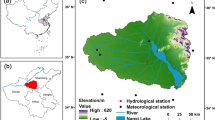
Abstract
Ecosystem water use efficiency (eWUE), defined as the ratio between carbon gains and water loss from the system, has been recognized as an important characteristic of carbon and water balances. The long-lasting “Grain for Green” Program (GFGP) initiated in 1999 in China’s Loess Plateau (CLP) is a large-scale ecological program in the world, which aims to improve the CLP’s ecosystem resilience by enhancing vegetation cover and productivity. Understanding how the GFGP can affect eWUE is imperative to ensuring sustainable water resources and to promoting sustainable management strategies. In this study, we evaluated the spatiotemporal variability of growing-season eWUE and examined its response to both climate change and vegetation coverage from 1982 to 2017. Our results indicate that growing-season eWUE, gross primary productivity (GPP), and evapotranspiration (ET) in CLP area increased significantly from 1982 to 2017. Specifically, eWUE, GPP, and ET increased more rapidly after China established the program. The most significant growth area of eWUE was found in main areas conducting GFGP project, including the Loess hilly and gully area (LHGA). Spatially, eWUE, GPP, and ET in the growing season increased from northwest to southeast, and higher eWUE was found in areas with high vegetation cover. The spatial and temporal variability of eWUE was related to vegetation cover (expressed as leaf area index, LAI) and climatic variability. Significant positive correlations were observed between growing-season LAI, temperature, and eWUE, because the LAI and temperature have a greater effect on photosynthesis than ET. Our results suggested that the GFGP was the main driving force that causes the spatial-temporal variability of eWUE in CLP.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Aguilos M, Stahl C, Burban B, Hérault B, Courtois E, Coste S, Wagner F, Ziegler C, Takagi K, Bonal D (2019) Interannual and seasonal variations in ecosystem transpiration and water use efficiency in a tropical rainforest. Forests. 10:14
Ahmadi B, Ahmadalipour A, Tootle G, Moradkhani H (2019) Remote sensing of water use efficiency and terrestrial drought recovery across the contiguous united states. Remote. Sens-Basel. 11:731
Ai Z, Wang Q, Yang Y, Manevski K, Yi S, Zhao X (2020) Variation of gross primary production, evapotranspiration and water use efficiency for global croplands. Agr. Forest. Meteorol. 287:107935
Belinda E (2017) Response of ecosystem water use efficiency to rising atmospheric CO2 concentrations: sensitivity and large scale biogeochemical implications. New. Phytol. 213:1654–1666
Cao R, Hu Z, Jiang Z, Yang Y, Zhao W, Wu G, Feng X, Chen R, Hao G (2020) Shifts in ecosystem water use efficiency on China’s loess plateau caused by the interaction of climatic and biotic factors over 1985-2015. Agr. Forest. Meteorol. 291:108100
Chen C, Park T, Wang X, Piao S, Xu B, Chaturvedi RK, Fuchs R, Brovkin V, Ciais P, Fensholt R, Tømmervik H, Bala G, Zhu Z, Nemani RR, Myneni RB (2019) China and India lead in greening of the world through land-use management. Nat. sustain. 2:122–129
Du X, Zhao X, Zhou T, Jiang B, Xu P, Wu D, Tang B (2019) Effects of climate factors and human activities on the ecosystem water use efficiency throughout Northern China. Remote. Sens-Basel. 11:2766
Feng X, Sun G, Fu B, Su C, Liu Y, Lamparski H (2012) Regional effects of vegetation restoration on water yield across the Loess Plateau. China. Hydrol. Earth. Syst. Sci. 16:2617–2628
Feng X, Fu B, Piao S, Wang S, Ciais P, Zeng Z, Lü Y, Zeng Y, Li Y, Jiang X (2016) Revegetation in China’s Loess Plateau is approaching sustainable water resource limits. Nat. Clim. Change. 6:1019–1022
Fensholt R, Proud SR (2012) Evaluation of earth observation based global long term vegetation trends—comparing GIMMS and MODIS global NDVI time series. Remote. Sens. Environ. 119:131–147
Gang C, Gao X, Peng S, Chen M, Guo L, Jin J (2019) Satellite observations of the recovery of forests and grasslands in Western China. J. Geophy. Res-Biogeo. 124:1905–1922
Guay KC, Beck PS, Berner LT, Goetz SJ, Baccini A, Buermann W (2014) Vegetation productivity patterns at high northern latitudes: a multi-sensor satellite data assessment. Global. Change. Biol. 20:3147–3158
Guo R, Lin Z, Mo X, Yang C (2010) Responses of crop yield and water use efficiency to climate change in the North China Plain. Agr. Water. Manage. 97:1185–1194
Guo L, Shan N, Zhang Y, Sun F, Liu W, Shi Z, Zhang Q (2019a) Separating the effects of climate change and human activity on water use efficiency over the Beijing-Tianjin Sand Source Region of China. Sci. Total. Environ. 690:584–595
Guo L, Sun F, Liu W, Zhang Y, Wang H, Cui H, Wang H, Zhang J, Du B (2019b) Response of ecosystem water use efficiency to drought over China during 1982-2015: spatiotemporal variability and resilience. Forests. 10:598
Hu Z, Yu G, Fu Y, Sun X, Li Y, Shi P, Wang Y, Zheng Z (2008) Effects of vegetation control on ecosystem water use efficiency within and among four grassland ecosystems in China. Global. Change. Biol. 14:1609–1619
Hu L, Fan W, Ren H, Liu S, Cui Y, Zhao P (2018) Spatiotemporal dynamics in vegetation GPP over the great khingan mountains using GLASS products from 1982 to 2015. Remote. Sens-Basel. 10:488
Huang M, Piao S, Sun Y, Ciais P, Cheng L, Mao J, Poulter B, Shi X, Zeng Z, Wang Y (2015) Change in terrestrial ecosystem water-use efficiency over the last three decades. Global. Change. Biol. 21:2366–2378
Huang L, He B, Han L, Liu J, Wang H, Chen Z (2017) A global examination of the response of ecosystem water-use efficiency to drought based on MODIS data. Sci. Total. Environ. 601:1097–1107
Jasechko S, Sharp ZD, Gibson JJ, Birks SJ, Yi Y, Fawcett PJ (2013) Terrestrial water fluxes dominated by transpiration. Nature 496:347–350
Jassal RS, Black TA, Spittlehouse DL, Brümmer C, Nesic Z (2009) Evapotranspiration and water use efficiency in different-aged Pacific Northwest Douglas-fir stands. Agr. Forest. Meteorol. 149:1168–1178
Jiang C, Zhang H, Tang Z, Labzovskii L (2017) Evaluating the coupling effects of climate variability and vegetation restoration on ecosystems of the Loess Plateau. China. Land. Use. Pol. 69:134–148
Jung M, Reichstein M, Margolis HA, Cescatti A, Richardson AD, Arain MA, Arneth A, Bernhofer C, Bonal D, Chen J (2011) Global patterns of land-atmosphere fluxes of carbon dioxide, latent heat, and sensible heat derived from eddy covariance, satellite, and meteorological observations. J Geophy Res-Biogeo 116:G00J07
Karnieli A, Agam N, Pinker RT, Anderson M, Imhoff ML, Gutman GG, Panov N, Goldberg A (2010) Use of NDVI and land surface temperature for drought assessment: merits and limitations. J. Climate. 23:618–633
Kendall MG (1948) Rank correlation methods. Griffin
Law BE, Falge E, Gu LV, Baldocchi DD, Bakwin P, Berbigier P, Davis K, Dolman AJ, Falk M, Fuentes JD (2002) Environmental controls over carbon dioxide and water vapor exchange of terrestrial vegetation. Agr. Forest. Meteorol. 113:97–120
Li M, Yang Y, Zhu Q, Chen H, Peng C (2016) Evaluating water use efficiency patterns of Qinling Mountains under climate change. Acta. Ecol. Sin. 36:936–945
Lin Y, Grace J, Zhao W, Dong Y, Zhang X, Zhou L, Fei X, Jin Y, Li J, Nizami SM (2018) Water-use efficiency and its relationship with environmental and biological factors in a rubber plantation. J. Hydrol. 563:273–282
Liu X, Hu B, Ren Z (2018) Spatiotemporal variation of water use efficiency and its driving forces on the loess plateau during 2000–2014. Sci Agric Sin 51:302–314
Liu D, Chen Y, Cai W, Dong W, Xiao J, Chen J, Zhang H, Xia J, Yuan W (2014) The contribution of China’s Grain to Green Program to carbon sequestration. Landscape. Ecol. 29:1675–1688
Liu Y, Xiao J, Ju W, Zhou Y, Wang S, Wu X (2015) Water use efficiency of China’s terrestrial ecosystems and responses to drought. Sci. Rep-UK. 5:13799
Liu W, Sun F, Sun S, Guo L, Wang H, Cui H (2019) Multi-scale assessment of eco-hydrological resilience to drought in China over the last three decades. Sci. Total. Environ. 672:201–211
Lu S, Tian F (2021) Spatiotemporal variations of agricultural water use efficiency and its response to the Grain to Green Program during 1982–2015 in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Phys. Chem. Earth 121(Parts A/B/C):102975
Martens B, Gonzalez Miralles D, Lievens H, Van Der Schalie R, De Jeu RA, Fernández-Prieto D, Beck HE, Dorigo W, Verhoest N (2017) GLEAM v3: Satellite-based land evaporation and root-zone soil moisture. Geosci. Model. Dev. 10:1903–1925
National Development and Reform Commission(NDRC), Ministry of Water Resources, Ministry of Agriculture, State Forestry Administration (2010) Outline of the program of integrated control and management of the Loess Plateau Region for Years 2010–2030. NDRC, Beijing (in Chinese)
Niu S, Xing X, Zhang Z, Xia J, Zhou X, Song B, Li L, Wan S (2011) Water-use efficiency in response to climate change: from leaf to ecosystem in a temperate steppe. Global. Change. Biol. 17:1073–1082
Song Q, Fei X, Zhang Y, Sha L, Liu Y, Zhou W, Wu C, Lu Z, Luo K, Gao J (2017) Water use efficiency in a primary subtropical evergreen forest in Southwest China. Sci. Rep-UK. 7:43031
Sun S, Song Z, Wu X, Wang T, Wu Y, Du W, Che T, Huang C, Zhang X, Ping B (2018) Spatio-temporal variations in water use efficiency and its drivers in China over the last three decades. Ecol. Indic. 94:292–304
Tian H, Chen G, Liu M, Zhang C, Sun G, Lu C, Xu X, Ren W, Pan S, Chappelka A (2010) Model estimates of net primary productivity, evapotranspiration, and water use efficiency in the terrestrial ecosystems of the southern United States during 1895–2007. Forest. Ecol. Manag. 259:1311–1327
Vicente-Serrano SM, Gouveia C, Camarero JJ, Beguería S, Trigo R, López-Moreno JI, Azorín-Molina C, Pasho E, Lorenzo-Lacruz J, Revuelto J (2013) Response of vegetation to drought time-scales across global land biomes. P. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 110:52–57
Vicente-Serrano SM, Miralles DG, Domínguez-Castro F, Azorin-Molina C, El Kenawy A, McVicar TR, Tomás-Burguera M, Beguería S, Maneta M, Peña-Gallardo M (2018) Global assessment of the Standardized Evapotranspiration Deficit Index (SEDI) for drought analysis and monitoring. J. Climate. 31:5371–5393
Wang Y, Li X, Shi F, Zhang S, Wu X (2019) The Grain for Green Project intensifies evapotranspiration in the revegetation area of the Loess Plateau in China. Chin. Sci. Bull 64:588–599
Xiao Z, Liang S, Wang J, Chen P, Yin X, Zhang L, Song J (2014) Use of general regression neuralnetworks for generating the GLASS leaf area index productfrom time-series MODIS surface reflectance. IEEE. T. Geosci. Remote 52(1):209–223
Xie B, Jia X, Qin Z, Shen J, Chang Q (2016) Vegetation dynamics and climate change on the Loess Plateau, China: 1982–2011. Reg. Environ. Change. 16:1583–1594
Xin Z, Xu J, Zheng W (2008) Spatiotemporal variations of vegetation cover on the Chinese Loess Plateau (1981–2006): impacts of climate changes and human activities. Sci. China Ser. D. 51:67–78
Yang Y, Guan H, Batelaan O, McVicar TR, Long D, Piao S, Liang W, Liu B, Jin Z, Simmons CT (2016) Contrasting responses of water use efficiency to drought across global terrestrial ecosystems. Sci. Rep-UK. 6:23284
Yang X, Yong B, Ren L, Zhang Y, Long D (2017) Multi-scale validation of GLEAM evapotranspiration products over China via China FLUX ET measurements. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 38:5688–5709
Yang X, Yong B, Yin Y, Zhang Y (2018) Spatio-temporal changes in evapotranspiration over China using GLEAM_V3. 0a products (1980–2014). Hydrolo. Res. 49:1330–1348
Yang S, Zhang J, Zhang S, Wang J, Bai Y, Yao F, Guo H (2020) The potential of remote sensing-based models on global water-use efficiency estimation: an evaluation and intercomparison of an ecosystem model (BESS) and algorithm (MODIS) using site level and upscaled eddy covariance data. Agr. Forest. Meteorol. 287:107959
Ye L, Fang L, Shi Z, Deng L, Tan W (2019) Spatio-temporal dynamics of soil moisture driven by ‘Grain for Green’program on the Loess Plateau. China. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 269:204–214
You N, Dong J, Xiao T, Liu J, Xiao X (2020) The effects of the“Grain for Green”project on gross primary productivity in the Loess Plateau. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 40(2):315–323
Yu GR, Zhu XJ, Fu YL, He HL, Wang QF, Wen XF, Li XR, Zhang LM, Zhang L, Su W (2013) Spatial patterns and climate drivers of carbon fluxes in terrestrial ecosystems of China. Global. Change. Biol. 19:798–810
Yu L, Kang R, Mulder J, Zhu J, Dörsch P (2017) Distinct fates of atmogenic NH 4+ and NO 3− in subtropical, N-saturated forest soils. Biogeochemistry. 133:279–294
Yuan W, Liu S, Yu G, Bonnefond J, Chen J, Davis K, Desai AR, Goldstein AH, Gianelle D, Rossi F (2010) Global estimates of evapotranspiration and gross primary production based on MODIS and global meteorology data. Remote. Sens. Environ. 114:1416–1431
Zhang K, Kimball JS, Nemani RR, Running SW (2010) A continuous satellite-derived global record of land surface evapotranspiration from 1983 to 2006. Water. Resour. Res. 46:W9522
Zhang B, Wu P, Zhao X, Wang Y, Gao X (2013) Changes in vegetation condition in areas with different gradients (1980–2010) on the Loess Plateau. China. Environ. Earth. Sci. 68:2427–2438
Zhang T, Peng J, Liang W, Yang Y, Liu Y (2016) Spatial–temporal patterns of water use efficiency and climate controls in China’s Loess Plateau during 2000–2010. Sci. Total. Environ. 565:105–122
Zhang K, Wang RY, Li QZ, Wang HL, Zhao H, Yang FL, Zhao FN, Qi Y (2018) Effects of elevated CO2 concentration on production and water use efficiency of spring wheat in semi-arid area. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 29:2959–2969
Zhao A, Zhang A, Lu C, Wang D, Wang H, Liu H (2017) Spatiotemporal variation of vegetation coverage before and after implementation of Grain for Green Program in Loess Plateau. China. Ecol. Eng. 104:13–22
Zhao A, Zhang A, Liu J, Feng L, Zhao Y (2019) Assessing the effects of drought and“Grain for Green”Program on vegetation dynamics in China's Loess Plateau from 2000 to 2014. Catena 175:446–455
Zheng H, Lin H, Zhou W, Bao H, Zhu X, Jin Z, Song Y, Wang Y, Liu W, Tang Y (2019a) Revegetation has increased ecosystem water-use efficiency during 2000–2014 in the Chinese Loess Plateau: evidence from satellite data. Ecol. Indic. 102:507–518
Zheng H, Lin H, Zhu X, Jin Z, Bao H (2019b) Divergent spatial responses of plant and ecosystem water-use efficiency to climate and vegetation gradients in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Global. Planet. Change. 181:102995
Zhou S, Yu B, Zhang Y, Huang Y, Wang G (2018) Water use efficiency and evapotranspiration partitioning for three typical ecosystems in the Heihe River Basin, northwestern China. Agr. Forest. Meteorol. 253:261–273
Zhu X, Yu G, Wang Q, Hu Z, Han S, Yan J, Wang Y, Zhao L (2014) Seasonal dynamics of water use efficiency of typical forest and grassland ecosystems in China. J. Forest. Res Jpn. 19:70–76
Zhu Z, Piao S, Lian X, Myneni RB, Peng S, Yang H (2017) Attribution of seasonal leaf area index trends in the northern latitudes with “optimally” integrated ecosystem models. Global. Change. Biol. 23(11):4798–4813
Liu X, Hu B, Ren Z 2018. Spatiotemporal variation of water use efficiency and its driving forces on the loess plateau during 2000–2014. Sci Agric Sin 51:302–314
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the “National Earth System Science Data Center, National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China (http://www.geodata.cn)” for the data support.
Funding
The work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42071246), the Ministry of education of Humanities and Social Science Project (No. 18YJCZH257), and a grant from State Key Laboratory of Resources and Environmental Information System.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Anzhou Zhao proposed a new idea about the response of cropland eWUE to drought. Qiuyan Yu helped with the review of this manuscript. Dongli Wang designed the experiments and carried them out. Anbing Zhang reviewed and edited this manuscript. Anzhou Zhao prepared the manuscript with contributions from all co-authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Xianliang Yi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, A., Yu, Q., Wang, D. et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of ecosystem water use efficiency over the Chinese Loess Plateau base on long-time satellite data. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 2298–2310 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15801-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15801-6