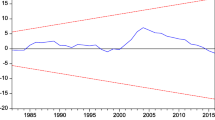
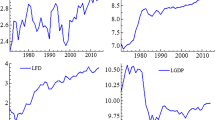
Abstract
The effect of a broad financial index (FD), hydro-energy output, and expansion of the economy on the intensity of carbon were investigated by incorporating the effect of financial expansion through the channel of hydro-energy. The cross-sectional autoregressive distributed lag (CS-ARDL), Mean Group (MG), Augmented Mean Group (AMG), and vector error correction mechanism causality approaches were employed to study panel data for the period from 1980 to 2017 for the top four hydro-energy producing states. The outcomes revealed that FD raises the intensity of carbon in both the short and long term. In contrast, hydro-energy output (HYP) is stated to be a significant factor for attaining a low carbon intensity in the short and long term. The outcomes also indicated that the expansion of the economy augments the intensity of carbon. However, FD lowers the intensity of carbon via the channel of hydro-energy. The causality test outcomes revealed a short-run causality moving from the intensity of carbon to hydro-energy as well as a short-term causality moving from GDP to the intensity of carbon. It was also observed that there is a long-term causality running from all the variables to the intensity of carbon. Important policy implications are suggested at the end of the research.
Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study is available on request.
References
Al Mamun A, Mohamad MR, Yaacob MRB, Mohiuddin M (2018) Intention and behavior towards green consumption among low-income households. J Environ Manag 227:73–86
Ali K, Bakhsh S, Ullah S. et al. (2021) Industrial growth and CO2 emissions in Vietnam: the key role of financial development and fossil fuel consumption. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 7515–7527. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10996-6
Alkhathlan K, Javid M (2013) Energy consumption, carbon emissions and economic growth in Saudi Arabia: an aggregate and disaggregate analysis. Energy Policy 62:1525–1532
Al-mulali U, Weng-Wai C, Sheau-Ting L, Mohammed AH (2015) Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis by utilizing the ecological footprint as an indicator of environmental degradation. Ecol Indic 48:315–323
Amin A, Dogan E, Khan Z (2020) The impacts of different proxies for financialization on carbon emissions in top-ten emitter countries. Sci Total Environ 740:140127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140127
Ang JB (2008) A survey of recent developments ın the lıterature of fınance and growth. J Econ Surv 28(3):536–576
Assi AF, Isiksal AZ, Tursoy T (2020) Highlighting the connection between financial development and consumption of energy in countries with the highest economic freedom. Energy Policy 147:111897
Bello MO, Solarin SA, Yen YY (2018) The impact of electricity consumption on CO2 emission, carbon footprint, water footprint and ecological footprint: the role of hydropower in an emerging economy. J Environ Manag 219:218–230
Bernanke BS, Gertler M, Gilchrist S (1999) The financial accelerator in a quantitative business cycle framework. Handbook of macroeconomics. 1:1341-1393.
Bildirici ME (2014) Hydropower energy consumption, environmental pollution, and economic growth. J Energy Dev 40(1/2):189–208
Bildirici ME, Gökmenoğlu SM (2017) Environmental pollution, hydropower energy consumption and economic growth: evidence from G7 countries. Renew Sust Energ Rev 75:68–85
Breusch TS, Pagan AR (1980) The Lagrange multiplier test and its applications to model specification in econometrics. Rev Econ Stud 47:239–253
Cetin M, Ecevit E, Yucel AG (2018) The impact of economic growth, energy consumption, trade openness, and financial development on carbon emissions: empirical evidence from Turkey. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:36589–36603
Chudik A, Mohaddes K, Pesaran MH, Raissi M (2016)Long-run effects in large heterogeneous panel data models with cross-sectionally correlated errors. Emerald Group Publishing Limited
Destek MA, Aslan A (2020) Disaggregated renewable energy consumption and environmental pollution nexus in G-7 countries. Renew Energy 151:1298–1306
Eberhardt M, Teal F (2010) Productivity analysis in global manufacturing production. Discussion Paper 515 Department of Economics, University of Oxford. Retrieved from: http://www.economics.ox.ac.uk/research/WP/pdf/paper515.pdfAccessed 01 Aug 2020
Eberhardt M, Teal F (2011) Econometrics for grumblers: a new look at the literature on cross-country growth empirics. J Econ Surv 2:109–155
Ecevit E (2015) Urbanization, energy consumption and CO2 emissions in sub-Saharan countries: a panel cointegration and causality. J Econ Dev Stud 3(2):66–76
Engle RF, Granger CWJ (1987)Co-integration and error correction: representation, estimation, and testing. Econometrica 55:251–276
Fearnside PM (1999) Social ımpacts of Brazil’s Tucuruí Dam. Environ Manag 24(4):485–495
Frey GW, Linke DM (2002) Hydropower as a renewable and sustainable energy resource meeting global energy challenges in a reasonable way. Energy Policy 30(14):1261–1265
Gagnon L, Vate JF (1997) Greenhouse gas emissions from hydropower: the state of research in 1996. Energy Policy 25(1):7–13
IMF (2019) Available at: https://www.imf.org/en/Data. Accessed on 1st of August 2020
Javid M, Sharif F (2016) Environmental Kuznets curve and financial development in Pakistan. Renew Sust Energ Rev 54:406–414
Lau E, Tan CC, Tang CF (2016) Dynamic linkages among hydroelectricity consumption, economic growth, and carbon dioxide emission in Malaysia, Energy Sources, Part B: Economics, Planning, and Policy, 11(11):1042-1049. DOI: 10.1080/15567249.2014.922135
Liang D, Tian Z, Ren F, Pan J (2020) Installed hydropower capacity and carbon emission reduction efficiency based on the EBM method in China. Front Energy Res 8:82
Lotfalipour MR, Falahi MA, Ashena M (2010) Economic growth, CO2 emissions, and fossil fuels consumption in Iran. Energy 35:5115–5120
Nasir MA, Canh NP, Le TNL (2020) Environmental degradation & role of financialisation, economic development, industrialisation and trade liberalisation. J Environ Manag 277:111471
O’Connell P (1998) The overvaluation of purchasing power parity. J Int Econ 44:1–19
Omri (2013) CO2 emissions, energy consumption and economic growth nexus in MENA countries: evidence from simultaneous equations models. Energy Econ 40(C):657–664
Pao HT, Chen CC (2019) Decoupling strategies: CO2 emissions, energy resources, and economic growth in the Group of Twenty. J Clean Prod 206:907–919
Pao HT, Tsai CM (2011) Modeling and forecasting the CO2 emissions, energy consumption, and economic growth in Brazil. Energy. 36:2450–2458 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2011.01.032
Pata K, Aydin M (2020) Testing the EKC hypothesis for the top six hydropower energy-consuming countries: evidence from Fourier Bootstrap ARDL procedure. J Clean Prod 264:121699
Pata UK, Yilanci V (2020) Financial development, globalization and ecological footprint in G7: further evidence from threshold cointegration and fractional frequency causality tests. Environ Ecol Stat 27(4):803–825
Pesaran MH (2004) General diagnostic tests for cross section dependence in panels. University of Cambridge, Cambridge Working Papers in Economics No. 0435
Pesaran MH (2006) Estimation and inference in large heterogenous panels with multifactor error structure. Econometrica 74:967–1012
Pesaran MH (2007) A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross-section dependence. J Appl Econ 22:265–312
Pesaran MH, Smith R (1995) Estimating long-run relationships from dynamic heterogeneous panels. J Econ 68(1):79–113
Pesaran MH, Yamagata T (2008) Testing slope homogeneity in large panels. J Econ 142(1):50–93
Rajan RG, Zingales L (2003) The great reversals: the politics of financial development in the 20th century. J Financ Econ 69(1):5–50
Rudberg PM, Escobar M, Gantenbein J, Niiro N (2015) Mitigating the adverse effects of hydropower projects: a comparative review of river restoration and hydropower regulation in Sweden and the United States. Geo Environ Law Rev 27:251–274
Rudd MD, Dahm PF, Rajab MH (1993) Diagnostic comorbidity in persons with suicidal ideation and behavior. Am J Psychiatry 150:928–934
Sadorsky P (2010) The impact of financial development on energy consumption in emerging economies. Energy Policy 38(5):2528–2535
SEEG (2019) Available at: http://seeg.eco.br/en. Accessed on 15th of August 2020
Shahbaz M, Hye QMA, Tiwari AK, Leitao NC (2013) Economic growth, energy consumption, financial development, international trade and CO2 emissions in Indonesia. Renew Sust Energ Rev 25:109–121
Shahbaz M, Omay T, Roubaud D (2018) Sharp and smooth breaks IN unit root testing OF renewable energy consumption. J Energy Dev 44:5–40
Solarin SA, Ozturk I (2016) The relationship between natural gas consumption and economic growth in OPEC members. Renew Sust Energ Rev 58(C):1348–1356
Solarin SA, Al-Mulali U, Ozturk I (2017) Validating the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in India and China: the role of hydroelectricity consumption. Renew Sust Energ Rev 80:1578–1587
Statista (2019) Available at: https://www.statista.com/. Accessed on 1st of August 2020
Tahir T, Luni T, Majeed MT (2021) The impact of financial development and globalization on environmental quality: evidence from South Asian economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:8088–8101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11198-w
Tahseen S, Karney B (2017) Opportunities for increased hydropower diversion at Niagara: an SWOT analysis. Renew Energy 101:757–770
Ummalla M, Samal A (2018) The impact of hydropower energy consumption on economic growth and CO2 emissions in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(35):35725–35737
Ummalla M, Samal A, Goyari P (2019) Nexus among the hydropower energy consumption, economic growth, and CO2 emissions: evidence from BRICS countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(34):35010–35022
UNIDO (2016) Industrial Development Report 2016. The role of technology and innovation in inclusive and sustainable industrial development
Vieira MA, Dalgaard KG (2013) The energy-security–climate-change nexus in Brazil. Environmental Politics 22(4):610–626
Wang R, Mirza N, Vasbieva DG, Abbas Q, Xiong D (2020) The nexus of carbon emissions, financial development, renewable energy consumption, and technological innovation: What should be the priorities in light of COP 21 Agreements? J Environ Manag 271(6–10):111027
Westerlund J (2007) Testing for error correction in panel data. Oxf Bull Econ Stat 69:709–748
World Bank (2008) Available at: https://documents.worldbank.org/en/publication/documents-reports/documentdetail/452391468323718231/the-world-bank-annual-report-2008-year-in-review. Accessed on 15th of October 2020
World Bank (2019) Available at: https://data.worldbank.org/. Accessed on 1st of August 2020
Yüksel I (2008) Hydropower in Turkey for a clean and sustainable energy future. Renew Sust Energ Rev 12(6):1622–1640
Zeqiraj V, Sohag K, Soytas U (2020) Stock market development and low-carbon economy: the role of innovation and renewable energy. Energy Econ 91:104908
Zhang (2011) The impact of financial development on carbon emissions: an empirical analysis in China. Energy Policy 39(4):2197–2203
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank the editor and anonymous reviewers for the insightful comments that helped to improve the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The author conducted conceptualization, data collection, methodology, and writing of the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Nicholas Apergis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Isiksal, A.Z. The decline in carbon intensity: the role of financial expansion and hydro-energy. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 16460–16471 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16117-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16117-1