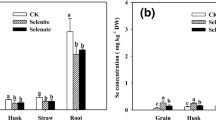
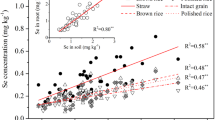
Abstract
This study aimed to investigate the effects of selenium application on cadmium absorption, transport, and soil cadmium forms of winter wheat at different stages. A pot experiment with one Cd application (6 mg·kg−1) and five Se application levels (0, 1, 2, 5, and 10 mg·kg−1) was conducted. The results showed that Se application increased the grain yield of winter wheat, especially at 5 mg·kg−1 under Cd stress. As Se was supplied at 5 (Se5) and 10 (Se10) mg·kg−1, the Cd concentrations in roots and shoots, including stems, spikes, glumes, and grains, decreased at different growth stages, and the decreases in grain were 46.1% and 70.9% respectively. Se5 and Se10 also significantly decreased the translocation factors of Cd from roots to shoots, roots to stems, stems to spikes, and glumes to grains, promoted the accumulation of Cd in roots, and inhibited the accumulation of Cd in shoots and final grains at different growth stages, and the accumulation of Cd in grains decreased by 16.9% and 68.1%, respectively. High levels of Se application (Se5 and Se10) decreased the concentrations and proportions of exchangeable Cd (EXC−Cd) and iron (Fe)−manganese (Mn) oxide−bound Cd (R2O3−Cd) but increased the concentration and proportion of residual Cd (RES−Cd) in both soils with wheat and fallow soil at different growth stages. Therefore, under Cd stress, high levels of Se application reduced the shoot Cd concentration by inhibiting the uptake and transport of Cd from roots to shoots, and decreased the bioavailability of Cd in both soil with wheat and fallow by enhancing the transformation and distribution of RES-Cd from EXC-Cd and R2O3-Cd.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- Cd:
-
Cadmium
- Se:
-
Selenium
- EXC−Cd:
-
Exchangeable Cd
- R2O3−Cd:
-
Iron (Fe)−manganese (Mn) oxide−bound Cd
- CA−Cd:
-
Carbonate−bound Cd
- OM−Cd:
-
Organic−bound Cd
- RES−Cd:
-
Residual Cd
References
Abedi S, Iranbakhsh A, Ardebili ZO, Ebadi M (2021) Nitric oxide and selenium nanoparticles confer changes in growth, metabolism, antioxidant machinery, gene expression, and flowering in chicory (Cichorium intybus L.): potential benefits and risk assessment. Environ Sci Pollut R 28:3136–3148
Bali AS, Sidhu GP, Kumar V (2020) Root exudates ameliorate cadmium tolerance in plants: a review. Environ Chem Lett 18:1243–1275
Bashir S, Ali U, Shaaban M, Gulshan AB, Iqbal J, Khan S, Husain A, Ahmed N, Mehmood S, Kamran M (2020) Role of sepiolite for cadmium (Cd) polluted soil restoration and spinach growth in wastewater irrigated agricultural soil. J Environ Manag 258:110020
Bataillard P, Cambier P, Picot C (2003) Short-term transformations of lead and cadmium compounds in soil after contamination. Eur J Soil Sci 54:365–376
Chang JD, Huang S, Konishi N, Wang P, Chen J, Huang XY, Ma JF, Zhao FJ (2020) Overexpression of the manganese/cadmium transporter OsNRAMP5 reduces cadmium accumulation in rice grain. J Exp Bot 71:5705–5715
Davies NA, Hodson ME, Black S (2003) The influence of time on lead toxicity and bioaccumulation determined by the OECD earthworm toxicity test. Environ Pollut 121:55–61
Delaqua D, Carnier R, Berton RS, Corbi FC, Coscione AR (2021) Increase of selenium concentration in wheat grains through foliar application of sodium selenate. J Food Compos Anal 99:103886
Fu H, Zhang B, Yang J, Liu H, Yang S, Zhao P (2018) Cadmium and lead speciation as affected by soil amendments in calcareous soil. Environ Eng Sci 35:937–942
Gao W, Zhao P, Sui F, Liu H, Fu H (2018) Influence of soil amendments on uptake and accumulation of Cd and Pb in maize (Zea mays L.). Environ Eng Sci 35:194–202
Guo Y, Mao K, Cao H, Ali W, Da L, Teng D, Chang C, Yang X, Yang Q, Niazi NK (2021) Exogenous selenium (cadmium) inhibits the absorption and transportation of cadmium (selenium) in rice. Environ Pollut 268:115829
Hamid Y, Tang L, Sohail MI, Cao X, Hussain B, Aziz MZ, Usman M, He Z, Yang X (2019) An explanation of soil amendments to reduce cadmium phytoavailability and transfer to food chain. Sci Total Environ 660:80–96
Huang Y, Chen J, Zhang D, Fang B, Yang T, Zou J, Chen Y, Su N, Cui J (2021) Enhanced vacuole compartmentalization of cadmium in root cells contributes to glutathione−induced reduction of cadmium translocation from roots to shoots in pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.). Ecotox Environ Safe 208:111616
Jiang P, Liu J, Chen M, Yu G, You S, Li J (2020) Exogenous selenium improves the physiological resistance of cucumber to cadmium stress. Toxicol Environ Chem 102:455–472
Juang KW, Ho PC, Yu CH (2012) Short−term effects of compost amendment on the fractionation of cadmium in soil and cadmium accumulation in rice plants. Environ Sci Pollut R 19:1696–1708
Liang Y, Wong JW, Wei L (2005) Silicon−mediated enhancement of cadmium tolerance in maize (Zea mays L.) grown in cadmium contaminated soil. Chemosphere 58:475–483
Liu K, Cai M, Hu C, Sun X, Cheng Q, Jia W, Yang T, Nie M, Zhao X (2019) Selenium (Se) reduces Sclerotinia stem rot disease incidence of oilseed rape by increasing plant Se concentration and shifting soil microbial community and functional profiles. Environ Pollut 254:113051
Liu N, Jiang Z, Li X, Liu H, Li N, Wei S (2020) Mitigation of rice cadmium (Cd) accumulation by joint application of organic amendments and selenium (Se) in high−Cd−contaminated soils. Chemosphere 241:125106
Lorenz SE, Hamon RE, McGrath SP (1994) Differences between soil solutions obtained from rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soils by water displacement and soil centrifugation. Eur J Soil Sci 45:431–438
Luo H, He L, Du B, Pan S, Mo Z, Duan M, Tian H, Tang X (2020) Biofortification with chelating selenium in fragrant rice: effects on photosynthetic rates, aroma, grain quality and yield formation. Field Crop Res 255:107909
Neysanian M, Iranbakhsh A, Ahmadvand R, Oraghi AZ, Ebadi M (2020) Comparative efficacy of selenate and selenium nanoparticles for improving growth, productivity, fruit quality, and postharvest longevity through modifying nutrition, metabolism, and gene expression in tomato; potential benefits and risk assessment. PLoS One 15:e0244207
Peng Y, Li Z, Yang X, Yang L, He M, Zhang H, Wei X, Qin J, Li X, Lu G (2020) Relation between cadmium body burden and cognitive function in older men: a cross−sectional study in China. Chemosphere 250:126535
Pieczyńska J, Grajeta H (2015) The role of selenium in human conception and pregnancy. J Trace Elem Med Biol 29:31–38
Qin X, Nie Z, Liu H, Zhao P, Qin S, Shi Z (2018) Influence of selenium on root morphology and photosynthetic characteristics of winter wheat under cadmium stress. Environ Exp Bot 150:232–239
Rajaee BS, Iranbakhsh A, Ebadi M, Majd A, Ardebili ZO (2020) Red elemental selenium nanoparticles mediated substantial variations in growth, tissue differentiation, metabolism, gene transcription, epigenetic cytosine DNA methylation, and callogenesis in bittermelon (Momordica charantia); an in vitro experiment. PLoS One 15:e0235556
Redjala T, Sterckeman T, Morel JL (2009) Cadmium uptake by roots: contribution of apoplast and of high−and low−affinity membrane transport systems. Environ Exp Bot 67:235–242
Riaz M, Kamran M, Rizwan M, Ali S, Parveen A, Malik Z, Wang X (2021) Cadmium uptake and translocation: synergetic roles of selenium and silicon in Cd detoxification for the production of low Cd crops: a critical review. Chemosphere 129690
Shanker K, Mishra S, Srivastava S, Srivastava R, Dass S, Prakash S, Srivastava MM (1995) Effect of selenite and selenate on plant uptake of cadmium by kidney bean (Phaseolus mungo) with reference to Cd—Se interaction. Chem Speciat Bioavailab 7:97–100
Shiyu Q, Hongen L, Zhaojun N, Rengel Z, Wei G, Chang L, Peng Z (2020) Toxicity of cadmium and its competition with mineral nutrients for uptake by plants: a review. Pedosphere 30:168–180
Sotoodehnia−Korani S, Iranbakhsh A, Ebadi M, Majd A, Ardebili ZO (2020) Selenium nanoparticles induced variations in growth, morphology, anatomy, biochemistry, gene expression, and epigenetic DNA methylation in Capsicum annuum; an in vitro study. Environ Pollut 265:114727
Tan L, Qu M, Zhu Y, Peng C, Wang J, Gao D, Chen C (2020) Zinc transporter5 and zinc transporter 9 function synergistically in zinc/cadmium uptake. Plant Physiol 183:1235–1249
Tessier A, Campbell PG, Bisson M (1979) Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal Chem 51:844–851
Ueno D, Koyama E, Yamaji N, Ma JF (2011) Physiological, genetic, and molecular characterization of a high−Cd−accumulating rice cultivar, Jarjan. J Exp Bot 62:2265–2272
Wan Y, Yu Y, Wang Q, Qiao Y, Li H (2016) Cadmium uptake dynamics and translocation in rice seedling: influence of different forms of selenium. Ecotox Environ Safe 133:127–134
Wu C, Dun Y, Zhang Z, Li M, Wu G (2020) Foliar application of selenium and zinc to alleviate wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cadmium toxicity and uptake from cadmium−contaminated soil. Ecotox Environ Safe 190:110091
Xian X (1989) Effect of chemical forms of cadmium, zinc, and lead in polluted soils on their uptake by cabbage plants. Plant Soil 113:257–264
Yamaji N, Ma JF (2014) The node, a hub for mineral nutrient distribution in graminaceous plants. Trends Plant Sci 19:556–563
Zhou J, Zhang C, Du B, Cui H, Fan X, Zhou D, Zhou J (2021) Soil and foliar applications of silicon and selenium effects on cadmium accumulation and plant growth by modulation of antioxidant system and Cd translocation: Comparison of soft vs. durum wheat varieties. J Hazard Mater 402:123546
Zou R, Wang L, Li YC, Tong Z, Huo W, Chi K, Fan H (2020) Cadmium absorption and translocation of amaranth (Amaranthus mangostanus L.) affected by iron deficiency. Environ Pollut 256:113410
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the Basic Research Project of Henan Education Department (Program No. 19zx007) and the Key Scientific and Technological Projects in Henan Province (202102110214).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhaojun Nie and Hongen Liu conceived and designed the experiments. Peng Zhao, Jiaojiao Zhu, Shiyu Qin, and Chang Li performed the experiments. Xiaoming Qin analyzed the data and wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 355 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, X., Zhao, P., Liu, H. et al. Selenium inhibits cadmium uptake and accumulation in the shoots of winte wheat by altering the transformation of chemical forms of cadmium in soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 8525–8537 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16290-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16290-3