Abstract
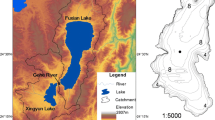
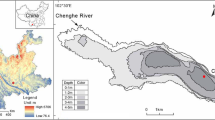
Eutrophication, climate change, water level fall, fish introduction, and salinity have been widely recorded to impact lake ecosystems around the world. However, the combined responding pattern in the lake ecosystem to the above multiple environmental stressors is not well understood. Here, we present diatom assemblage and geochemical indicators (total organic carbon (TOC), total nitrogen (TN), and total phosphorous (TP)) in lake sediment to investigate the long-term trends in the aquatic ecosystem in response to multiple environmental stressors in Lake Chenghai, a deep brackish lake located on Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, SW China, during the past 80 years. We identified 8 genera and 15 species of diatom reaching a relative abundance of ≥ 2% in at least one sample, with the dominant taxa such as Cyclotella rhomboideo-elliptica and Aulacoseira alpigena through the sediment core. There was a clear shift in the diatom community from oligotrophic species of C. rhomboideo-elliptica to eutrophic species such as Cyclotella meneghiniana and Cyclostephanos dubius becoming dominant since ca. 1998 CE. In addition, the changes in the fish introduction, water level, temperature, and salinity also resulted in the variation in abundance of planktonic and benthic diatoms. The increase in the abundance of diatoms of C. rhomboideo-elliptica since ca. 1986 CE may be related to the decline in water level and increasing fish production. For one thing, the decline in water level reduces the concentrations of benthic diatoms but increases the relative biomass of planktonic diatoms. For another, the increasing fish production results in the decrease in the zooplankton biomass, thus reducing the predation pressure on planktonic algae. Besides, some specific species such as C. meneghiniana may respond to the increased nutrient release and increased salinity since ca. 1998 CE. Combined, our findings demonstrate that trophic level is the main driver of diatom assemblage changes, and other environmental variables including water level, fish introduction, and climate warming also contribute to diatom community variation in this brackish plateau lake during the last 80 years.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Amsinck SL, Jeppesen E, Ryves D (2003) Cladoceran stratigraphy in two shallow brackish lakes with special reference to changes in salinity, macrophyte abundance and fish predation. J Paleolimnol 29:495–507
Appleby PG (2001) Chronostratigraphic techniques in recent sediments. In: Last WM, Smol JP (eds) Tracking environmental change using lake sediments. volume 1: basin analysis, coring, and chronological techniques. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht
Appleby PG, Oldfield F (1978) The calculation of 210Pb dates assuming a constant rate of supply of unsupported 210Pb to sediment. CATENA 5:1–8
Appleby PG, Nolan PJ, Battarbee DW (1986) 210Pb dating by low background gamma counting. Hydrobiologia 141:21–27
Appleby PG, Richardson N, Nolan PJ (1991) 241Am dating of lake sediments. Hydrobiologia 214:35–42
Battarbee RW, Jones VJ, Flower RJ, Cameron NG, Bennion H, Carvalho L, Juggins S (2001) Diatoms. In: Smol JP, Birks HJB, Last WM (eds) Tracking environmental change using lake sediments. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Netherlands, pp 155–202
Bennett KD (1996) Determination of the number of zones in a biostratigraphical sequence. New Phytol 132:155–170
Bradshaw EG, Anderson NJ (2003) Environmental factors that control the abundance of Cyclostephanos dubius (Bacillariophyceae) in Danish lakes, from seasonal to century scale. British Phycol Bull 38:265–276
Canfield DE, Hoyer MV (1992) Aquatic macrophytes and their relation to limnology of Florida Lakes. Department of Fisheries and Aquaculture, Center for Aquatic Plants, University of Florida, Florida
Chen JY, Zhang EL (2015) Sediment record of subfossil chironomid assemblages in the ecosystem evolution of Lake Chenghai. Ecol Sci 34:1–8 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen C, Zhao L, Zhu C, Wang J, Jiang J, Yang S (2014a) Response of diatom community in Lugu Lake (Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, China) to climate change over the past century. J Paleolimnol 51:357–373
Chen X, Li YL, Metcalfe S, Xiao XY, Yang XD, Zhang EL (2014b) Diatom response to Asian monsoon variability during the Late Glacial to Holocene in a small treeline lake, SW China. Holocene 24:1369–1377
Chen XK, Liu XB, Zhang YY, Zhao EL, Wang RN, Feng SX, Dong F (2018) Study on variation of water level and water balance in Chenghai Lake. Water Res Power 36:28–32 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen XK, Liu XB, Peng WQ, Dong F, Chen QC, Sun YL, Wang RN (2019) Hydroclimatic influence on the salinity and water volume of a plateau lake in southwest China. Sci Total Environ 659:746–755
Choi TS, Kang EJ, Kim JH, Kim KY (2010) Effect of salinity on growth and nutrient uptake of Ulva pertusa (Chlorophyta) from an eelgrass bed. Algae 25:17–26
Dixit SS, Dixit AS, Smol JP (1991) Paleolimnological investigation of three manipulated lakes from Sudbury, Canada. Hydrobiologia 214:245–252
Dong YX, Tan ZW, Wang JS (2011) Current status and evolution trend of aquatic vegetation in Chenghai Lake. Plant Diver Res 33:451–457 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Du JF (2006) Ecological status and comprehensive control measures in Chenghai Lake Basin. For Invent Plan 31:130–131 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Finlay BJ, Monaghan EB, Maberly SC (2002) Hypothesis: the rate and scale of dispersal of freshwater diatom species is function of their global abundance. Protist 153:261–273
Gibson CE, Anderson NJ, Haworth EY (2003) Aulacoseira subarctica: taxonomy, physiology, ecology and palaeoecology. Brit Phycol Bull 38:83–101
Gong ZJ, Li YL, Shen J, Xie P (2009) Diatom community succession in the recent history of a eutrophic Yunnan Plateau lake, Lake Dianchi, in subtropical China. Limnology 10:247–253
Gliwicz ZM, Pijanowska J (1988) Predation and resource depth distribution in shaping behaviour of vertical of vertical migration in zooplankton. Bull Mar Sci 43:695–709
Grimm EC (1993) TILIA v2.0 (Computer Software). Illinois State Museum, Research and Collections Centre, Springfield
Hadley KR, Pterson K, Ruhland H, White B, Wolfe W, Smol JP (2019) Biological and geochemical changes in shallow lakes of the Huson Bay Lowlands: a response to recent warming. J Paleolimnology 61:313–328
Hall RI, Smol JP (1999) Diatoms as indicators of lake eutrophication. In: Stoermer EF, Smol JP (eds) The diatoms: applications for the environmental and earth science. Cambridge University Press, London
Hansson S, Larsson U, Johansson S (1990) Selective predation by herring and mysids, and zooplankton community structure in a Baltic Sea coastal area. J Plankton Res 12:1099–1116
Hu W, Ji J, Pan H (1992) A preliminary study of water quality and salinazation in Chenghai Lake. J Lake Sci 4:60–66 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Jeppesen E, Jensen JP, Kristensen P, Søndergaard M, Mortensen E, Sortkjær O, Olrik K (1990) Fish manipulation as a lake restoration tool in shallow, eutrophic, temperate lakes 2: threshold levels, long-term stability and conclusions. Hydrobiologia 200(201):219–227
Jeppesen E, Søndergaard M, Jensen JP, Kanstrup E, Petersen B (1997) Macrophytes and turbidity in brackish lakes with special emphasis on top-down control. In: Jeppesen E, Søndergaard M, Christoffersen K (eds) The structuring role of submerged macrophytes in lakes. Springer, Heidelberg
Jeppesen E, Meerhoff M, Holmgren K, González-Bergonzoni I, Teixeira-de Mello F, Declerck S, De Meester L, Søndergaard M, Lauridsen T, Bjerring R, Conde-Porcuna JM, Mazzeo N, Iglesias C, Reizenstein M, Malmquist HJ, Liu ZW, Balayla D, Lazzaro X (2010) Impacts of climate warming on lake fish community structure and potential ecosystem effects. Hydrobiologia 646:73–90
Ji K (2014) Historical evolution and influencing factors of water level in Chenghai Lake. Proceedings of the annual academic exchange of Yunnan Water Conservancy Society, Kunming. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ji M, Li YL, Shen J (2013) Past and recent lake eutrophication evidenced by microfossil (over 160 years) diatom succession in sediments, lake xingyun (Southwest China). Pol J Ecol 61:729–737
Jin X, Tu Q (1990) Investigation criteria for lake eutrophication. Chinese Environmental Science Press, Beijing
Kang WG, Chen GJ, Wang JY, Huang LP, Wang L, Li R, Hu K, Liu YY, Tao JS, Blais JM, Smol JP (2019) Assessing the impact of long-term changes in climate and atmospheric deposition on a shallow alpine lake from southeast Tibet. Sci Total Environ 650:713–724
Krammer K, Lange-Bertalot H (1986) Bacillariophyceae 1. Teil: Naviculaceae. In: Ettl H, Gärtner G, Gerloff J, Heynig H, Mollenhauer D (eds) Süsswasserflora von Mitteleuropa 2/1, 1-876. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Jena
Krammer K, Lange-Bertalot H (1988) Bacillariophyceae 2. Teil: Bacillariaceae, Epithemiaceae, Surirellaceae. In: Ettl H, Gärtner G, Gerloff J, Heynig H, Mollenhauer D (eds) Süsswasserflora von Mitteleuropa 2/2. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Jena
Krammer K, Lange-Bertalot H (1991) Bacillariophyceae 3. Teil: Centrales, Fragilariaceae, Eunotiaceae. In: Ettl H, Gärtner G, Gerloff J, Heynig H, Mollenhauer D (eds) Süsswasserflora von Mitteleuropa 2/3. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Jena
Krammer K, Lange-Bertalot H (1991) Bacillariophyceae 4. Teil: Achnanthaceae, Kritische Ergänzungen zu Navicula (Lineolate) und Gomphonema. In: Ettl H, Gärtner G, Gerloff J, Heynig H, Mollenhauer D (eds) Süsswasserflora von Mitteleuropa 2/4. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Jena
Lange-Bertalot H (2001) Diatoms of Europe Vol. 2. Navicula sensu stricto, 10 Genera separated from Navicula sensu stricto, Frustulia. A.R.G. Gantner Verlag K.G., Königstein, Germany.
Lercari D, Defeo O (2006) Large-scale diversity and abundance trends in sandy beach macrofauna along full gradients of salinity and morphodynamics. Estuarine Coastal Shelf Sci 68:27–35
Li SH, Yu MJ, Li GZ, Ceng JJ, Chen JY, Gao BY, Huang HJ (1963) Limnological survey of the lakes of Yunnan Plateau. Oceanologia Et Limnologia Sinca 5:87–114 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li Y, Gong Z, Xia W, Shen J (2011) Effects of eutrophication and fish yield on the diatom community in Lake Fuxian, a deep oligotrophic lake in southwest China. Diatom Res 26:56–61
Li Y, Gong Z, Shen J (2012) Effects of eutrophication and temperature on Cyclotella rhomboideo-elliptica Skuja, endemic diatom to China. Phycol Res 60:288–296
Li YL, Liu XY, Xiao XY, Zhang EL, Ji M (2015) Diatom response to Asian monsoon variability during the Holocene in a deep lake at the southeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Boreas 44:785–793
Liu G, Liu Z, Smoak JM, Gu B (2015) The dynamics of cladoceran assemblages in response to eutrophication and planktivorous fish introduction in Lake Chenghai, a plateau saline lake. Quatern Int 355:188–193
Liu D, Yuan P, Tian Q, Liu H, Fan W (2019) Lake sedimentary biogenic silica from diatoms constitutes a significant global sink for aluminium. Nat Commun 10:4829
Liu YY, Chen GJ, Huang LP, Chen ZD, Huang GC, Liu XL, Li R (2020) Long-term pattern of lake ecosystem in response to eutrophication and water regulation in Chenghai Lake, Yunnan, China. Chin J Appl Ecol 31:1725–1734 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu YY, Chen GJ, Meyer-Jacob C, Huang LP, Liu XL, Huang GC, Klamt A, Smol JP (2021) Land-use and climate controls on aquatic carbon cycling and phototrophs in karst lakes of southwest China. Sci Total Environ 751:14138
Lotter AF, Pienitz R, Schmidt R (1999) Diatoms as indicators of environmental change near Arctic and Alpine treeline. In: Stoermer EF, Smol JP (eds) The diatoms: application for the environmental and earth sciences. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Meyers PA (1994) Preservation of elemental and isotopic source identification of sedimentary organic matter. Chem Geol 114:289–302
Meyers PA, Teranes JL (2001) Sediment organic matter. In: Last WM, Smol JP (eds) Tracing environmental changes ysing lake sediments volume 2: physical and geochemical methods. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston
Michelutti N, Laing TE, Smol JP (2001) Diatom assessment of past environmental changes in lakes located near the Noril’sk (Siberia) smelters. Water Air Soil Pollut 125:231–241
Moser KA, MacDonald GM, Smol SP (1996) Applications of freshwater diatoms to geographical research. Prog Phys Geogr 20:21–52
Moss B (1994) Brackish and freshwater shallow lakes—different systems or variations on the same theme? Hydrobiologia 275(276):1–14
Nunnery JA, Fritz SC, Baker PA, Selenbien W (2018) Lake-level variability in Salar de Coipasa, Bolivia during the past ∼40,000 yr. Quat Res 91:1–11
Qi Y (1995) Flora Algarum sinicarum aquae dulcis, tomus IV bacillariophyta centricae. Science Press, Beijing
Qian J, Zhang L, Le M (1990) The determination of total nitrogen and total phosphorus by digestion of persulphate. Soils 22:258–262 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Randsalu-Wendrup L, Conley DJ, Carstensen J, Fritz SC (2016) Paleolimnological records of regime shifts in lakes in response to climate change and anthropogenic activities. J Paleolimnol 56:1–14
Reavie ED, Hall RI, Smol JP (1995) An expanded weighted averaging model for inferring past total phosphorus concentrations from diatom assemblages in eutrophic British Columbia (Canada) Lakes. J Paleolimnol 14:49–67
Round F, Crawford R, Man D (2007) The diatoms biology and morphology of the genera. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Roubeix V, Lancelot C (2008) Effect of salinity on growth, cell size and silicification of an euryhaline freshwater diatom: Cyclotella meneghiniana Kütz. Transit Waters Bull 2:331–338
Schriver P, Bogestrand J, Jeppesen E, Søndergaard M (1995) Impact of submerged macrophytes on fish zooplankton–phytoplankton interactions: large-scale enclosure experiments in a shallow eutrophic lake. Freshwater Biol 33:255–270
Shan Z (1996) Studies on the hydrochemistry of Chenghai Lake during 1992. J Yunnnan Normal Univ 16:21–28 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Shapiro J (1980) The importance of trophic-level interactions to the abundance and species composition of algae in lakes. In: Barica J, Mur LR (eds) Developments in Hydrobiology, vol 2. Springer, Dordrecht
Skuja H (1937) Algae. In: Handel-Mazzetti H (ed) Symbolae Sinicae, botanische Ergebnisse der expedition der Akademic der Wissenschaften in Wien nach Südwest-China 1914/1918 1. Julius Springer, Vienna
Smol JP, Stoermer EF (2010) The diatoms: applications for the environmental and earth sciences. Cambridge University Press
Sun WW, Jiang QF, Liu EF, Chang J, Zhang EL (2018) Climate change dominates recent sedimentation and organic carbon burial in Lake Chenghai, southwest China. J Limnol 77:372–384
Sylvestre F, Servant-Vildary S, Roux M (2001) Diatom-based ionic concentration and salinity models from the south Bolivian Altiplano (15–23°S). J Paleolimnol 25:279–295
Tao W, Xia F, Jing C (1999) On environmental issues of Lake Chenghai and its management strategy. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin 8:210–214 (in Chinese)
Wang S, Dou H (1998) Lakes in China. Science Press, Beijing, pp 337–378
Wang R, Qian C (1988) An investigation and research of the algal flora in Chenghai Lake. J Yunnan Univ 10:250–258 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang L, Rioual P, Panizzo VN, Lu HY, Gu Z, Chu G, Yang D, Han J, Liu J, Mackay AW (2012) A 1000-yr record of environmental change in NE China indicated by diatom assemblages from marr lake Erlongwan. Quat Res 78:24–34
Wang Q, Yang X, Anderson NJ, Zhang E, Li Y (2014) Diatom response to climate forcing of a deep, alpine lake (Lugu Hu, Yunnan, SW China) during the Last Glacial Maximum and its implications for understanding regional monsoon variability. Quat Sci Rev 86:1–12
Wang Q, Yang X, Anderson NJ, Ji JF (2015) Diatom seasonality and sedimentation in a sub-tropical alpine lake (Lugu Hu, Yunnan-Sichuan, SW China). Arct Antarct Alp Res 527:461–472
Wang Q, Yang XD, Anderson NJ, Dong XH (2016) Direct versus indirect climate controls on holocene diatom assemblages in a sub-tropical deep, alpine lake (Lugu Hu, Yunnan, SW China). Quat Res 86:1–12
Wang YJ, Peng JP, Gao XF, Xu Y, Yu HW, Duan GQ, Qu JH (2020) Isotopic and chemical evidence for nitrate sources and transformation processes in a plateau lake basin in Southwest China. Sci Total Environ 711:134856
Wu J, Wang SM (2003) Stable isotopic tracing of historical progressive eutrophication from Lake Chenghai. Yunnan in China Quat Sci 23(5):557–564 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wu J, Gagan MK, Jiang X, Xia W, Wang S (2004) Sedimentary geochemical evidence for recent eutrophication of Lake Chenghai, Yunnan, China. J Paleolimnol 32:85–94
Wu J, Schleser GH, Lucke A, Li S (2007) A stable isotope record from freshwater lake shells of the eastern Tibetan Plateau, China, during the past two centuries. Boreas 36:38–46
Xiao YY, Haberle SG, Li YL, Liu EF, Shen J, Zhang EL, Yin JJ, Wang SM (2018) Evidence of Holocene climatic change and human impact in northwestern Yunnan Province: high-resolution pollen and charcoal records from Chenghai Lake, southwestern China. The Holocene 28:127–139
Yan DN, Xu H, Yang M, Lan JH, Hou WG, Wang FS, Zhang JX, Zhou KG, An ZS, Goldsmith Y (2019) Responses of cyanobacteria to climate and human activities at Lake Chenghai over the past 100 years. Ecol Indic 104:755–763
Yang J, Zhang W, Feng W, Shen Y (2005a) Freshwater testate amoebae of nine Yunnan Plateau lakes, China. J Freshwater Ecol 20:743–750
Yang XD, Dong XH, Gao G, Pan HX, Wu JL (2005b) Relationships between surface sediment diatoms and summer water quality in shallow lakes of the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River. J Integr Plant Biol Form Acta Botan Sinica 47:153–164
Yu ZZ, Liu EF, Zhang EL, Lin Q, Shen J, Wang R, Li YL (2017) Spatio-temporal variations, contamination and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in the sediments of Chenghai Lake. Environ Sci 38:4169–4177 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zan FY, Huo SL, Xi BD, Zhang JT, Liao HQ, Wang Y, Yeager KM (2012) A 60-year sedimentary record of natural and anthropogenic impacts on Lake Chenghai, China. J Enviro Sci 24:602–609
Zhang X, Xie P, Chen F, Li Y, Li S, Guo N, Qin J (2005) Present status and changes of phytoplankton community after invasion of Neosalanx taihuensis since 1982 in a deep oligotrophic plateau lake, Lake Fuxian in the subtropical China. J Environ Sci 17:389–394
Zhang E, Tang H, Cao Y, Langdon P, Wang R, Yang X, Shen J (2013) The effects of soil erosion on chironomid assemblages in Lugu Lake over the past 120 years. Int Rev Hydrobiol 98:165–172
Zhang YL, Huo SL, Zan FY, Xi BD, Zhang JT, Wu FC (2015) Historical records of multiple heavy metals from dated sediment cores in Lake Chenghai, China. Environ Earth Sci 74:1–10
Zheng WX, Wang R, Zhang EL, Chang J (2019) Complex relationship between the diversity and stability of chironomid assemblages in the recent sediments of two large alpine lakes in SW China. Sci Total Environ 684:705–714
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Guimin Liu, Prof. Zhijun Gong, Prof. Enlou Zhang for their help in the field.
Funding
This work was supported by the projects of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41877296, 41672173, and 41572149).
National Natural Science Foundation of China,41877296,Yanling Li,41672173,Yanling Li,41572149,Yanling Li
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Han Wu and Yanling Li designed outlines and wrote the draft of the manuscript. Qi Liu prepared the figures of the manuscript. Yun Zhang and Jishu Guo wrote some part of the manuscript. Mengna Liao reviewed the manuscript. Yanling Li and Qi Liu proposed original idea and reviewed the scientific contents of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final submitted version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication.
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Thomas Hein
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, H., Liao, M., Guo, J. et al. Diatom assemblage responses to multiple environmental stressors in a deep brackish plateau lake, SW China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 33117–33129 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17853-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17853-0