oliveira-De Jesus PM (2019) Effect of generation capacity factors on carbon emission intensity of electricity of Latin America & the Caribbean, a temporal IDA-LMDI analysis. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 101:516–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.11.030
Diakoulaki D, Mandaraka M (2007) Decomposition analysis for assessing the progress in decoupling industrial growth from CO2 emissions in the EU manufacturing sector. Energy Econ 29:636–664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2007.01.005
Ding T, Li W (2019) Peak forecast of carbon emissions in the power industry from the perspective of economic growth and emission reduction[J]. Sci Technol Manag Res 39(18):246–253
Dotse SQ, Dagar L, Petra MI, Silva LD (2016) Evaluation of national emissions inventories of anthropogenic air pollutants for Brunei Darussalam. Atmos Environ 133:81–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.03.024
Du G, Sun C, Ouyang X, Zhang C (2018) A decomposition analysis of energy-related CO2 emissions in Chinese six high-energy intensive industries. J Clean Prod 184:1102–1112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.304
Freitas L, Kaneko S (2011) Decomposing the decoupling of CO2 emissions and economic growth in Brazil. Ecol Econ 70:1459–1469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2011.02.011
He Y, Xing Y, Ji Y, Zhang L (2020) On influential factors and regional difference in carbon emissions from power industry at home in China[J]. J Saf Environ 20(06):2343–2350. https://doi.org/10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2019.1395
Khan Z, Sisi Z, Siqun Y (2019) Environmental regulations an option: Asymmetry effect of environmental regulations on carbon emissions using non-linear ARDL. Energy Sourc 41:137–155. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2018.1504145
Kjaer LL, Pigosso DCA, Niero M, Bech NM, Mcaloone TC, Lifset R (2019) Product/service-systems for a circular economy: The route to decoupling economic growth from resource consumption?[J]. J Ind Ecol 23(1):22–35. https://doi.org/10.1111/jiec.12747
Langnel Z, Amegavi GB (2020) Globalization, electricity consumption and ecological footprint: An autoregressive distributive lag (ARDL) approach. Sustain Cit Soc 63:102482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2020.102482
Li R, Wang Q, Liu Y, Jiang R (2021) Per-capita carbon emissions in 147 countries: The effect of economic, energy, social, and trade structural changes. Sustain Prod Consum. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2021.02.031
Liu Y, Feng C (2020) Decouple transport CO2 emissions from China’s economic expansion: a temporal-spatial analysis. Transport Res D Transport Environ 79:102225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2020.102225
Loo BPY, Banister D (2016) Decoupling transport from economic growth: Extending the debate to include environmental and social externalities. J Transp Geogr. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2016.10.006
Ma J, Qin F, Xie X (2019) Decoupling the inbound tourism carbon emissions off the tourism economic growth[J]. J Xinjiang Univ 47(02):16–23. https://doi.org/10.13568/j.cnki.issn1000-2820.2019.02.002
Narayan PK, Smyth R (2005) Electricity consumption, employment and real income in Australia evidence from multivariate Granger causality tests. Energy Policy 33:1109–1116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2003.11.010
Parker S (2021) A decoupling analysis of transport CO2 emissions from economic growth: Evidence from Vietnam. Int J Sustain Transp. https://doi.org/10.1080/15568318.2021.1952661
Perron P (1994) Further evidence on breaking trend functions in macroeconomic variables[C]
Pesaran MH, Shin Y, Smith RJ (2001) Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. J Appl Economet 16:289–326. https://doi.org/10.1002/jae.616
Project Synthesis Report Writing Group, He J, Xie Z, Li Z, Zhang X (2020) Comprehensive report on “China's long-term low-carbon development strategy and transformation path”. 30(11):1–25. https://doi.org/10.12062/cpre.20201025
Román-Collado R, Cansino JM, Botia C (2018) How far is Colombia from decoupling? Two-level decomposition analysis of energy consumption changes. Energy 148:687–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.01.141
Sinn H-W (2008) Public policies against global warming: a supply side approach. Int Tax Public Financ 15:360–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10797-008-9082-z
Smulders S, Tsur Y, Zemel A (2012) Announcing climate policy: can a green paradox arise without scarcity? J Environ Econ Manag. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeem.2012.02.007
Sun J (2020) Research on the decoupling status and mitigation potential of China’s CO2 emissions at provincial level[D]. China University of Mining and Technology
Tapio P (2005) Towards a theory of decoupling: degrees of decoupling in the EU and the case of road traffic in Finland between 1970 and 2001. Transp Policy 12:137–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranpol.2005.01.001
Vehmas J, Kaivo-oja J, Luukkanen J (2003) Global trends of linking environmental stress and economic growth. Turku: Finland Futures Research Centre 6
Wang Q, Wang L (2020) Renewable energy consumption and economic growth in OECD countries: A nonlinear panel data analysis. Energy 207:118200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.118200
Wang Q, Zhang F (2021) What does the China’s economic recovery after COVID-19 pandemic mean for the economic growth and energy consumption of other countries? J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126265
Wang H, Zhou P (2018) Multi-country comparisons of CO2 emission intensity: the production-theoretical decomposition analysis approach. Energy Econ 74:310–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2018.05.038
Wang Q, Jiang XT, Li R (2017) Comparative decoupling analysis of energy-related carbon emission from electric output of electricity sector in Shandong Province, China. Energy 127:78–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.03.111
Wen L, Huang L, Yan F (2019) Cluster analysis of CO_2 emissions by the Chinese power industry. Polish J Environ Stud 28:913–921. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/81703
Wu H, Gu S, Zhou H, Wang X, Dong D, Hu Y (2011) Relationships between energy comsumption-carbon emissions and economic growth in Hebei Province[J]. Resour Sci 33(10):1897–1905
Wu N, Shen L, Zhong S, Zhang C (2019) Spatio-temporal coupling relationship between economic growth and carbon emission in Shanxi-Shaanxi-Inner Mongolia[J]. Econ Geogr 39(09):17–23. https://doi.org/10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2019.09.003
Xie P, Fan Y, Mu Z, Gao S (2020) Influencing factors of the decoupling relationship between CO 2 emission and economic development in China’s power industry. Energy 209:118341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.118341
Xing H (2019) Empirical study of energy consumption, carbon emission and economic growth in the Changjiang River economic zone———based on elastic decoupling model[J]. Resour Dev Market 35(10):1244–1251. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1005-8141.2019.10.004
Yang Y, Guo Y, Zhu W, Huang J (2018) Discussion of spatio-temporal differentiation for decoupling carbon emissions from economic growth in China’s aluminum Industry[J]. Min Metallurg Eng 38(06):168–172
Yang G, Chen Y, Wang D, Zhang J (2020a) Decoupling and regional differences of electricity consumption in China[J]. Power Syst Clean Energy 36(08):1–8
Yang Y, Tang D, Zhang P (2020) Double effects of environmental regulation on carbon emissions in China: empirical research based on spatial econometric model. Discr Dyn Nature Soc 2020:1284946. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1284946
Yang J, Hao Y, Feng C (2021) A race between economic growth and carbon emissions: What play important roles towards global low-carbon development? Energy Econ 100:105327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105327
Ye Q, Zeng G, Dai S, Wang F (2018) Research on the effects of different policy tools on China’s emissions reduction innovation: based on the panel data of 285 prefectural-level municipalities[J]. Chin Popul Resour Environ 28(02):115–122
Yu B, Wang C, Gong W, Chen Z, Shi K, Wu B, Hong Y, Li Q, WU J (2021) Nighttime light remote sensing and urban studies: data, methods, applications, and prospects [J]. J Remote Sens 25(01):342–364
Yuan Q, Yan Z (2020) Threshold effect and regional differences of environmental regulation on carbon emission[C]. IOP Publishing, p 32057
Zhang Y (2015) An analysis of influencing factors and scenario of carbon emission decoupling in Fujian Province[J]. J Southwest Petrol Univ (Soc Sci Edit) 17(04):13–20. https://doi.org/10.11885/j.issn.1674-5094.2014.11.01.02
Zhang H, Wei X (2014) Green paradox or forced emission-reduction: dual effect of environmental regulation on carbon emissions[J]. China Popul Resour Environ 24(09):21–29. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2014.09.004
Zhu W, Huang Y, Li D (2020) Research on the decoupling relationship between carbon emissions and economic growth in the transportation industry of national central cities[J]. Econ Res Guide 14:104–108
Funding
This paper is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.71964022) and North China Electric Power University Central University Fund (Grant No. 2014MS150).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yanmei Li: conceptualization, validation, resources, review and editing, supervision, data curation, funding acquisition, and project administration. Dandan Niu: methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, and writing—original draft preparation. Jiawei Song: material preparation, data collection, analysis, and revision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent for participation
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ilhan Ozturk
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Niu, D. & Song, J. Decoupling analysis of carbon emissions in China’s power industry—based on ARDL model. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 56535–56554 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19765-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19765-z