Abstract
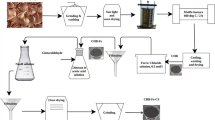
Triclosan (TCS) is widely used in the production of antibacterial products, being often found in wastewater. Therefore, this study developed new materials via soybean hulls (SBHF) and açaí seeds (AÇSF) functionalization with iron oxide nanoparticles to be applied in the TCS adsorption. The characterization confirmed the functionalization of the materials. The adsorption results indicated that the equilibrium of the process occurred after 480 and 960 min for SBHF and AÇSF, respectively. The maximum adsorptive capacity values were 158.35 and 155.09 mg g−1 for SBHF and AÇSF, respectively, at 318 K. The kinetic and isothermal data better fitted to the pseudo-second-order and Langmuir models. Thermodynamics indicated that the processes had an endothermic, spontaneous, and reversible character. The main adsorption mechanisms were H-bond and π-interactions. The pH and ionic strength studies indicated that the adsorption efficiency has not been reduced pronouncedly. The biosorbents reuse was effective for five cycles. In the synthetic mixture, the removal rate was satisfactory (92.53% and 57.02%, respectively for SBHF and AÇSF). These results demonstrate the biosorbents high potential for large-scale application.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Andrade MB, Santos TRT, Fernandes Silva M et al (2019) Graphene oxide impregnated with iron oxide nanoparticles for the removal of atrazine from the aqueous medium. Sep Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2018.1549077
Awad AM, Shaikh SMR, Jalab R, et al (2019) Adsorption of organic pollutants by natural and modified clays: A comprehensive review. Sep Purif Technol
Azari A, Gholami M, Torkshavand Z, et al (2015) Evaluation of basic violet 16 adsorption from aqueous solution by magnetic zero valent iron-activated carbon nanocomposite using response surface method: Isotherm and kinetic studies. J Maz Univ Med Sci
Bansal RC, Goyal M (2005) Activated carbon adsorption
Beltrame KK, Cazetta AL, de Souza PSC et al (2018) Adsorption of caffeine on mesoporous activated carbon fibers prepared from pineapple plant leaves. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.08.034
Chandane V, Singh VK (2016) Adsorption of safranin dye from aqueous solutions using a low-cost agro-waste material soybean hull. Desalin Water Treat 57:4122–4134. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.991758
Chen X, Gu X, Bao L et al (2021) Comparison of adsorption and desorption of triclosan between microplastics and soil particles. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127947
Cho EJ, Kang JK, Moon JK et al (2021) Removal of triclosan from aqueous solution via adsorption by kenaf-derived biochar: Its adsorption mechanism study via spectroscopic and experimental approaches. J Environ Chem Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106343
Cusioli LF, Quesada HB, Baptista ATA et al (2019) Soybean Hulls as A Low-Cost Biosorbent for Removal of Methylene Blue Contaminant. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.13328
Cusioli LF, Quesada HB, Barbosa de Andrade M et al (2021) Application of a novel low-cost adsorbent functioned with iron oxide nanoparticles for the removal of triclosan present in contaminated water. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2021.111328
Czech B, Kończak M, Rakowska M, Oleszczuk P (2021) Engineered biochars from organic wastes for the adsorption of diclofenac, naproxen and triclosan from water systems. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125686
Da Silva Vasconcelos De Almeida A, Vieira WT, Bispo MD, et al (2021) Caffeine removal using activated biochar from acai seed (Euterpe oleracea Mart): Experimental study and description of adsorbate properties using Density Functional Theory (DFT). J Environ Chem Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104891
do Nascimento RF, de Lima ACA, Vidal CB et al (2014) Adsorção: aspectos teóricos e aplicaçoes ambientais. Imprensa Universitária, Fortaleza
Dos Santos TRT, Mateus GAP, Silva MF et al (2018a) Evaluation of Magnetic Coagulant (Α-Fe2O3-MO) and its Reuse in Textile Wastewater Treatment. Water Air Soil Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3747-8
Dos Santos TRT, Silva MF, de Andrade MB et al (2018b) Magnetic coagulant based on moringa oleifera seeds extract and super paramagnetic nanoparticles: Optimization of operational conditions and reuse evaluation. Desalin Water Treat. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2018.22065
Dou R, Zhang J, Chen Y, Feng S (2017) High efficiency removal of triclosan by structure-directing agent modified mesoporous MIL-53(Al). Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8583-7
Fachina YJ, de Andrade MB, Guerra ACS et al (2020) Graphene oxide functionalized with cobalt ferrites applied to the removal of bisphenol A: ionic study, reuse capacity and desorption kinetics. Environ Technol (united Kingdom). https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2020.1830183
Gao JF, Wu ZL, Duan WJ, Zhang WZ (2019) Simultaneous adsorption and degradation of triclosan by Ginkgo biloba L. stabilized Fe/Co bimetallic nanoparticles. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.194
Gonçalves AC, Schwantes D, Campagnolo MA et al (2018) Removal of toxic metals using endocarp of açaí berry as biosorbent. Water Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2018.032
Gupta G, Khan J, Singh NK (2021) Application and efficacy of low-cost adsorbents for metal removal from contaminated water: A review. In: Materials Today: Proceedings
Han R, Zhang L, Song C et al (2010) Characterization of modified wheat straw, kinetic and equilibrium study about copper ion and methylene blue adsorption in batch mode. Carbohydr Polym. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.10.054
Januário EFD, Fachina YJ, Wernke G, et al (2022a) Application of activated carbon functionalized with graphene oxide for efficient removal of COVID-19 treatment-related pharmaceuticals from water. ChemosphereChemosphere 133213
Januário EFD, Vidovix TB, Calsavara MA et al (2022b) Membrane surface functionalization by the deposition of polyvinyl alcohol and graphene oxide for dyes removal and treatment of a simulated wastewater. Chem Eng Process - Process Intensif. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2021.108725
Januário EFD, Vidovix TB, de Araújo LA et al (2021a) Investigation of Citrus reticulata peels as an efficient and low-cost adsorbent for the removal of safranin orange dye. Environ Technol 1–37. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2021.1946601
Januário EFD, Vidovix TB, de Camargo Lima Beluci N, et al (2021b) Advanced graphene oxide-based membranes as a potential alternative for dyes removal: A review. Sci Total Environ 789:147957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147957
Jiang N, Shang R, Heijman SGJ, Rietveld LC (2020) Adsorption of triclosan, trichlorophenol and phenol by high-silica zeolites: Adsorption efficiencies and mechanisms. Sep Purif Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.116152
Kadhom M, Albayati N, Alalwan H, Al-Furaiji M (2020) Removal of dyes by agricultural waste. Sustain Chem Pharm
Kaur H, Bansiwal A, Hippargi G, Pophali GR (2018) Effect of hydrophobicity of pharmaceuticals and personal care products for adsorption on activated carbon: Adsorption isotherms, kinetics and mechanism. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0054-7
Kaur H, Hippargi G, Pophali GR, Bansiwal A (2019) Biomimetic lipophilic activated carbon for enhanced removal of triclosan from water. J Colloid Interface Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.09.093
Koch CC (2007) Structural nanocrystalline materials: An overview. J Mater Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0609-3
Kong X, Li F, Li Y et al (2020) Molecularly imprinted polymer functionalized magnetic Fe3O4 for the highly selective extraction of triclosan. J Sep Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201900924
Langmuir I (1917) The Constitution and Fundamental Properties of Solids and Liquids. J Am Chem Soc. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja02254a006
Lin Y, Jin X, Owens G, Chen Z (2019) Simultaneous removal of mixed contaminants triclosan and copper by green synthesized bimetallic iron/nickel nanoparticles. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133878
Lu YC, Mao JH, Zhang W et al (2020) A novel strategy for selective removal and rapid collection of triclosan from aquatic environment using magnetic molecularly imprinted nano−polymers. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124640
Luo Z, He Y, Zhi D et al (2019) Current progress in treatment techniques of triclosan from wastewater: A review. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133990
Ma J, Yu F, Zhou L et al (2012) Enhanced adsorptive removal of methyl orange and methylene blue from aqueous solution by alkali-activated multiwalled carbon nanotubes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:5749–5760. https://doi.org/10.1021/am301053m
Ma J, Zhao J, Zhu Z et al (2019) Effect of microplastic size on the adsorption behavior and mechanism of triclosan on polyvinyl chloride. Environ Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113104
Mahanna H, Samy M (2020) Adsorption of reactive red 195 dye from industrial wastewater by dried soybean leaves modified with acetic acid. Desalin Water Treat. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2020.24960
Mohd Khori NKE, Hadibarata T, Elshikh MS et al (2018) Triclosan removal by adsorption using activated carbon derived from waste biomass: Isotherms and kinetic studies. J Chinese Chem Soc. https://doi.org/10.1002/jccs.201700427
Mpatani FM, Aryee AA, Kani AN et al (2020) Uptake of micropollutant-bisphenol A, methylene blue and neutral red onto a novel bagasse-β-cyclodextrin polymer by adsorption process. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127439
Paixão RM, Reck IM, Bergamasco R et al (2018) Activated carbon of Babassu coconut impregnated with copper nanoparticles by green synthesis for the removal of nitrate in aqueous solution. Environ Technol (United Kingdom) 39:1994–2003. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2017.1345990
Pathania D, Sharma A, Kumar S et al (2021a) Bio-synthesized Cu–ZnO hetro-nanostructure for catalytic degradation of organophosphate chlorpyrifos under solar illumination. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130315
Pathania D, Srivastava AK, Sharma A (2021b) Bio-inspired fabrication of Cu–ZrO2 nanocomposites for the remediation of Cr(VI) from water system. Curr Res Green Sustain Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crgsc.2021.100073
Phuekphong A (Fern), Imwiset K (Jaa), Ogawa M (2021) Adsorption of Triclosan onto Organically Modified-Magadiite and Bentonite. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater. 10.1007/s10904-021-01919-0
Phuekphong AF, Imwiset KJ, Ogawa M (2020) Organically Modified Bentonite as an Efficient and Reusable Adsorbent for Triclosan Removal from Water. Langmuir. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c00407
Qian X, Xu L, Zhu Y et al (2021) Removal of aqueous triclosan using TiO2 nanotube arrays reactive membrane by sequential adsorption and electrochemical degradation. Chem Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127615
Quan B, Li X, Zhang H, et al (2019) Technology and principle of removing triclosan from aqueous media: A review. Chem Eng J
Quesada HB, Baptista ATA, Cusioli LF, et al (2019a) Surface water pollution by pharmaceuticals and an alternative of removal by low-cost adsorbents: A review. Chemosphere
Quesada HB, Cusioli LF, de Oliveira BC et al (2019b) Acetaminophen adsorption using a low-cost adsorbent prepared from modified residues of Moringa oleifera Lam. seed husks. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 94:3147–1357. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.6121
Qureshi UA, Hameed BH, Ahmed MJ (2020) Adsorption of endocrine disrupting compounds and other emerging contaminants using lignocellulosic biomass-derived porous carbons: A review. J Water Process Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101380
Radoń A, Drygała A, Hawełek Ł, Łukowiec D (2017) Structure and optical properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method with different organic modifiers. Mater Charact. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2017.06.034
Sahmoune MN (2019) Evaluation of thermodynamic parameters for adsorption of heavy metals by green adsorbents. Environ Chem Lett
Saleh TA, Tuzen M, Sari A (2017) Magnetic activated carbon loaded with tungsten oxide nanoparticles for aluminum removal from waters. J Environ Chem Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.05.038
Santaeufemia S, Abalde J, Torres E (2019) Eco-friendly rapid removal of triclosan from seawater using biomass of a microalgal species: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. J Hazard Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.02.083
Santos TRT, Andrade MB, Silva MF et al (2019) Development of α- and γ-Fe2O3 decorated graphene oxides for glyphosate removal from water. Environ Technol (united Kingdom). https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2017.1411397
Sharipova AA, Aidarova SB, Bekturganova NY et al (2017) Triclosan adsorption from model system by mineral sorbent diatomite. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2017.06.012
Sharma A, Sharma G, Naushad M et al (2018) Remediation of anionic dye from aqueous system using bio-adsorbent prepared by microwave activation. Environ Technol (united Kingdom). https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2017.1317293
Sills DL, Gossett JM (2012) Using FTIR to predict saccharification from enzymatic hydrolysis of alkali-pretreated biomasses. Biotechnol Bioeng. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.23314
Sing KSW, Everett DH, Haul RAW et al (1985) International union of pure and applied chemistry physical chemistry division reporting physisorption data for gas/soils systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity. Pure Appl Chem. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac198557040603
Souza RM, Quesada HB, Cusioli LF et al (2021) Adsorption of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) by agro-industrial by-product with chemical and thermal modification: Adsorption studies and mechanism. Ind Crops Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.113200
Tian H, Ma YJ, Li WY, Wang JW (2018) Efficient degradation of triclosan by an endophytic fungus Penicillium oxalicum B4. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-1186-5
Triwiswara M, Lee CG, Moon JK, Park SJ (2020) Adsorption of triclosan from aqueous solution onto char derived from palm kernel shell. Desalin Water Treat. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2020.24872
Vidovix TB, Januário EFD, Bergamasco R, Vieira AMS (2019a) Bisfenol A adsorption using a low-cost adsorbent prepared from residues of babassu coconut peels. Environ Technol (United Kingdom). https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2019.1701568
Vidovix TB, Quesada HB, Bergamasco R et al (2021) Adsorption of Safranin-O dye by copper oxide nanoparticles synthesized from Punica granatum leaf extract. Environ Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2021.1914180
Vidovix TB, Quesada HB, Januário EFD et al (2019b) Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Punica granatum leaf extract applied to the removal of methylene blue. Mater Lett 257:126685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.126685
Weatherly LM, Gosse JA (2017) Triclosan exposure, transformation, and human health effects. J Toxicol Environ Heal - Part B Crit Rev
Weber WJ, Morris JC (1963) Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J Sanit Eng Div 89:31–60
Wernke G, Silva MF, da Silva EA et al (2021) Ag and CuO nanoparticles decorated on graphene oxide/activated carbon as a novel adsorbent for the removal of cephalexin from water. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.127203
Wu J Lin, Ji F, Zhang H, et al (2019) Formation of dioxins from triclosan with active chlorine: A potential risk assessment. J Hazard Mater. 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.12.088
Wu X, Liu P, Huang H, Gao S (2020) Adsorption of triclosan onto different aged polypropylene microplastics: Critical effect of cations. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137033
Ya V, Martin N, Choo KH et al (2019) High-pressure electrocoagulation system with periodic air replenishment for efficient dye wastewater treatment: Reaction dynamics and cost evaluation. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.249
Yang ZF, Li LY, Te HC, Juang RS (2018) Co-precipitation of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles onto carbon nanotubes for removal of copper ions from aqueous solution. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.11.009
Yegane Badi M, Azari A, Pasalari H et al (2018) Modification of activated carbon with magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticle composite for removal of ceftriaxone from aquatic solutions. J Mol Liq. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.04.019
Yin CY, Aroua MK, Daud WMAW (2007) Review of modifications of activated carbon for enhancing contaminant uptakes from aqueous solutions. Sep Purif Technol
Yokoyama JTC, Cazetta AL, Bedin KC et al (2019) Stevia residue as new precursor of CO 2 -activated carbon: Optimization of preparation condition and adsorption study of triclosan. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.01.096
Zhang L, Dong WF, Sun HB (2013) Multifunctional superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Design, synthesis and biomedical photonic applications. Nanoscale
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) and Higher Education Personnel Improvement Coordination (CAPES) Financing Coode 001. The authors also thank the Complex of Research Support Center (COMCAP) of the State University of Maringá (UEM) for the characterization analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Taynara Basso Vidovix: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing-reviewing and editing, Project administration. Eduarda Freitas Diogo Januário: Formal analysis, Writing—original draft, Visualization, Investigation, Validation. Micael Furioso Araújo: Conceptualization, Methodology, Visualization. Rosângela Bergamasco: Resources, Formal analysis. Angélica Marquetotti Salcedo Vieira: Resources, Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vidovix, T.B., Januário, E.F.D., Araújo, M.F. et al. Investigation of two new low-cost adsorbents functionalized with magnetic nanoparticles for the efficient removal of triclosan and a synthetic mixture. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 46813–46829 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19187-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19187-x