Abstract
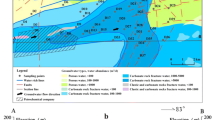
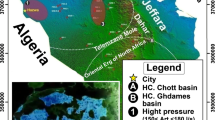
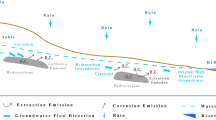
A fractured karst aquifer polluted by petroleum hydrocarbons (PH) for several decades was selected to study the influences of PH on the hydrochemical environment. The research was implemented using the hydrochemical indicators (Ca2+, Mg2+, Na++K+, HCO3−, NO3−, Cl−, F−, and SO42−) and PH with the help of GIS and origin platforms, statistical analyses, and graphical methods. Results showed that PH had significant influences on the hydrochemical environment over the last several decades. The main principle elements influencing the evolution processes of hydrochemical environment were carbonates dissolution, leaking wastewater, and biodegradation processes from 1977 to 2019, and hydrochemistry types changed from HCO3–Ca–Mg and HCO3–Ca to HCO3–Cl–Ca–Mg and HCO3-Cl-Ca. The contribution rate of PH biodegradation to the representative ion increased at first, then decreased over time, which has a close relationship with the variation characteristics of PH. The dynamic evolution processes of hydrochemical environment have significances for indentifying the influencing mechanisms of hydrogeochemical reactions, which could provide valuable scientific suggestions for the local administrators to take effective efforts to optimize and protect the karst groundwater environment.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Borden RC, Gomez CA, Becker MT (1995) Geochemical indicators of intrinsic bioremediation. Groundwater 33:180–189
Chen YD, Zhu XY (1999) Mechanisms of biodegradation of hydrocarbon contaminants in the groundwater in Dawu well field in Zibo. Guangxi Geol 12:31–34 (in Chinese)
Chien LC, Yu HL, Schootman M (2013) Efficient mapping and geographic disparities in breast cancer mortality at the county-level by race and age in the U.S. Spatial Spatio-temporal Epidemiol 5:27–37
Deng T (2010) Study on the migration and transformation of oil-contaminants in vadose zone. Changan University (in Chinese)
Desforges JW, Sonne C, Levin M, Siebert U, Guise SD, Dietz R (2016) Immunotoxic effects of environmental pollutants in marine mammals. Environ Int 86:126–139
Flathman PE, Jerger DE, Bottomley LS (1989) Remediation of contaminated groundwater using biological techniques. Groundwater Monit R 9:105–119
Gao ZJ, Sun JF, Lu TM, Wang XY, Yang LZ, Liu ZZ (2019) Types and assessment of organic pollutants in groundwater of Dawu source area in Zibo. J Shandong Univ Sci Technol 38:1–9 (in Chinese)
GB8978-1996 (1996) Integrated wastewater discharge standard. In: People’s Republic of China, Environmental Protection Agency, State Bureau of Technical Supervision
Giger W, Schaffner C (1981) Groundwater pollution by volatile organic chemicals. Stud Environ Sci 17:517–522
Guo YL, Zhai YZ, Wu Q, Teng YG, Jiang GH, Wang JS, Guo F, Tang QJ, Liu SH (2016) Proposed APLIE method for groundwater vulnerability assessment in karst-phreatic aquifer, Shandong Province, China: a case study. Environ Earth Sci 75:112
Guo YL, Wu Q, Li CS, Zhao ZH, Sun B, He SY, Jiang GH, Zhai YZ, Guo F (2018) Application of the risk-based early warning method in a fracture-karst water source, North China. Water Environ Res 90:206–219
Guo YL, Wen Z, Zhang C, Jakada H (2020a) Contamination and natural attenuation characteristics of petroleum hydrocarbons in a fractured karst aquifer, North China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(18):22780–22794
Guo YL, Quan XQ, Wang QG, Zhang C, Wu Q (2020b) Characteristics of groundwater chemistry in Dawu karst water source. South-to-North Water Transf Water Sci Technol 18(4):130–140 (in Chinese)
Guo YL, Quan XQ, Wu Q (2020c) Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of volatile organic compounds of a typical karst groundwater source in North China. J Guangxi Normal Univ 38:102–113 (in Chinese)
Guo YL, Wen Z, Zhang C, Jakada H (2021) Contamination characteristics of chlorinated hydrocarbons in a fractured karst aquifer using TMVOC and hydro-chemical techniques. Sci Total Environ 794:148717
Henson WR, Huang L, Graham WD, Ogram A (2017) Nitrate reduction mechanisms and rates in an unconfined eogenetic karst aquifer in two sites with different redox potential. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 122:1062–1077
Hillebrand O, Nödler K, Sauter M, Licha T (2015) Multitracer experiment to evaluate the attenuation of selected organic micropollutants in a karst aquifer. Sci Total Environ 506:338–343
Huang XJ, Wang GC, Liang XY, Cui LF, Ma L, Xu QY (2018) Hydrochemical and stable isotope (δD and δ18O) characteristics of groundwater and hydrogeochemical processes in the Ningtiaota Coalfeld, Northwest China. Mine Water Environ 37:119–136
Iván V, Mádl-Szőnyi J (2017) State of the art of karst vulnerability assessment: overview, evaluation and outlook. Environ Earth Sci 76:112
Jiang WN (2020) Study on identification of natural attenuation of pollutants in groundwater in petrochemical contaminated site. Jilin University, Jilin (in Chinese)
Lan JK (1996) Simulation models of water-rock interaction in the aquifer of Linzi area, Zibo city, Shandong. J Guilin Inst Technol 16(4):410–414 (in Chinese)
Li D, Song XL, Niu PS (2001) A simulation of the groundwater environment and study on control of the petroleum pollution in water supply source of Dawu. Beijing Geol 13(4):20–24 (in Chinese)
Li MR, Wang WS, Ren SJ, Wang JS, Li J (2014) Screening typical pollutants by modified comprehensive evaluation method —— a case study of typical pollutants screening in groundwater of Dawu water source. Environ Pollut Control 36:72–77 (in Chinese)
Liang SH, Kao CM, Kuo YC (2011) In situ oxidation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated groundwater by using passive ISCO system. Water Res 45:2496–2506
Liang YP, Gao XB, Zhao CH, Tang CL, Shen HY, Wang ZH, Wang YX (2018) Review: Characterization, evolution, and environmental issues of karst water systems in Northern China. Hydrogeol J 26:1371–1385
Liu SL (2013) The analysis of water quality evaluation regular pattern and the pollution trend prediction of groundwater in Dawu well field, Zibo City. China University of Geosciences, Beijing postgraduate thesis
Liu XH, Dai QL (1996) Remediation programme study on oil pollution in groudwater system. J South China Univ Technol 24:188–192 (in Chinese)
Liu XH, Fu JM, Shen ZL, Zhong ZS (1996) Hydrogeochemical change induced by oil sewage leakage – a case of the groundwater source in Zibo city, Shandong province, China. Geochimica 25:331–338 (in Chinese)
Logeshwaran P, Megharaj M, Chadalavada S, Bowman M, Naidu R (2018) Petroleum hydrocarbons (PH) in groundwater aquifers: An overview of environmental fate, toxicity, microbial degradation and risk-based remediation approaches. Environ Technol Inno 10:175–193
Lu H (2019) Study on the early warning of groundwater system chlorinated hydrocarbons pollution in the eastern area of Jinan. University of Jinan (in Chinese)
Lv H (2014) Research on biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminants and enhanced in-situ remediation in groundwater. Jilin University (in Chinese)
Lv H, Wang Y, Wang H (2019) Determination of major pollutant and biogeochemical processes in an oil-contaminated aquifer using human health risk assessment and multivariate statistical analysis. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25(3):505–526
Marić N, Matić I, Papić P, Beškoski VP, Ilić M, Gojgić-Cvijović G, Miletić S, Nikić Z, Vrvić MM (2018) Natural attenuation of petroleum hydrocarbons—a study of biodegradation effects in groundwater (Vitanovac, Serbia). Environ Monit Assess 190:89
Meckenstock RU, Boll M, Mouttaki H, Koelschbach JS, Tarouco PC, Weyrauch P, Dong X, Himmelberg AM (2016) Anaerobic degradation of benzene and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 26:92–118
Monjerezi M, Vogt RD, Aagaard P, Saka JDK (2011) Hydro-geochemical processes in an area with saline groundwater in lower Shire River valley, Malawi: an integrated application of hierarchical cluster and principal component analyses. Appl Geochem 26(8):1399–1413
Souza EC, Vessoni-Penna TC, Oliveira RPDS (2014) Biosurfactant-enhanced hydrocarbon bioremediation: an overview. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 89:88–94
Squillace PJ, Moran MJ (2007) Factors associated with sources, transport, and fate of volatile organic compounds and their mixtures in aquifers of the United States. Environ Sci Technol 41(7):2123–2130
Tfincsics A, Szabo I, Bake E, Szoboszlay S, Kukolya J, Kriszt B, Marialigeti K (2010) Investigation of catechol 2, 3-dioxygenase and 16S rRNA gene diversity in hypoxic, petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated groundwater. Syst Appl Microbiol 33(7):398–406
Varjani SJ (2017) Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons. Bioresour Technol 223:277–286
Varjani SJ, Upasani VN (2017) A new look on factors affecting microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbon pollutants. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 120:71–83
Wang YX, Ma R, Wang WK, Su XS (2018) Preface: Groundwater sustainability in fast-developing China. Hydrogeol J 26:1295–1300
Wei C (2015) The chlorinated hydrocarbon pollution mechanism of groundwater system in the eastern city. University of Jinan (in Chinese)
Wu NJ, Zhang W, Wei WX, Yang SC, Wang HJ, Sun ZP, Song Y, Li PZ, Wang Y (2020) Field study of chlorinated aliphatic hydrocarbon degradation in contaminated groundwater via micron zero-valent iron coupled with biostimulation. Chem Eng J 384:123349
Xu P, Song CQ, Ding SY (2000) Water environmental problems in Dawu water resource area and prevention countermeasures. Shandong Geol 16(3):36–40 (in Chinese)
Yang J, Meng L, Guo L (2019) In situ remediation of chlorinated solvent-contaminated groundwater using ZVI/organic carbon amendment in China: field pilot test and full-scale application. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(6):5051–5062
Yu X, Ghasemizadeh R, Padilla I, Irizarry C, Kaeli D, Alshawabkeh A (2015) Spatiotemporal changes of CVOC concentrations in karst aquifers: analysis of three decades of data from Puerto Rico. Sci Total Environ 511:1–10
Zhang YL, Qian H, Wang JL, Si CQ, Chen ZY, Dang JY, Zhang ZY (2017) Variations in the environmental characteristics of groundwater slightly contaminated with petroleum: effects of enhanced bioremediation in northeast China. Environ Earth Sci 76:90
Zhu XY, Zhu GR, Liu YH, Xie XY (1990) Modeling of karst-fracture groundwater resource in Xidian area, China. Memoires of the 22nd Congress of IAH 56-65.
Zhu XY, Xu SH, Si JF (1997) Application of tracing test to the remediation of contaminated fracture-karst water in Zibo city. Carsolog Sin 16:131–144 (in Chinese)
Zhu XY, Liu JL, Zhu JJ, Chen YD (2000) Characteristics of distribution and transport of petroleum contaminants in frature-karst water in Zibo area, Shandong Province, China. Sci China 43(2):141–150
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the editors and reviewers who read the draft of this paper for their constructive comments.
Funding
Financial support was provided by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2020YFE0204700, 2021YFE0107100), Global Karst Resource Ecology United laboratory-Comparative study of classical karst areas between China and Slovenia (KY201802009), National Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province (2021GXNSFBA075013), Project (201501001) supported by Research Center of Groundwater Resources and Environment Engineering in Shandong province, Hydrological and Environmental Survey for Karst Groundwater Resources System of Fengshui Spring Basin in Shandong Province (12120113103900), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (41702277, 42022018) and UNESCO/IUGS (IGCP 661).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yuming Peng and Yongli Guo: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, and writing. Qing Wu, Huanliang Chen, Chao Ma, and Chuanlei Li: investigation, methodology, and editing. Wen Liu: conceptualization, methodology, and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Xianliang Yi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Yuming Peng and Yongli Guo are the first author of this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, ., Guo, Y., Wu, Q. et al. Hydrochemical environment of a fractured karst aquifer influenced by petroleum hydrocarbons. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 2244–2257 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15661-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15661-0