Abstract
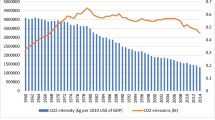
Global climate change brings environmental quality sensitivity, especially in European countries. In this context, European countries are striving to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050. Renewable energy use can be an effective way to curtail the increasing environmental degradation. How the oil prices shape the energy use pattern and environmental quality remains unclear to date. Therefore, the present research examines the linkage between energy use (non-renewable and renewable energy), oil prices, and CO2 emissions in 30 European countries between 1997 and 2017. The study applied fully modified ordinary least squares (FMOLS), Westerlund (2007) cointegration and the Driscoll-Kraay Regression tests to explore these associations. The result of individual samples and the full sample provides the same intimations for the use of energy in Europe. The outcomes of the research ratify the existence of a long-run relationship among variables and found that non-renewable energy consumption increases CO2 emissions, while renewable energy consumption mitigates CO2 emissions. Furthermore, when the oil prices rise, people switch towards substitute energy sources that reduce CO2 emissions. Based on the results, the study suggests that European countries should increase the share of renewable energy, promote the use of clean energy resources, and discourage fossil fuel energy consumption to ensure sustainability.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Corresponding authors can provide data used in the study on appropriate request.
References
Adebayo TS, Acheampong AO (2021) Modelling the globalization-CO2 emission nexus in Australia:evidence from quantile-on-quantile approach. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 7(2):1–16
Adebayo TS, Kirikkaleli D (2021) Impact of renewable energy consumption, globalization, and technologicalinnovation on environmental degradation in Japan: application of wavelet tools. Environment, Development andSustainability 5(12):1–26
Adebayo TS, Rjoub H (2021) A new perspective into the impact of renewable and nonrenewable energyconsumption on environmental degradation in Argentina: a time–frequency analysis. Environmental Science andPollution Research 12(5):1–17
Ahamada I, Fodha M, Kirat D (2017) Regional differences in CO2 emissions from the French residential sector: determinants and distributional consequences. Revue D’economie Politique 127:353–374
Ahmad M, Ahmed Z, Majeed A, Huang B (2021a) An environmental impact assessment of economic complexity and energy consumption: does institutional quality make a difference? Environ Impact Assess Rev 89:106603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2021.106603
Ahmad M, Ahmed Z, Yang X et al (2021b) Financial development and environmental degradation: do human capital and institutional quality make a difference? Gondwana Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GR.2021.09.012
Ahmeed Z, Wang Z, Mahmood F, Hafeez M, Ali N (2019) Does globalization increase the ecologicalfootprint? Empirical evidence from Malaysia. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 26(18):18565–18582
Ahmed K, Mujeeb UR, Ozturk I (2017) What drives carbon dioxide emissions in the long-run? Evidence from selected South Asian Countries. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 70:1142–1153
Ahmed Z, Ahmad M, Rjoub H et al (2021) Economic growth, renewable energy consumption, and ecological footprint: exploring the role of environmental regulations and democracy in sustainable development. Sustain Dev 1–11.https://doi.org/10.1002/SD.2251
Akadiri SS, Adebayo TS (2021) Asymmetric nexus among financial globalization, non-renewable energy, renewable energy use, economic growth, and carbon emissions: impact on environmental sustainability targets inIndia. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 5(4):1–13
Akhmat G, Zaman K, Shukui T, Sajjad F (2014) Does energy consumption contribute to climate change? Evidence from major regions of the world. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 36:123–134
Almulali U, Sab CN, Fereidouni HG (2012) Exploring the bi-directional long run relationship between urbanization, energy consumption, and carbon dioxide emission. Energy 46:156–167
Alola AA, Adebayo TS, Onifade ST (2021) Examining the dynamics of ecological footprint in China withspectral Granger causality and quantile-on-quantile approaches. International Journal of Sustainable Development & World Ecology 5(14):1–14
Apergis N, Payne JE, Menyah K, Rufael YW (2010) On the causal dynamics between emissions, nuclear energy, renewable energy, and economic growth. Ecol Econ 69:2255–2260
Apergis N, Payne JE (2015) Renewable energy, output, carbon dioxide emissions, and oil prices: evidence from South America. Energy Sources Part B 10:281–287
Adebayo TS, Awosusi AA, Kirikkaleli D, Akinsola GD, Mwamba MN (2021) Can CO 2 emissions andenergy consumption determine the economic performance of South Korea? A time series analysis. EnvironmentalScience and Pollution Research 2(4):1–16
Azad AK, Rasul MG, Khan MM, Sharma SC, Bhuiya MM (2015) Study on Australian energy policy, socio-economic, and environment issues. J Renew Sustain Energy 07:1–19
Balogh JM, Jambor A (2017) Determinants of CO2 emission: a global evidence. Int J Energy Econ Policy 07:217–226
Bibi A, Zhang X, Umar M (2021) The imperativeness of biomass energy consumption to the environmentalsustainability of the United States revisited. Environmental and Ecological Statistics 6(4):1–21
Bekun FV, Alola AA, Sarkodie SA (2019) Toward a sustainable environment: nexus between CO2 emissions, resource rent, renewable and nonrenewable energy in 16-EU countries. Sci Total Environ 657:1023–1029
Belaid F, Youssef M (2017) Environmental degradation, renewable and non-renewable electricity consumption, and economic growth: assessing the evidence from Algeria. Energy Policy 102:277–288
Bento C, Paulo J (2014) The determinants of CO2 emissions: empirical evidence from Italy. Munich Personal RePEc Archive (MPRA) 01–18
Bento JP, Moutinho V (2016) CO2 Emissions, non-renewable and renewable electricity production, economic growth, and international trade in Italy. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 55:142–155
Berk I, Kasman A, Kilinc D (2018) Towards a common renewable future: the System-GMM approach to assess the convergence in renewable energy consumption of EU countries. Energy Econ 87:01–06
Bhattacharya M, Churchill SA, Paramati SR (2017) The dynamic impact of renewable energy and institutions on economic output and CO2 emissions across regions. Renew Energy 111:157–167
Bilan Y, Streimikiene D, Vasylieva T, Lyulyov O, Pimonenko T, Pavlyk A (2019) Linking between renewable energy, CO2 emissions, and economic growth: challenges for candidates and potential candidates for the EU membership. Sustainability 11:01–16
Chin MY, Puah CH, Teo CL, Joseph J (2018) The determinants of CO2 emissions in Malaysia: a new aspect. Int J Energy Econ Policy 8:190–194
Chaudhry IS, Baloch ZA, Tan Q, Iqbal N, Mohsin M, Abbas Q, Iqbal W (2020) Trilemma assessmentof energy intensity, efficiency, and environmental index: evidence from BRICS countries. Environmental Scienceand Pollution Research 27(27):34337–34347
Danish, Baloch MA, Wang B (2019) Analyzing the role of governance in CO2 emissions mitigation: the BRICS experience. Struct Chang Econ Dyn 51:119–125
Dogan E, Seker F (2016) Determinants of CO2 emissions in the European Union: the role of renewable and non-renewable energy. Renew Energy 94:429–439
Driscoll JC, Kraay AC (1998) Consistent covariance matrix estimation with spatially dependent panel data. Rev Econ Stat 80(4):549–560
Fareed Z, Salem S, Adebayo TS, Pata UK, Shahzad F (2021) Role of export diversification and renewable energy on the load capacity factor in Indonesia: A Fourier quantile causality approach. Frontiers in Environmental Science 4(5):37–49
Hossain MS (2011) Panel estimation for CO2 emissions, energy consumption, economic growth, trade openness and urbanization of newly industrialized countries. Energy Policy 39:6991–6999
Hasanov FJ, Khan Z, Hussain M, Tufail M (2021) Theoretical framework for the carbon emissions effectsof technological progress and renewable energy consumption. Sustainable Development. 4(2):23–37
Hao LN, Umar M, Khan Z, Ali W (2021) Green growth and low carbon emission in G7 countries: how critical the network of environmental taxes, renewable energy and human capital is? Sci Total Environ 752:141853
He X, Adebayo TS, Kirikkaleli D, Umar M (2021) Consumption-based carbon emissions in Mexico: an analysis using the dual adjustment approach. Sustain Prod Consum 27:947–957
Keho Y (2015) An Econometric Study of the Long-Run Determinants of CO2 Emissions in Cote d’Ivoire. J Financ Econ 03:11–21
Khan I, Khan N, Yaqub A, Sabir M (2019) An empirical investigation of the determinants of CO2 emissions: evidence from Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:9099–9112
Khan SAR, Yu Z, Umar M (2021) A road map for environmental sustainability and green economicdevelopment: an empirical study. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 5(12):1–9
Kirikkaleli D, Adebayo TS (2020) Do renewable energy consumption and financial development matter for environmental sustainability? New Glob Evid Sustain Dev 29(4):583–594
Lean HH, Smyth R (2010) Co2 emissions, electricity consumption and output in ASEAN. Appl Energy 87:1858–1864
Kirikkaleli D, Adebayo TS (2021) Do public-private partnerships in energy and renewable energyconsumption matter for consumption-based carbon dioxide emissions in India? Environmental Science andPollution Research 12(7):1–14
Kirikkaleli D, Ahmed Z, Ahmad M, Murshed M, Vaseer AI (2021) The trade-off between energyconsumption, economic growth, militarization, and CO2 emissions: does the treadmill of destruction exist in themodern world? Environmental Science and Pollution Research 3(16):1–14
Kihombo S, Ahmed Z, Chen S, Adebayo TS, Kirikkaleli D (2021) Linking financial development, economic growth, and ecological footprint: what is the role of technological innovation?. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–11
Li J, Zhao Y, Zhang A et al (2021a) Effect of grazing exclusion on nitrous oxide emissions during freeze-thaw cycles in a typical steppe of Inner Mongolia. Agric Ecosyst Environ 307:107217. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AGEE.2020.107217
Li L, Sun W, Hu W, Sun Y (2021b) Impact of natural and social environmental factors on building energy consumption: based on bibliometrics. J Build Eng 37:102136. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JOBE.2020.102136
Lin X, Zhao Y, Ahmad M, Ahmed Z, Rjoub H, Adebayo TS (2021) Linking innovative human capital, economic growth, and CO2 emissions: an empirical study based on Chinese provincial panel data. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(16):8503
Mahmood M, Danish, Wang Z, Zhang B (2020) The role of nuclear energy in the correction of environmental pollution: evidence from Pakistan. Nucl Eng Technol 52:1327–1333
Mamun MI, Sohag K, Mia MA, Uddin GS, Ozturk I (2014) Regional differences in the dynamic linkage between CO2 emissions, sectoral output and economic growth. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 34:1–11
Magazzino C, Cerulli G (2019) The determinants of CO2 emissions in MENA countries: a responsiveness scores approach. Int J Sust Dev World 06:522–534
Panait M, Adebayo TS, Awosusi AA, Rjoub H, Popescu C (2021) Asymmetric impact of international trade on consumption-based carbon emissions in MINT Nations. Energies 14(20):6581
Meng M, Fu Y, Wang T, Jing K (2017) Analysis of low-carbon economy efficiency of Chinese industrial sectors based on a RAM model with undesirable outputs. Sustainability 09:02–17
Murshed M, Li ZZ, Li RYM, Malik MY, Khan Z, Umar M (2021) Determinants of carbon emission inChina: how good is green investment? Sustainable Production and Consumption 2(7):392–401
Naseem S, Guang Ji T (2020) A system-GMM approach to examine the renewable energy consumption, agriculture and economic growth’s impact on CO2 emission in the SAARC region. GeoJournal 86(5):23–36
Nordin SK, Samat KF, Ismail SF, Hamzah K, Halim BA, Kune SA (2014) Determinants of CO2 emissions in ASEAN countries using energy and mining indicators. International Conference on Mathematics, Engineering and Industrial Applications AIP Conference Proceedings 1660, 01-06
Orhan A, Adebayo TS, Genç SY, Kirikkaleli D (2021) Investigating the linkage between economic growthand environmental sustainability in India: do agriculture and trade openness matter? Sustainability 13(9):4753
Olanrewaju VO, Adebayo TS, Akinsola GD, Odugbesan JA (2021) Determinants of environmentaldegradation in Thailand: empirical evidence from ARDL and wavelet coherence approaches. Pollution 7(1):181–196
Ramzan M, Iqbal HA, Adebayo TS, Awosusi AA, Akinsola GD (2021) The environmental sustainability effects of financial development and urbanization in Latin American countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–14
Rahman ZU, Ahmad M, Khan Z, Khattak SI, Khan ZU (2021) Can innovation shocks determine CO2 emissions (CO2e) in the OECD economies? A new perspective. Econ Innov New Technol 30(1):89–109
Rjoub H, Akinsola GD, Adebayo TS, Oladipupo SD (2021) The asymmetric effects of renewable energy consumption and trade openness on carbon emissions in Sweden: new evidence from quantile-on-quantile regression approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–12
Rjoub H, Adebayo TS, Akinsola GD, Oladipupo SD (2021) The asymmetric effects of renewable energyconsumption and trade openness on carbon emissions in Sweden: New evidence from quantile-on-quantileregression approach. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 4(12):1–12
Sapkota P, Bastola U (2017) Foreign direct investment, income, and environmental pollution in developing countries: panel data analysis of Latin America. Energy Economics 64:206–212
Sarkodie SA, Strezov V (2019) Effect of foreign direct investments, economic development and energy consumption on greenhouse gas emissions in developing countries. Sci Total Environ. 646:862–871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.365
Sarkodie SA, Ozturk I (2020) Investigating the environmental Kuznets Curve hypothesis in Kenya: a multivariate analysis. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 117:01–12
Shahzad SJH, Ahmed Z, Le HP (2021) Toward environmental sustainability: how do urbanization, economic growth, and industrialization affect biocapacity in Brazil? Environment, Development and Sustainability 2(14):1–21
Shan S, Ahmad M, Tan Z, Adebayo TS, Li RYM, Kirikkaleli D (2021) The role of energy prices and non-linear fiscal decentralization in limiting carbon emissions: tracking environmental sustainability. Energy 234:121243
Sharma SS (2011) Determinants of carbon dioxide emissions: empirical evidence from 69 countries. Appl Energy 88:376–382
Shen C, Feng R, Yu B, Liao Z (2018) Industrial CO2 emissions efficiency and its determinants in China: analyzing differences across regions and industry sectors. Pol J Environ Stud 27:1239–1254
Su ZW, Umar M, Kirikkaleli D, Adebayo TS (2021) Role of political risk to achieve carbon neutrality: evidence from Brazil. J Environ Manag 298:113463
Udemba EN, Adebayo TS, Ahmed Z, Kirikkaleli D (2021) Determinants of consumption-based carbon emissions in Chile: an application of non-linear ARDL. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–15
Udemba EN, Ahmed Z, Adebayo TS, Kirikkaleli D (2021) Determinants of consumption-based carbonemissions in Chile: an application of non-linear ARDL. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 5(7):1–15
Union (2015) Preparations for the 21st session of the Conference of the Parties (COP 21) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the 11th session of the Meeting of the Parties to the Kyoto Protocol (CMP 11), Press Release (2015) 657/15, Paris 2015
Wang F, Lu Y, Li J, Ni J (2021) Evaluating environmentally sustainable development based on the PSR framework and variable weigh analytic hierarchy process. Int J Environ Res Public Heal 18:2836. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJERPH18062836
Wang Z, Rasool Y, Zhanga B, Ahmed Z, Wang B (2020) Dynamic linkage among industrialization, urbanisation, and CO2 emissions in APEC realms: evidence based on DSUR estimation. Struct Chang Econ Dyn 52:382–389
Westerlund J (2007) Testing for error correction in panel data. Oxford Bulletin of Economics and statistics 69(6):709–748
Wu B, Monfort A, Jin C, Shen X (2022) Substantial response or impression management? Compliance strategies for sustainable development responsibility in family firms. Technol Forecast Soc Change 174:121214. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TECHFORE.2021.121214
Yang J, Rizvi SKA, Tan Z, Umar M, Koondhar MA (2021) The competing role of natural gas and oil as fossil fuel and the non-linear dynamics of resource curse in Russia. Resour Policy 72:102100
Yu B, Li C, Mirza N, Umar M (2022) Forecasting credit ratings of decarbonized firms: comparative assessment of machine learning models. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 174:121255
Yuping L, Ramzan M, Xincheng L, Murshed M, Awosusi AA, Bah SI, Adebayo TS (2021) Determinants of carbon emissions in Argentina: the roles of renewable energy consumption and globalization. Energy Rep 7:4747–4760
Zafeiriou E, Arabatzis G, Tampakis S, Soutsas K (2014) The impact of energy prices on the volatility of ethanol prices and the role of gasoline emissions. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 33:87–95
Zhang L, Li Z, Kirikkaleli D, Adebayo TS, Adeshola I, Akinsola GD (2021) Modeling CO2 emissions in Malaysia: an application of Maki cointegration and wavelet coherence tests. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(20):26030–26044
Vaseer, A. I., Ahmed, Z., Kihombo, S., Chen, S., Kirikkaleli, D., & Adebayo, T. S. (2021). Is there a tradeoff between financial globalization, economic growth, and environmental sustainability? An advanced panel analysis. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 3(12), 1-11.
Funding
This research work is funded by ILMA University under the ILMA Research Publication Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MQR, and AH: Conceptualization, data collection, empirical analysis, writing original manuscript. TSA: Methodology, formal analysis, revision, editing, writing original manuscript. ZA: Editing, proofreading, comments, revision, contributed in analysis. MA: Writing review and editing, proofreading. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
NA
Consent for publication
NA
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Roula Inglesi-Lotz
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rasheed, M.Q., Haseeb, A., Adebayo, T.S. et al. The long-run relationship between energy consumption, oil prices, and carbon dioxide emissions in European countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 24234–24247 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17601-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17601-4