Abstract
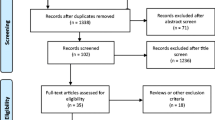
The aim of this review was to evaluate if micronucleus assay in oral exfoliated cells is a suitable tool for biomonitoring children exposed to environmental pollutants. Through the electronic databases PubMed/Medline, Scopus, and Web of Science, all published studies until April 2021 that examined the relationship between exposure to environmental pollutants and micronucleus frequency in oral cells were searched. All relevant articles using a combination of the following keywords—“children,” “micronucleus,” “oral cells,” and “environmental pollution”—were considered. A total of 20 papers met the criteria for inclusion in the systematic review. The results regarding the cytogenetic damage induced by environmental pollutants are conflicting. Some authors have demonstrated that environmental pollution induces mutagenesis in oral cells while others did not. Following the parameters of the Project for Effective Public Health Practices (EPHPP) and after extensive reading of all the articles included, a total of 12 articles had moderate and strong scores and 8 had a classification considered weak. Taken together, this review was able to demonstrate the association between micronucleus frequency and exposure to environmental pollutants in oral exfoliated cells of children.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing is not available in this article.
References
Abdel-Daim MM, Abo-El-Sooud K, Aleya L, Bungau SG, Najda A, Saluja R (2018) Alleviation of drugs and chemicals toxicity: biomedical value of antioxidants. Oxid Med Cell Longev 1–2
Alpire MES, Cardoso CM, Seabra Pereira CD, Ribeiro DA (2021) Genomic instability in Buccal mucosal cells of children living in abnormal conditions from Santos-Sao Vicente Estuary. Int J Environ Health Res 31(2):179–185
Anguiano-Vega GA, Cazares-Ramirez LH, Rendon-Von Osten J, Santillan-Sidon AP, Vazquez-Boucard CG (2020) Risk of genotoxic damage in schoolchildren exposed to organochloride pesticides. Sci Rep 10(1):1–12
Bernardi NG, Gentile NE, Mañas FJ, Méndez Á, Gorla NBM, Aiassa DE (2015) Assessment of the level of damage to the genetic material of children exposed to pesticides in the province of Córdoba. Arch Argent Pediatr 113(2):126–131
Bolognesi C, Bonassi S, Knasmueller S, Fenech M, Bruzzone M, Lando C, Ceppi M (2015) Clinical application of micronucleus test in exfoliated buccal cells: a systematic review and metanalysis. Mutat Res 766:20–31
Bonassi S, Coskun E, Ceppi M, Lando C, Bolognesi C, Burgaz S, Fenech M (2011) The Human MicroNucleus project on eXfoLiated buccal cells (HUMNXL): the role of lifestyle, host factors, occupational exposures, health status, and assay protocol. Mutat Res 728(3):88–97
Bungau S, Tit DM, Behl T, Aleya L, Zaha DC (2021) Aspects of excessive antibiotic consumption and environmental influences correlated with the occurrence of resistance to antimicrobial agents. Curr Opin Environ Sci Health 19:100224
Bungau Prada IF, Prada M, Bungau C (2019) Design and operation of construction: a healthy living environment - parametric studies and new solutions. Sustainability 11(23):6824
Carlsson H, Aasa J, Kotova N, Vare D, Sousa PF, Rydberg P, Törnqvist M (2017) Adductomic screening of hemoglobin adducts and monitoring of micronuclei in school-age children. Chem Res Toxicol 30(5):1157–1167
Castañeda-Yslas IJ, Arellano-García ME, García-Zarate MA, Ruíz-Ruíz B, Zavala-Cerna MG, Torres-Bugarín O (2016) Research article biomonitoring with micronuclei test in buccal cells of female farmers and children exposed to pesticides of Maneadero agricultural valley, Baja California, Mexico. J Toxicol 2016:7934257
Cavalcante DNDC, Sposito JCV, Crispim BDA, Nascimento AVD, Grisolia AB (2017) Genotoxic and mutagenic effects of passive smoking and urban air pollutants in buccal mucosa cells of children enrolled in public school. Toxicol Mech Method 27(5):346–351
Ceppi M, Biasotti B, Fenech M, Bonassi S (2010) Human population studies with the exfoliated buccal micronucleus assay: statistical and epidemiological issues. Mutat Res 705(1):11–19
Ceretti E, Donato F, Zani C, Villarini M, Verani M, De Donno A, MAPEC_LIFE Study Group (2020) Results from the European Union MAPEC_LIFE cohort study on air pollution and chromosomal damage in children: are public health policies sufficiently protective? Environ Sci Eur 32:1–11
Ceretti E, Feretti D, Viola GCV, Zerbini I, Limina RM, Zani C, Gelatti U (2014) DNA damage in buccal mucosa cells of pre-school children exposed to high levels of urban air pollutants. PloS One 9(5):e96524
Chokeli R, Baharuddin NA, How V, Yuswir NS, Mohd SA, Noor HYB, Hashim Z (2019) The chromosomal DNA damage in buccal mucosa cells among schools children in the vicinity of mobile base stations in Selangor. Malaysian J Med Health Sci 15:204
Countryman PI, Heddle JA (1976) The production of micronuclei from chromosome aberrations in irradiated cultures of human lymphocytes. Mutat Res 41(2–3):321–332
De Donno A, Grassi T, Ceretti E, Viola GCV, Levorato S, Vannini S, MAPEC_life study group, (2016) Air pollution biological effects in children living in Lecce (Italy) by buccal micronucleus cytome assay (the MAPEC_LIFE study). Int J Sust Develop Plan 11(4):500–510
Deckbar D, Jeggo PA, Löbrich M (2011) Understanding the limitations of radiation-induced cell cycle checkpoints. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 46(4):271–283
Dos Santos MAL, de Santana FS, Soares AF, de Sousa SF, Menezes LS, Takeshita WM (2020) Genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of mobile phone use on the oral epithelium: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Gen Dent 68(6):70–74
Dórea JG (2019) Environmental exposure to low-level lead (Pb) co-occurring with other neurotoxicants in early life and neurodevelopment of children. Environ Res 177:108641
Durmaz B, Taslidere H, Koturoglu G, Gunduz C, Orman M, Cogulu O (2019) Determination of lymphocyte cytokinesis-block micronucleus values in apparently healthy children by means of age and sex. BioMed Res Int 2019:8729561
Fleck ADS, Vieira M, Amantéa SL, Rhoden CR (2014) A comparison of the human buccal cell assay and the pollen abortion assay in assessing genotoxicity in an urban-rural gradient. Int J Environ Public Health 11(9):8825–8838
Gajski G, Gerić M, Oreščanin V, Garaj-Vrhovac V (2013) Cytogenetic status of healthy children assessed with the alkaline comet assay and the cytokinesis-block micronucleus cytome assay. Mutat Res 750(1–2):55–62
Gajski G, Milković Đ, Ranogajec-Komor M, Miljanić S, Garaj-Vrhovac V (2011) Application of dosimetry systems and cytogenetic status of the child population exposed to diagnostic X-rays by use of the cytokinesis-block micronucleus cytome assay. J Applied Toxicol 31(7):608–617
Gamiño-Gutiérrez SP, González-Pérez CI, Gonsebatt ME, Monroy-Fernández MG (2013) Arsenic and lead contamination in urban soils of Villa de la Paz (Mexico) affected by historical mine wastes and its effect on children’s health studied by micronucleated exfoliated cells assay. Environ Geochem Health 35(1):37–51
Gomez-Arroyo S, Martinez-Valenzuela C, Calvo-Gonzalez S, Villalobos-Pietrini R, Waliszewski SM, Calderón-Segura ME, Lagarda-Escarrega A (2013) Assessing the genotoxic risk for Mexican children who are in residential proximity to agricultural areas with intense aerial pesticide applications. Rev IntContaminAmb 29(3):217–225
Hisamuddin NH, Jalaludin J, Yusof AN (2020) Genotoxic effects of exposure to urban traffic related air pollutants on children in Klang Valley. Malaysia Aerosol Air Quality Res 20:20
Holland N, Bolognesi C, Kirsch-Volders M, Bonassi S, Zeiger E, Knasmueller S, Fenech M (2008) The micronucleus assay in human buccal cells as a tool for biomonitoring DNA damage: the HUMN project perspective on current status and knowledge gaps. Mutat Res 659:93–108
How V, Hashim Z, Ismail P, Md Said S, Omar D, BahriMohdTamrin S (2014) Exploring cancer development in adulthood: cholinesterase depression and genotoxic effect from chronic exposure to organophosphate pesticides among rural farm children. J Agromed 19(1):35–43
Idolo A, Grassi T, Bagordo F, Panico A, De Giorgi M, Serio F, De Donno A (2018) Micronuclei in exfoliated buccal cells of children living in a cluster area of Salento (Southern Italy) with a high incidence of lung cancer: the IMP. AIR study. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15(8):1659
Isaevska E, Moccia C, Asta F, Cibella F, Gagliardi L, Ronfani L, Rusconi F, Stazi MA, Richiardi L (2021) Exposure to ambient air pollution in the first 1000 days of life and alterations in the DNA methylome and telomere length in children: a systematic review. Environ Res 193:110504
Kapka-Skrzypczak L, Czajka M, Sawicki K, Matysiak-Kucharek M, Gabelova A, Sramkova M, Kruszewski M (2019) Assessment of DNA damage in Polish children environmentally exposed to pesticides. Mutat Res 843:52–56
Khan MR, Sudha S (2012) Evaluation of genotoxicity in automobile mechanics occupationally exposed to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons using micronuclei and other nuclear abnormalities. Iran J Cancer Prev 5(2):87
Kim EH, Kim S, Lee JH, Kim J, Han Y, Kim YM, Kim GB, Jung K, Cheong HK, Ahn K (2015) Indoor air pollution aggravates symptoms of atopic dermatitis in children PLoSOne 10(3):e0119501
Lemos AT, de Lemos CT, Coronas MV, da Rocha JR, Vargas VMF (2020) Integrated study of genotoxicity biomarkers in schoolchildren and inhalable particles in areas under petrochemical influence. Environ Res 188:109443
López Guzmán OD, Costilla Salazar R, Pelallo Martínez N, Alcaraz Contreras Y, Bocanegra Salazar M, Rocha Amador DO (2017) Micronucleus in exfoliated buccal cells of children from Durango, Mexico, exposed to arsenic through drinking water. Rev IntContaminAmbiental 33(2):281–287
Lorenzoni DC, Fracalossi ACC, Carlin V, Ribeiro DA, Sant’Anna EF, (2013) Mutagenicity and cytotoxicity in patients submitted to ionizing radiation: a comparison between cone beam computed tomography and radiographs for orthodontic treatment. Angle Orthod 83(1):94–109
Marcon A, Fracasso ME, Marchetti P, Doria D, Girardi P, Guarda L, de Marco R (2014) Outdoor formaldehyde and NO2 exposures and markers of genotoxicity in children living near chipboard industries. Environ Health Perspect 122(6):639–645
Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, Stewart LA (2015) Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Systematic Rev 4(1):1–9
Negruti N, Rus M, Pantis C, Maghiar O, Cseppento CD, Uivarosan D, Stanescu AM, Spinu DA, Fratila O, Bungau S (2020) Considerations on the influence of zinc on infectious diseases in children. Rev Chim 71(4):571
Neri M, Bonassi S, Knudsen LE, Sram RJ, Holland N, Ugolini D, Merlo DF (2006) Children’s exposure to environmental pollutants and biomarkers of genetic damage. I Overview and critical issues. Mutat Res 612(1):1–13
Nhung NTT, Schindler C, Dien TM, Probst-Hensch N, Künzli N (2019) Association of ambient air pollution with lengths of hospital stay for Hanoi children with acute lower-respiratory infection, 2007–2016. Environ Pollut 247:752–762
Nielsen GD, Larsen ST, Wolkoff P (2013) Recent trend in risk assessment of formaldehyde exposures from indoor air. Arch Toxicol 87(1):73–98
Pampanin DM, Brooks SJ, Grøsvik BE, Le Goff J, Meier S, Sydnes MO (2017) DNA adducts in marine fish as biological marker of genotoxicity in environmental monitoring: the way forward. Mar Environ Res 125:49–62
Panait DE, Jufa AC, Floroian L, Pascu AM, Badea M, Popa M, Macocian EV, Cioca G, Bungau S (2019) Electromagnetic pollution of the environment due leakage radiation from microwave ovens. Mater Plast 56(1):82–86
Panico A, Grassi T, Bagordo F, Idolo A, Serio F, Tumolo MR, De Donno A (2020) Micronucleus frequency in exfoliated buccal cells of children living in an industrialized area of Apulia (Italy). Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(4):1208
Ruggieri F, Majorani C, Domanico F, Alimonti A (2017) mercury in children: current state on exposure through human biomonitoring studies. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14(5):519
Sabah JT (2021) Evaluation of genotoxic damage in buccal mucosa cytome assays in Iraqi school children exposed to air pollutants emanating from oil fields. Mutat Res 863:503304
Silva CS, Rossato JM, Rocha JAV, Vargas VMF (2015) Characterization of an area of reference for inhalable particulate matter (PM2. 5) associated with genetic biomonitoring in children. Mutat Res 778:44–55
Sisenando HÁ, de Medeiros SRB, Artaxo P, Saldiva PH, de Souza HS (2012) Micronucleus frequency in children exposed to biomass burning in the Brazilian Legal Amazon region: a control case study. BMC Oral Health 12(1):1–7
Sram RJ, Svecova V, Rossnerova A (2016) Systematic review of the use of the lymphocyte cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay to measure DNA damage induced by exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res 770(Pt A):162–169
Thomas BH, Ciliska D, Dobbins M, Micucci S (2004) A process for systematically reviewing the literature: providing the research evidence for public health nursing interventions. Worldviews Evid Based Nursing 1(3):176–184
Villarini M, Levorato S, Salvatori T, Ceretti E, Bonetta S, Carducci A, Zagni L (2018) Buccal micronucleus cytome assay in primary school children: a descriptive analysis of the MAPEC_LIFE multicenter cohort study. Int J Hyg Environ Health 221(6):883–892
Wu X, Cobbina SJ, Mao G, Xu H, Zhang Z, Yang L (2016) A review of toxicity and mechanisms of individual and mixtures of heavy metals in the environment. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23(9):8244–8259
Xavier LADC, Bezerra JF, de Rezende AA, Oliveira RADC, Dalmolin RJS, do Amaral VS, (2017) Analysis of genome instability biomarkers in children with non-syndromicorofacial clefts. Mutagenesis 32(2):313–321
Yang D, Yang X, Deng F, Guo X (2017) ambient air pollution and biomarkers of health effect. AdvExp Med Biol 1017:59–102
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge research grants received from CNPq (ConselhoNacional de DesenvolvimentoCientifico e Tecnológico) and CAPES. DVS thanks CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior) for the grants received and scholarship. DAR and ACMR thank CNPq for productivity fellowships.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: ITM and DAR. Data search: ITM, DVS, MESA, ACFS, and DAR. Formal analysis: ITM, DVS, ACMR, and DAR. Writing—review and editing: all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malacarne, I.T., De Souza, D.V., Alpire, M.E.S. et al. Is micronucleus assay in oral exfoliated cells a suitable tool for biomonitoring children exposed to environmental pollutants? A systematic review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 65083–65093 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16810-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16810-1