Abstract
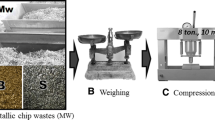
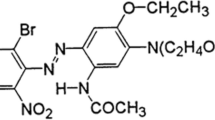
The indigo blue dye is widely used in the textile industry, specifically in jeans dyeing, the effluents of which, rich in organic pollutants with recalcitrant characteristics, end up causing several environmental impacts, requiring efficient treatments. Several pieces of research have been conducted in search of effective treatment methods, among which is electrocoagulation. This treatment consists of an electrochemical process that generates its own coagulant by applying an electric current on metallic electrodes, bypassing the use of other chemical products. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the potential use of iron slag in the electrocoagulation of a synthetic effluent containing commercial indigo blue dye and the effluent from a textile factory. The quantified parameters were color, turbidity, pH, electrical conductivity, sludge generation, phenol removal, chemical oxygen demand (COD), and total organic carbon (TOC). The electrocoagulation treatment presented a good efficiency in removing the analyzed parameters, obtaining average removal in the synthetic effluent of 85% of color and 100% of phenol after 25 min of electrolysis. For the effluent from the textile factory, average reductions of 80% of color reaching 177.54 mg Pt CoL−1, 91% of turbidity reaching 93.83 NTU (nephelometric turbidity unit), 100% of phenol, 55% of COD with a final concentration of 298.8 mg O2 L−1, and 73% of TOC with a final concentration of 56.21 mg L−1, in 60 min of electrolysis. The reduced time for removal of color and phenolic compounds in synthetic effluent demonstrates the complexity of treating the real effluent since to obtain removals of the same order a 60-min period of electrolysis was necessary. The results obtained demonstrate the potential of using iron slag as an electrode in the electrocoagulation process in order to reuse industrial waste and reduce costs in the treatment and disposal of solid waste. Thus, the slag can be seen as an alternative material to be used in electrocoagulation processes for the treatment of effluents from the textile industry under the experimental conditions presented, its only limitation being the fact that it is a waste and therefore does not have a standardization in the amounts of iron present in the alternative electrodes.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelileh M, Manian A, Rhomberg D, Ticha MB, Meksi N, Aguiló-Aguayo N, Bechtold T (2020) Calcium-iron-D-gluconate complexes for the indirect cathodic reduction of indigo in denim dyeing: a greener alternative to non-generable chemicals. J Clean Prod 121753https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121753
Albuquerque LF, Salgueiro AA, Melo JL, Chiavone-Filho O (2013) Coagulation of índigo blue presente in dyeing wastewater using a residual bittern. Sep Purif Technol 104:246–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2012.12.005
APHA, AWWA, WEF (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. Amer Public Health Assn, Washington
Ashrafi SD, Safari GH, Sharafi K, Kamani H, Jaafari J (2021) Adsorption of 4-Nitrophenol on calcium alginate-multiwall carbon nanotube beads: modeling, kinetics, equilibriums and reusability studies. Int J Biol Macromol 185:66–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.06.081
Azarian G, Rahmani RA, Masoudi M, Atashzaban Z, Nematollahi D (2018) New batch electro-coagulation process for treatment and recovery of high organic load and low volume egg processing industry wastewater. Process Saf Environ Prot 119:96–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2018.07.025
Bande RM, Prasad B, Mishra IM, Wesawar KL (2008) The oil effluent water treatment for safe disposal by electroflotation. Chem Eng J 137:503–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2007.05.003
Bener S, Bulca O, Palas B, Tekin G, Atalay S, Ersoz G (2019) Electrocoagulation process for the treatment of real textile wastewater: effect of operative conditions on the organic carbon removal and kinetic study. Process Saf Environ Prot 129:47–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2019.06.010
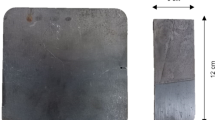
Bragagnolo L, Ferrazzo ST, Muscope FP, Korf EP, Vargas GDLP, Rosa CD, Piazzetta LVH, Tormen FA (2018) Caracterização de resíduos da fundição de ferro e avaliação de possíveis aplicações na construção civil. Revista Brasileira De Ciências Ambientais 50:61–77. https://doi.org/10.5327/Z2176-947820180390
Buscio V, Marín MJ, Crespi M, Gutiérrez-Bouzán C (2015) Reuse of textile wastewater after homogenization–decantation. Chem Eng J 265:122–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.12.057
Carmelio JS et al (2018) Guia ABIFA de Fundição. Associação Brasileira de Fundição, ABIFA, São Paulo
Cerqueira A, Russo C, Marques MRC (2009) Electroflocculation for textile wastewater treatment. Braz J Chem Eng 26:659–668. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0104-66322009000400004
Chakraborty JN (2014) Wastewater problems in textile industry. In: Chakraborty JN. Fundamentals and practices in colouration of textiles. Woodhead Publishing India pp. 515–545
Chen G (2004) Electrochemical technologies in wastewater treatment. Sep Purif Technol 38:11–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2003.10.006
Conama (2005) Resolução CONAMA n° 357/2005. Brasília. http://www2.mma.gov.br/port/conama/legiabre.cfm?codlegi=459. Accessed 27 fev 2020
Conama (2011) Resolução CONAMA n° 430/2011. Brasília. http://www2.mma.gov.br/port/conama/legiabre.cfm?codlegi=646. Accessed 23 jan 2018
da Silva LF, Barbosa AD, de Paula HM, Romualdo LL, Andrade LS (2016) Treatment of paint manufacturing wastewater by coagulation/electrochemical methods: proposals for disposal and/or reuse of treated water. Water Research 101:467–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.05.006
Gendel Y, Lahav O (2010) A new approach to increasing the efficiency of low-pH Fe-electrocoagulation applications. J Hazard Mater 183(1–3):596–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.07.066
Ghalwa NMA, Saqer AM, Farhat NB (2016) Removal of reactive red 24 dye by clean electrocoagulation process using iron and aluminum electrodes. Journal of Chemical Engineering & Process Technology Palestine 7:1–7. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7048.1000269
Ghanbari F, Moradi M, Eslami A (2014) Emamjomeh MM (2014) Electrocoagulation/flotation of textile wastewater with simultaneous application of aluminum and iron as anode. Environ Process 1:447–457. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-014-0029-3
Ghazanfari SZ, Jaafari J, Seyed Davoud Ashrafi SD, Taghavi K (2021) Decolourisation of direct red dye 81 from aqueous solutions by SnO2/H2O2 hybrid process. Int J Environ Anal Chem 1-15.https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2021.1921758
Goerck J, Wolff DB, de Araújo RK, Decezaro ST (2021) Electrocoagulation as post-treatment of the effluent from a vertical flow constructed wetland. Engenharia Sanitária Ambiental 26:113–121. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1413-415220190068
Golbaz S, Nabizadeh R, Rafiee M, Yousefi M (2020) Comparative study of RSM and ANN for multiple target optimisation in coagulation/precipitation process of contaminated waters: mechanism and theory. Int J Environ Anal Chem 1-20.https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1849663
Hendaoui K, Trabelsi-Ayadi M, Ayari F (2021) Optmization and mechanisms analysis of indigo dye removal using continuos electrocoagulation. Chinese Journal of Chamical Engineering 29:242–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2020.07.065
Holkar CR, Jadhav AJ, Pinjari DV, Mahamuni NM, Pandit AB (2016) critical review on textile wastewater treatments: possible approaches. J Environ Manage 182:351–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.07.090
Jaafari J, Yaghmaeian K (2019) Response surface methodological approach for optimizing heavy metal biosorption by the blue-green alga Chroococcus disperses. Desalin Water Treat 142:225–234. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.23406
Jaafari J, Barzanouni H, Mazloomi S, Farahani NAA, Sharafi K, Soleimani P, Haghighat GA (2020) Effective adsorptive removal of reactive dyes by magnetic chitosan nanoparticles: kinetic, isothermal studies and response surface methodology. Int J Biol Macromol 164:344–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.042
Kabdasli I, Gurel M, Tunay O (2010) Characterization and treatment of textile printing wastewaters. Journal Environmental Technology 21:1147–1155. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2000.9619001
Khan AH, Aziz1 HA, Khan NA, Hasan MA, Ahmed S, Farooqi IH, Dhingra A, Vambol V, Changani F, Yousefi M, Islam S, Mozaffari N, Mahtab MS (2021) Impact, disease outbreak and the eco-hazards associated with pharmaceutical residues: a critical review. Int J Environ Sci Technol.https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03158-9
Khandegar V, Saroha AK (2013) Electrocoagulation for the treatment of textile industry effluent – a review. J Environ Manage 128:949–963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2013.06.043
Lee SY, Gagnon GA (2014) Review of the factors relevant to the design and operation of an electrocoagulation system for wastewater treatment. Environ Rev 22:421–429. https://doi.org/10.1139/er-2014-0009
Liu S, Li B, Qi P, Yu W, Zhao J, Liu Y (2019) Performance of freshly generated magnesium hydroxide (FGMH) for reactive dye removal. Colloid and Interface Science Communications 28:34–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colcom.2018.11.004
Matias MS, Melegari SP, Vicentini DS, Matias WG, Ricordel C, Hauchard D (2015) Synthetic wastewaters treatment by electrocoagulation to remove silver nanoparticles produced by different routes. J Environ Manage 159:147–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.05.006
Mollah MYA, Morkovsky P, Gomes JAG, Kesmez M, Parga J, Cocke DL (2004) Fundamentals, present and future perspectives of electrocoagulation. J Hazard Mater 114:199–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2004.08.009
Mook WT, Aroua MK, Szlachta M, Lee CS (2017) Optimisation of reactive black 5 dye removal by electrocoagulation process using response surface methodology. Water Sci Technol 75:952–962. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2016.563
Nariyan E, Sillanpaa M, Wolkersdorfer C (2017) Electrocoagulation treatment of mine water from the deepest working European metal mine-Performance, isotherm and kinetic studies. Sep Purif Technol 177:363–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2016.12.042
Núñez J, Yeber M, Cistemas N, Thibault R, Medina P, Carrasco C (2019) Application of electrocoagulation for the efficient pollutants removal to reuse the treated wastewater in the dyeing process of the textile industry. J Hazard Mater 371:705–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.03.030
Paschoal FMM, Trenuukuisi-Filho G (2005) Aplicação da tecnologia de eletrofloculação na recuperação do corante índigo blue a partir de efluentes industriais. Quím Nova 28(5):766–772. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40422005000500006
Ramazan K, Can OT, Aygun A, Tek A (2019) Comparison of the effects of various supporting electrolytes on the treatment of a dye solution by electrocoagulation process. Colloid and Interface Science Communications 33:100210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colcom.2019.100210
Sirma B, Ozlem B, Burcu P, Gulen T, Suheyda A, Gulin E (2019) Electrocoagulation process for the treatment of real textile wastewater: effect of operative conditions on the organic carbon removal and kinetic study. Process Saf Environ Prot 129:47–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2019.06.010
Verma AK (2017) Treatment of textile wastewaters by electrocoagulation employing Fe-Al composite electrode. Journal of Water Process Engineering 20:168–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2017.11.001
Volkov VV, Chelli R, Righini R, Perry CC (2020) Indigo chromophores and pigments: structure and dynamics. Dyes Pigm 172:107761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2019.107761
Wang CT, Chou WL, Kuo YM (2009) Removal of COD from laundry wastewater by electrocoagulation. J Hazard Mater 164:81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.07.122
Yin C, Tan X, Bie B, Ma H, Yi H (2020) Practical and environment-friendly indirect electrochemical reduction of indigo and dyeing. Scientific Reports 10:4927. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-61795-5
Zakeri HR, Yousefi M, Mohammadi AA, Baziar M, Mojiri SA, Salehnia S, Hosseinzadeh A (2021) Chemical coagulation-electro fenton as a superior combination process for treatment of dairy wastewater: performance and modelling. Int J Environ Sci Technol 29:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03149-w
Zaroual Z, Azzi M, Saib N, Chainet E (2006) Contribution to the study of electrocoagulation mechanism in basic textile effluent. J Hazard Mater 131:73–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.09.021
Zazou H, Afanga H, Akhouairi S, Ouchtak H, Addi AA (2019) Treatment of textile industry wastewater by electrocoagulation coupled with electrochemical advanced oxidation process. Journal of Water Process Engineering 28:214–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.02.006
Zazouli MA, Taghavi M (2012) Phenol removal from aqueous solutions by electrocoagulation technology using iron electrodes: effect of some variables. J Water Resour Prot 4:980-983. https://doi.org/10.13140/2.1.1837.6967
Zodi S, Potier O, Lapicque JP (2009) Treatment of the textile wastewaters by electrocoagulation: effect of operating parameters on the sludge settling characteristics. Sep Purif Technol 69:29–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2009.06.028
Funding
Federal University of Fronteira Sul (UFFS) was responsible for the laboratory area and the acquisition of reagents and equipment; Rio Grande do Sul State Research Support Foundation (FAPERGS) for the financial support (scientific initiation scholarship n ° 194/UFFS/2019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Rafaela De Maman, Gean Delise Leal Pasquali, Vilson Conrado da Luz, Laura Behling, Clarissa Dalla Rosa, and Adriana Dervanoski. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Rafaela De Maman, Laura Behling, Vilson Conrado da Luz, and Gean Delise Leal Pasquali and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Weiming Zhang
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Maman, R., da Luz, V.C., Behling, L. et al. Electrocoagulation applied for textile wastewater oxidation using iron slag as electrodes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 31713–31722 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18456-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18456-5