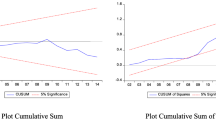
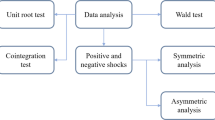
Abstract
The paper examines the impact of macroeconomic variables on CO2 emissions, very few research studies are available to estimate the asymmetric impact and causality. Because of the significance of asymmetries, this paper examines the asymmetric impact of economic growth, crude oil use, and FDI inflows on CO2 emissions in the India wherein COP (Crude oil price) is comprised as the extra variable. The implicate aggressive growth of selected variables over the period 1990–2020 is also assessed. This study uses the methodology ARDL and NARDL model to determine the macroeconomics variable's effects on CO2 emission over the period 1990-2020. Additionally, also applied the EKC (Environmental Kuznets Curve) hypothesis with an application of ARDL and NARDL model. With help of the ARDL and NARDL model, the study shows the results that a rise in economic growth would reduce CO2 (carbon dioxide) emissions while a decrease in economic growth would raise CO2 emissions which indicates an inverted U-shaped Curved relationship between economic growth and CO2 emissions. The positive and negative shockwaves in COP (crude oil prices) have a satisfactory and substantial impact on CO2 emissions as well. Besides, the crude oil consumption with positive shockwave confirmations has a positive and substantial impact on CO2 emission. In addition, the results of FDI inflows support the pollution heaven hypothesis. In light of these outcomes, this paper also recommended policy implications and future research, the policy implications are where the descending flow of FDI allows limited space to India in FDI selection; however, the existence of emission merging and implementation of carbon pricing may facilitate India in achieving its environmental targets.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable
References
Abdullah L (2015) Linear Relationship between CO2 Emissions and Economic Variables: Evidence from a Developed Country and a Developing Country J Sustain Develop, 8 (2)
Acharyya J (2015) FDI, growth and the environment: Evidence from India on CO2 emission during the last two decades. J Econ Dev 2009(34):43–58
Ali W, Abdullah A, Azam M (2017) Re-visiting the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis for Malaysia: Fresh evidence from ARDL bounds testing approach. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 77:990–1000
Amri F (2016) The relationship amongst energy consumption, foreign direct investment and output in developed and developing countries. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 64:694–702
An T, Xu C, Liao X (2021) The impact of FDI on environmental pollution in China: Evidence from spatial panel data. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 1–13
Antón A (2020) Taxing crude oil: A financing alternative to mitigate climate change? Energy Policy 136:111031
Apergis N (2016) Environmental Kuznets curves: new evidence on both panel and country-level CO2 emissions. Energy Econ 54:263–271
Arminen H, Menegaki AN (2019) Corruption, climate and the energy-environment-growth nexus. Energy Econ 80:621–634
Baek J (2016) A new look at the FDI-income-energy-environment nexus: Dynamic panel data analysis of ASEAN. Energy Policy 91:22–27
Behera SR, Dash DP (2017a) Effect of urbanization, energy consumption, and foreign direct investment on the carbon dioxide emission in the SSEA (South and Southeast Asian) region. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 70:96–106
Behera SR, Dash DP (2017b) The effect of urbanization, energy consumption, and foreign direct investment on the carbon dioxide emission in the SSEA (South and Southeast Asian) region. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 70:96–106
Bhattacharya M, Churchill SA, Paramati SR (2017) The dynamic impact of renewable energy and institutions on economic output and CO2 emissions across regions. Renew Energy 111:157–167
Boutabba MA (2014) The impact of financial development, income, energy and trade on carbon emissions: Evidence from the Indian economy. Econ Modell 40:33–41
Chen PY, Chen ST, Hsu CS, Chen CC (2016) Modeling the global relationships among economic growth, energy consumption, and CO2 emissions. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 65:420–431
Chen T, Gozgor G, Koo CK, Lau CKM (2020) Does international cooperation affect CO 2 emissions? Evidence from OECD countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–9
Galeotti M, Lanza A, Pauli F (2006) Reassessing the environmental Kuznets curve for CO2 emissions: A robustness exercise. Ecol Econ 57(1):152–163
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1995) Economic Growth and the Environment. Quarterly J Econ 110(2):353–377
Haug AA, Ucal M (2019) The role of trade and FDI for CO2 emissions in Turkey: Nonlinear relationships. Energy Econ 81:297–307
He J (2006) Pollution haven hypothesis and environmental impacts of foreign direct investment: the case of industrial emission of sulfur dioxide (SO2) in Chinese provinces. Ecol Econ 60(1):228–245
Iwata H, Okada K, Samreth S (2012) Empirical study on the determinant of CO2 emissions: evidence from OECD Countries., Applied Economics, 44
Jiang S, Chen Z, Shan L, Chen X, Wang H (2017) Committed CO2 emissions of China’s coal-fired power generators from 1993 to 2013. Energy Policy 104:295–302
Kacar SB, Kayalica MO (2014) Environmental Kuznets Curve and sulfur emissions: A comparative econometric analysis. Environ Econ 5:8–20
Kahouli B (2018) The causality link between energy electricity consumption, CO2 emissions, R&D stocks and economic growth in Mediterranean countries (MCs. ). Energy 145:388–399
Karasoy A, Akcay S (2019) Effects of renewable energy consumption and trade on environmental pollution: The Turkish case. Manag Environ Quality: Int J 30(2):437–455
Lee JW (2013a) The contribution of foreign direct investment to clean energy use, carbon emissions and economic growth. Energy Policy 55:483–489
Lee JW (2013b) The contribution of foreign direct investment to clean energy use, carbon emissions and economic growth. Energy Policy 55:483–489
Lee JW (2013c) The contribution of foreign direct investment to clean energy use, carbon emissions and economic growth. Energy Policy 55(1):483–489
Levinson A, Taylor MS (2008) Unmasking the Pollution Haven Effect. Int Econ Rev, 49 (1)
Liu X, Bae J (2018) Urbanization and industrialization impact of CO2 emissions in China. J Cleaner Product 172:178–186
Lv Z (2017) The Effect of Democracy on CO2 Emissions in Emerging Countries: Does the Level of Income Matter? Renewable Sustain Energy Rev 72:900–906
Mazzanti AM, Roberto Z (2007) Economic Dynamics, Emission Trends and the EKC Hypothesis New Evidence Using NAMEA and Provincial Panel Data for Italy Massimiliano
Narayan PK, Narayan S (2010) Carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth: Panel data evidence from developing countries. Energy Policy 38:661–666
Nkengfack H, Kaffo FH (2019) Energy consumption, economic growth and carbon emissions: Evidence from the top three emitters in Africa. Modern Economy 10(01):52–71
Oxelheim L, Ghauri P (2008) EU –China and the non -transparent race for inward FDI. J Asian Econ 19(4):358–370
Ozturk I, Al-Mulali U (2015) Investigating the validity of the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in Cambodia. Ecol Indic 57:324–330
Pao H-T, Tsai C-M (2011) Multivariate Granger causality between CO2 emissions, energy consumption, FDI (foreign direct investment) and GDP (gross domestic product): Evidence from a panel of BRIC (Brazil, Russian Federation, India, and China) countries. Energy 36(1):685–693
Pata UK (2018) Renewable energy consumption, urbanization, financial development, income and CO2 emissions in Turkey: Testing EKC hypothesis with structural breaks. J Cleaner Prod 187:770–779
Paul S, Bhattacharya RN (2004) Causality between energy consumption and economic growth in India: A note on conflicting results. Energy Econ 26:977–983
Ponce P, Alvarado R (2019) Air pollution, output, FDI, trade openness, and urbanization: evidence using DOLS and PDOLS cointegration techniques and causality. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(19):19843–19858
Raggad B (2020) Economic development, energy consumption, financial development, and carbon dioxide emissions in Saudi Arabia: new evidence from the nonlinear and asymmetric analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–20
Rehman MU, Rashid M (2017) Energy consumption to environmental degradation, the growing appetite in SAARC nations. Renew Energy 111:284–294
Richard JP (2010) Environmental Kuznets curve for CO2 in Canada. Ecol Econ 69(5):1083–1093
Sbia R, Shahbaz M, Hamdi H (2014) A contribution of foreign direct investment, clean energy, trade openness, carbon emissions and economic growth to energy demand in UAE. Econ Modell 36:191–197
Schmalensee R, Stoker TM, Judson RA (1998) World Carbon Dioxide Emissions: 1950 -2050. Rev Econ Stat 80(1):15–27
Seker F, Ertugrul HM, Cetin M (2015) The impact of foreign direct investment on environmental quality: A bounds testing and causality analysis for Turkey. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 52:347–356
Selden TM, Song D (1994) Environmental quality and development: Is there a Kuznets curve for air pollution emissions? J Environ Econ Manag 27(2):147–162
Shahbaz M, Sharma R, Sinha A, Jiao Z (2020) Analyzing the nonlinear impact of economic growth drivers on CO2 emissions: designing an SDG framework for India. Energy Policy 148:111965
Sreenu N (2019a) The Effects of Oil Price Shock on the Indian Economy—A Study. Indian Econ J 66(1–2):190–202 2018 © 2019
Sreenu N (2019b) A study on financial constraints of capital structure theories and dividend policy: evidence from Indian capital market. J Int Business Entrepreneurship Develop 12(1):22–36
Sreenu N (2020) Cashless Payment Policy and Its Effects on Economic Growth of India: An Exploratory Study. ACM Trans. Manage. Inf. Syst. 11, 3, Article 15 (August 2020), 10 pages
Sreenu N, Rao KSS, Kishan D (2021) The macroeconomic variables impact on commodity futures volatility: A study on Indian markets. Cogent Business & Manag 8(1):1939929
Toumi S, Toumi H (2019) Asymmetric causality among renewable energy consumption, CO 2 emissions, and economic growth in KSA: evidence from a non-linear ARDL model. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(16):16145–16156
Varghese G (2017) Inflationary effects of oil price shocks in the Indian economy. J Public Affairs 17(3):e1614 -n/a
Wang SS, Zhou DQ, Zhou P, Wang QW (2011) CO2 emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in China: a panel data analysis. Energy Policy 39:4870–4875
Yaduma N, Kortelainen M, Wossink A (2015) The environmental Kuznets curve at different levels of economic development: a counterfactual quantile regression analysis for CO2 emissions. J Environ Econ Policy 4(3):1–26
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
for this paper the author only conceptualized the idea, design the method, literature review, analysis and overall developed the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
No human participants involved in this research study
Consent to publish
manuscript does not contain data from any individual person and not applicable,
Competing interests
no competing interests
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Nicholas Apergis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sreenu, N. Impact of FDI, crude oil price and economic growth on CO2 emission in India: - symmetric and asymmetric analysis through ARDL and non -linear ARDL approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 42452–42465 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19597-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19597-x